Objective-C Learning notes
There Some points in Objective-C just like NSString,NSArray,NSDictionary,Protocol,interface,abort dealing,Delegate,Listeners and more details.
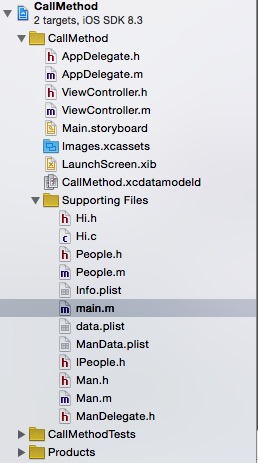
At first I want to show the structure of my learning Project.:
As we can see,I have defined my own interface which are People,Man and Hi as well as I also have defined my own protocol which are IPeople and ManDelegate.
I have finished the studying of the Objective-C fundamental syntax in this simple project.
I mainly want to show some details in the supporting files.Because I haven’t used the UIKit which is the main framework for iOS.
First I can spread my introduction with the file main.m,let’s see the code of the main.m:
// main.m
// CallMethod
//
// Created by 趙天宇 on 15/4/14.
// Copyright (c) 2015年 Panda. All rights reserved.
#import <UIKit/UIKit.h>
#import "AppDelegate.h"
//#include "Hi.h"
#import "People.h"
#import "Hi.h"
#import "Man.h" Now there are some questions about the main.m:
- Where are the interfaces which include People,Man and Hi defined?
- Where are the protocol which include IPeople and ManDelegate
defined? - What are contents of the data.plist and ManData.plist?
- There are some operations that we need to see how they work.
- How can we achieve the Delegate?
Let us see some file in my project:
For the question 1:
People.h:
//
// People.h
// CallMethod
//
// Created by 趙天宇 on 15/4/14.
// Copyright (c) 2015年 Panda. All rights reserved.
//
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@interface People : NSObject{
int _age;
int _num;
NSString *_name;
}//define the attributes of People.
+(People*)peopleWithNum:(int)num andName:(NSString*)name;
//This is a factory method to deal with some thing
//Use this method to convert the num and name into people.
-(id)initWithNum:(int)num andName:(NSString *)name;
//init the num and people.
-(int)getNum;
-(NSString*)getName;
@property int age;
@endHi.h:
#ifndef CallMethod_Hi_h
#define CallMethod_Hi_h
void sayHi();
#endifMan.h:
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
#import "IPeople.h"
#import "ManDelegate.h"
@interface Man : NSObject<IPeople>{//Define the Man interface which observe the protocol IPeople.
int _age;
}
//there are the functions we need to achieve because IPeople protocol.
-(id)init;
-(NSString*)getName;
-(int)getAge;
-(void)setAge:(int)age;
@property id<ManDelegate> delegate;
@endFor the question 2:
IPeople.h:
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@protocol IPeople <NSObject>//Define the protocol in the IPeople.h .so other files can quote this protocol.
-(int)getAge;
-(NSString*)getName;
-(void)setAge:(int)age;
@endManDelegate.h:
#ifndef CallMethod_ManDelegate_h
#define CallMethod_ManDelegate_h
#endif
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@protocol ManDelegate <NSObject>//Define the ManDelegate protocol in the ManDelegate.h.
-(void)onAgeChanged:(int)age;
@endFor the question 3:
data.plist
ManData.plist:
For the question 4:
People.m:
#import "People.h"
@implementation People
//achieve some method of people in this area.
+(People*)peopleWithNum:(int)num andName:(NSString *)name{//achieve factory method in there.
return [[People alloc] initWithNum:num andName:name];
}
-(instancetype)initWithNum:(int)num andName:(NSString *)name{
self = [super init];
if (self) {
_num = num;
_name = name;
}
return self;
}
-(void)setAge:(int)age{//iOS system have generated methods - "setter" and "getter"
//in this way , we can rewrite it by ourself to reduce some useless operations.
NSLog(@"Set age");
_age = age;
}
-(int)age{
NSLog(@"Get age");
return _age;
}
-(int)getNum{
return _num;
}
-(NSString*)getName{
return _name;
}
@endMan.m:
#import "Man.h"
@implementation Man//this is the implementation of the Man interface.
-(instancetype)init{
self = [super init];
if (self) {
self.delegate = nil;//at first the Listener is nil to wait for some changes.
_age = 20;
}
return self;
}
-(int)getAge{
return _age;
}
-(NSString*)getName{
return @"Panda";
}
-(void)setAge:(int)age{
if (age!=_age) {
if (self.delegate) {//if we find the age is changed we can set a message to the application.
[self.delegate onAgeChanged:age];
//if the message is sent successfully,We can say the ManListener is built successfully.
}
}
_age = age;
}
@endFor the question 5:
if we are willing to use delegate to build a listener to listen the status of the p.ages,first we need to define a protocol-ManDelegate to limit the ManListener interface.In order to achieve the ManListener ,we need to obey the rule of ManDelegate.So we have to the function onAgeChanged:(int)age{} when @implementation ManListener.
Now everything has been readied for the ManListener. So we can use ManListener to listen the status of p.age.When the age is changed,ManListener will send a message.
相關推薦
Objective-C Learning notes
There Some points in Objective-C just like NSString,NSArray,NSDictionary,Protocol,interface,abort dealing,Delegate,Listeners and mo
objective-c learning note(1)
(1)create class’s object and initialize property create a project in projectname.m: #import <Foundation/Foundation.h> #import
Objective-C 執行AppleScript腳本
url alloc use 文件中 path str lee nss app 在Objective-C裏事實上也能夠執行AppleScript 第一種方式是Source 將腳本寫到變量字符串裏 NSAppleEventDescriptor *eventDescr
Swift、Objective-C 單例模式 (Singleton)
app 賦值 uil imp ide 效果 func instance 發現 本文的單例模式分為嚴格單例模式和不嚴格單例模式。單例模式要求一個類有一個實例,有公開接口可以訪問這個實例。嚴格單例模式,要求一個類只有一個實例;不嚴格單例模式,可以創建多個實例。 有的類只能有一個
Using Swift with Cocoa and Objective-C下載
target cocoa 下載地址 obj swift nbsp 地址 bject uil 《Using Swift with Cocoa and Objective-C Building App 》 下載地址 http://download.csdn.net/
Objective-C 中的Runtime的詳細使用
enc ring 博客 document 每次 tps htm lec guid Runtime全面了解 一直以來,OC被大家冠以動態語言的稱謂,其實是因為OC中包含的runtime機制。Runtime 又叫運行時,是一套底層的 C 語言 API,其為 iO
Swift和Objective-C混合編程——Swift調用OC
分享 發現 load 另一個 == 方法 代碼 swift 應用 在iOS應用的開發中。Swift必將代替OC,兩者的趨勢是“短期共存,長期代替”。但曾經有太多的代碼是用OC語言完畢的,而Swift的開發也從 OC中繼承了非常多的特性。兩者也是有非常多的類
Objective-C之成魔之路【8-訪問成員變量和屬性】
order 線程安全 ring 內容 時間 targe 簡化 音樂 blank 郝萌主傾心貢獻,尊重作者的勞動成果。請勿轉載。 假設文章對您有所幫助,歡迎給作者捐贈,支持郝萌主,捐贈數額任意,重在心意^_^ 我要捐贈: 點擊捐贈 Cocos2d-X源代碼
Swift,Objective-C語言性能對照測試
popu ref span ngs htm post 沒有 接受 string 原文發表於踏得網Swift包括了非常多現代語言特性尤其是從一些腳本語言如Javascript/Ruby中汲取了營養。此外蘋果公布Swift時,使用特別選用的一些樣例來宣稱Swift性能對於Oj
objective-c 中數據類型之四 字典(NSDictionary)
bject ted ray 初始化 -c lec com lock led // 1. 字典初始化、賦值方式1 NSMutableDictionary *m_dictionary = [[NSMutableDictionary alloc] initWithCa
第 1 條:了解 Objective-C 語言的起源
還在 特性 只知道 程序 開發 不能 核心 nbsp 原因 馬上就要發布 Swift 4 了,自己也在學習 Swift,後面 iOS 編程估計也快是 Swift 的天下了,我卻還在這抱著一本講 OC 的書在啃,怪只能怪自己之前太懶了,按定價好幾十塊錢買的書不讀完,簡直對
objective-c 中數據類型之二 字符串(NSString)
option 大小 edas 字符串長度 seq scan 後者 code form // 1. 聲明一個NSString對象,註意對象前要加‘*’。 NSString *string1; // 賦值方
Objective-C - NSInteger轉換NSString
cast you 字符 instr pen compile ber 技術 exclusive NSInteger不是對象, 轉換為long匹配64位系統, 再組成字符串(%ld). NSString *inStr = [NSString strin
Swift 4 和 Objective-C 混合編程(一) 快速起步
命名方式 import 編譯器 選擇性 工程 Swift 4 和 Objective-C 在同一個工程裏的混搭編程的方法你可以在 xcode 裏同時使用 Swift 和 Objective-C(以下簡稱OC)來寫代碼,混搭編程的好處很多,比如允許大量代碼的復用,在性能和開發效率之間找到平衡
objective-c訪問控制符
mod ont 生成 外部 ble 外部程序 data char prot objective-c中成員變量的四個訪問控制符: @private:僅僅有當前類的內部才幹訪問 @public:全部人都可訪問 @pr
Objective-C 空指針和野指針
cti info alt mage log 存儲 報錯 .com 指針 一、什麽是空指針和野指針 1.空指針 1> 沒有存儲任何內存地址的指針就稱為空指針(NULL指針) 2> 空指針就是被賦值為0的指針,在沒有被具體初始化之前,其值為0。 下面兩個都是
Objective-C NSFileManager 文件管理總結
obj mat cto desktop hint ora reat eat fit createFileAtPath //創建文件 NSFileManager *fm = [NSFileManager defaultManager]; N
深入理解Objective-C:Category
fix 忽略 DDU 相關 情況 內存布局 先生 們的 ntc https://tech.meituan.com/DiveIntoCategory.html 摘要 無論一個類設計的多麽完美,在未來的需求演進中,都有可能會碰到一些無法預測的情況。那怎麽擴展已有的類呢?一般而言
Objective-C 內存管理retain和release
計數 nco 優雅 tracking con void sep res 釋放資源 OC使用引用計數來管理內存,每個繼承NSObject的對象,內部都維護了一個引用計數器retainCount。當對象創建時(調用alloc或者new)引用計數器會+1, 手動調用retai
iOS開發核心語言Objective C —— 面向對象思維、setter和getter方法及點語法
才幹 各路 alt .net 行為 變量的作用域 fadein 格式 讀取 本分享是面向有意向從事iOS開發的夥伴們。或者已經從事了iOS的開發人員。假設您對iOS開發有極高的興趣,能夠與我一起探討iOS開發。一起學習,共同進步。假設您是零基礎,建議您先