Canvas繪圖介面(曲線)
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-22
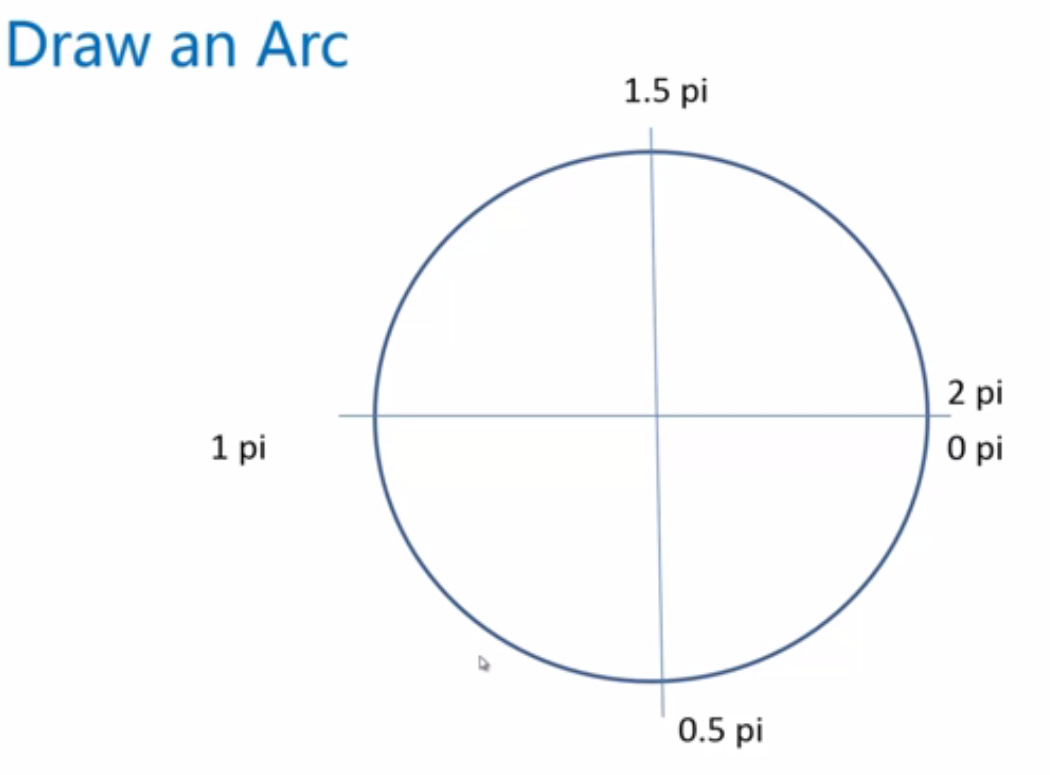
繪製一段弧線
使用arc()繪製弧線
context.arc(
centerx,centery,radius,//圓心座標,圓弧的半徑
startingAngle,endingAngle,//開始角度,結束角度
anticlockwise=false//可選,是都是逆時針的繪製,預設false順時針繪製
)
<script type="text/javascript">
/*繪製一段弧線*/
var canvas = document.getElementById('canvas');
canvas.width = 800 繪製一個圓角矩形
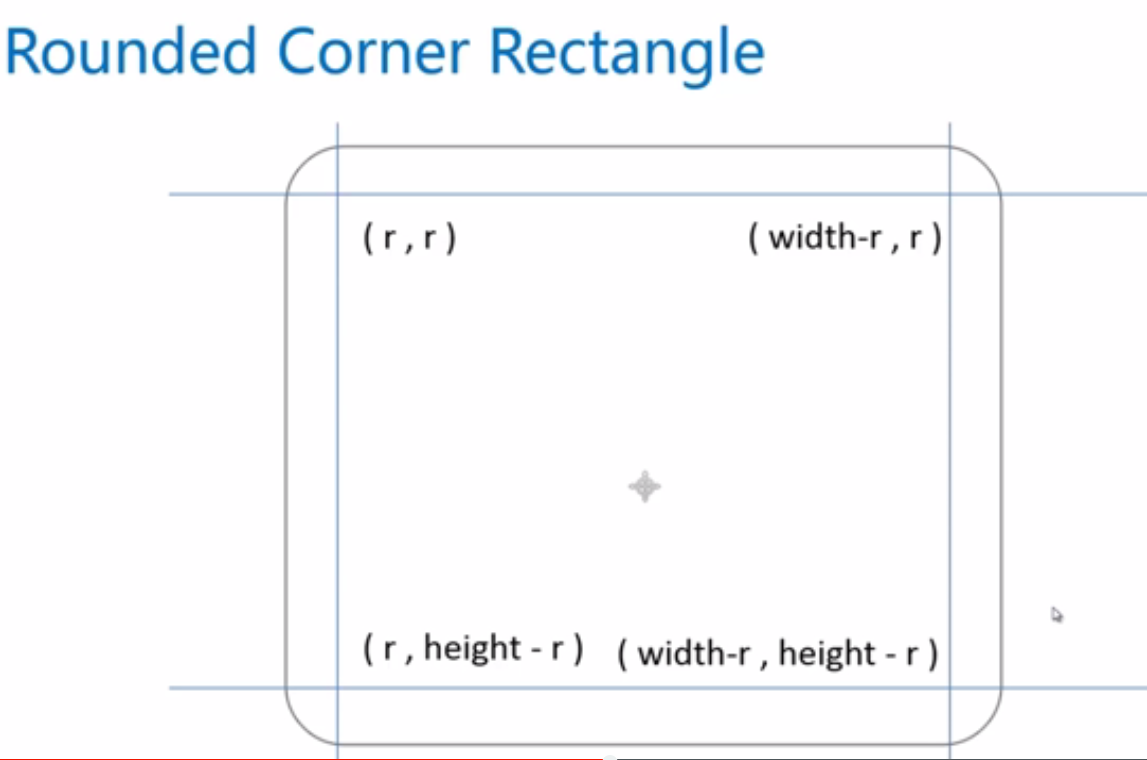
/*繪製一個圓角矩形*/
/**
* [drawRoundRect 繪製一個圓角矩形]
* @param {[type]} cxt [description]
* @param {[type]} x [左上角的座標]
* @param {[type]} y [左上角的座標]
* @param 下面是經過改造的兩個畫圓角矩形的方法
//畫出填充矩形
function fillRoundRect(cxt,x,y,width,height,radius,fillColor){
//這裡進行判斷,防止半徑過大,這樣矩形就會變形
if(2*radius > width || 2*radius > height){
return;
}
cxt.save();
cxt.translate(x,y);
pathRoundRect(cxt,width,height,radius);
cxt.fillStyle = fillColor || 'black';
cxt.fill();
cxt.restore();
}
//畫出邊框矩形
function strokeRoundRect(cxt,x,y,width,height,radius,strokeColor,lineWidth){
//這裡進行判斷,防止半徑過大,這樣矩形就會變形
if(2*radius > width || 2*radius > height){
return;
}
cxt.save();
cxt.translate(x,y);
pathRoundRect(cxt,width,height,radius);
cxt.lineWidth = lineWidth || 1;
cxt.strokeStyle = strokeColor || 'black';
cxt.stroke();
cxt.restore();
}實現2048遊戲的棋盤
/*使用圓角矩形繪製一個2048的棋盤*/
//首先繪製一個大的填充的圓角矩形,即底盤
fillRoundRect(context,150,150,500,500,10,'#bbada0');
//繪製16個小矩形
for(var i = 0;i<4; i++){
for(var j = 0 ; j < 4 ; j++){
fillRoundRect(context, 170 + i * 120 , 170 + j * 120 , 100,100,6,'#ccc0b3');
}
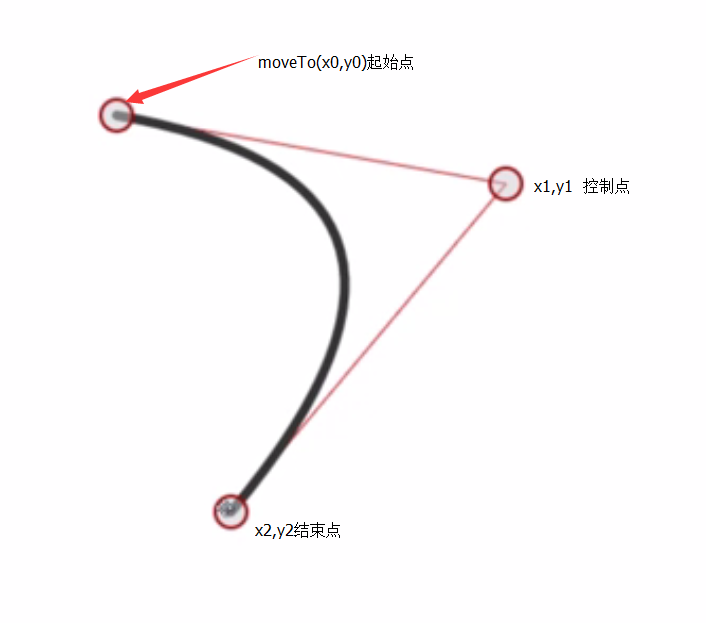
}使用arcTo()繪製弧線
控制點
context.moveTo(x0,y0);
context.arcTo(x1,y1,x2,y2,radius);
會將x0,y0作為起始點,x1,y1位控制點,在使用arcTo繪製弧線時,從(x0,y0)開始繪製,起點是(x0,y0),但是不一定弧線就是從(x0,y0)開始的,而是在(x0,y0)~(x1,y1)相切的點事弧線的開始,但是中線不一定就是x2,y2,因為arcTo會找到(x1,y1)~(x2,y2)的相切的點為終止點
arcToTest(context,150,100,650,100,650,600,500);
//arcTo繪製進行抽象到方法中
function arcToTest(cxt,x0,y0,x1,y1,x2,y2,R){
/*使用arcTo()繪製弧線*/
cxt.beginPath();
cxt.moveTo(x0,y0);
cxt.arcTo(x1,y1,x2,y2,R);
cxt.lineWidth = 10;
cxt.strokeStyle = 'red';
cxt.stroke();
//繪製兩條直線做輔助線,即(x0,y0)--(x1,y1)和(x1,y1)--(x2,y2)這兩條直線
cxt.beginPath();
cxt.moveTo(x0,y0);
cxt.lineTo(x1,y1);
cxt.lineTo(x2,y2);
cxt.lineWidth = 2;
cxt.strokeStyle = '#aaa';
cxt.stroke();
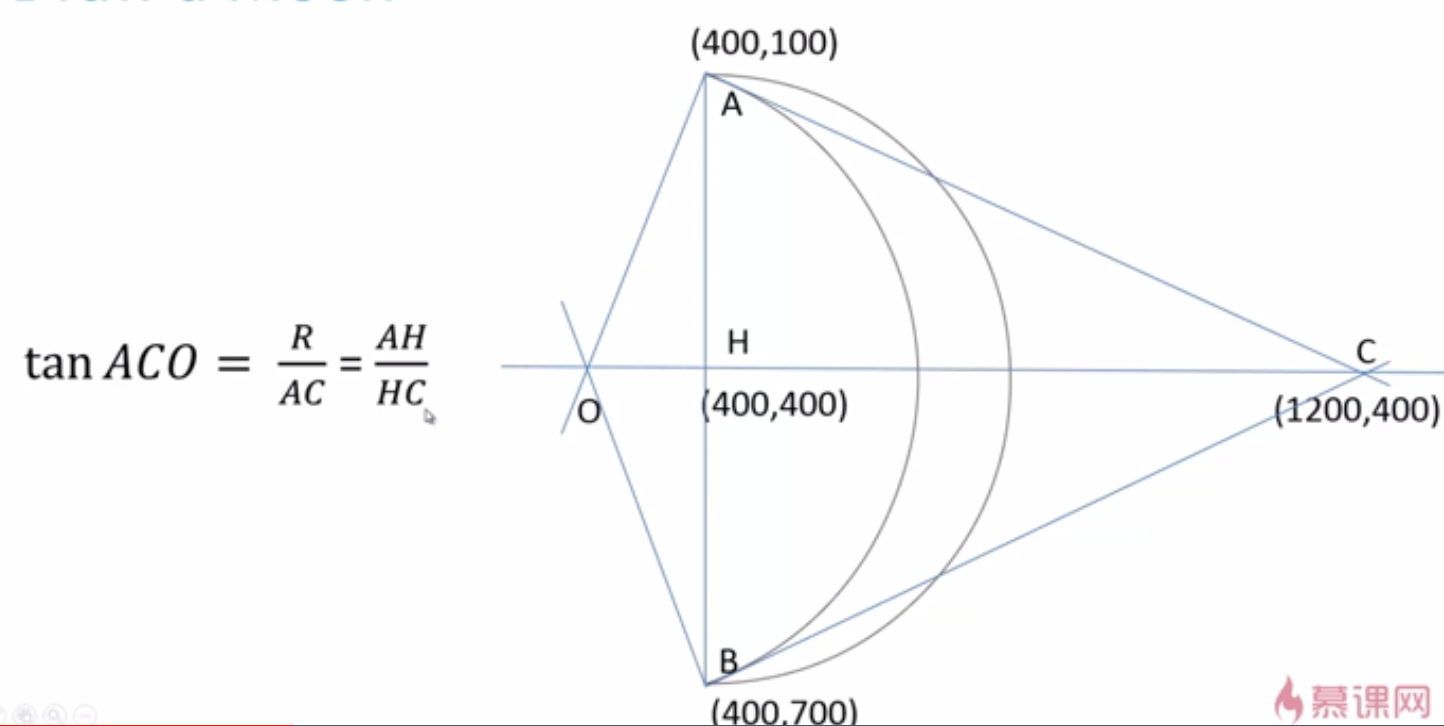
}使用arc和arcTo繪製一輪彎月
固定繪製一個彎月
<script type="text/javascript">
/*繪製一輪彎月*/
/**
* 彎月外面的弧是一段半圓弧線,使用arc繪製即可
* 裡面是一段弧線,要用arcTo繪製
*/
context.arc(400,400,300,0.5 * Math.PI,1.5 * Math.PI ,true);
context.moveTo(400,100);
context.arcTo(1200,400,400,700,(400 - 100) * dis(1200,400,400,100) /(1200 - 400));
context.stroke();
//直角三角形求斜邊長度
function dis(x1,y1,x2,y2){
return Math.sqrt((x1 - x2)*(x1 - x2) + (y1-y2) * (y1-y2));
}
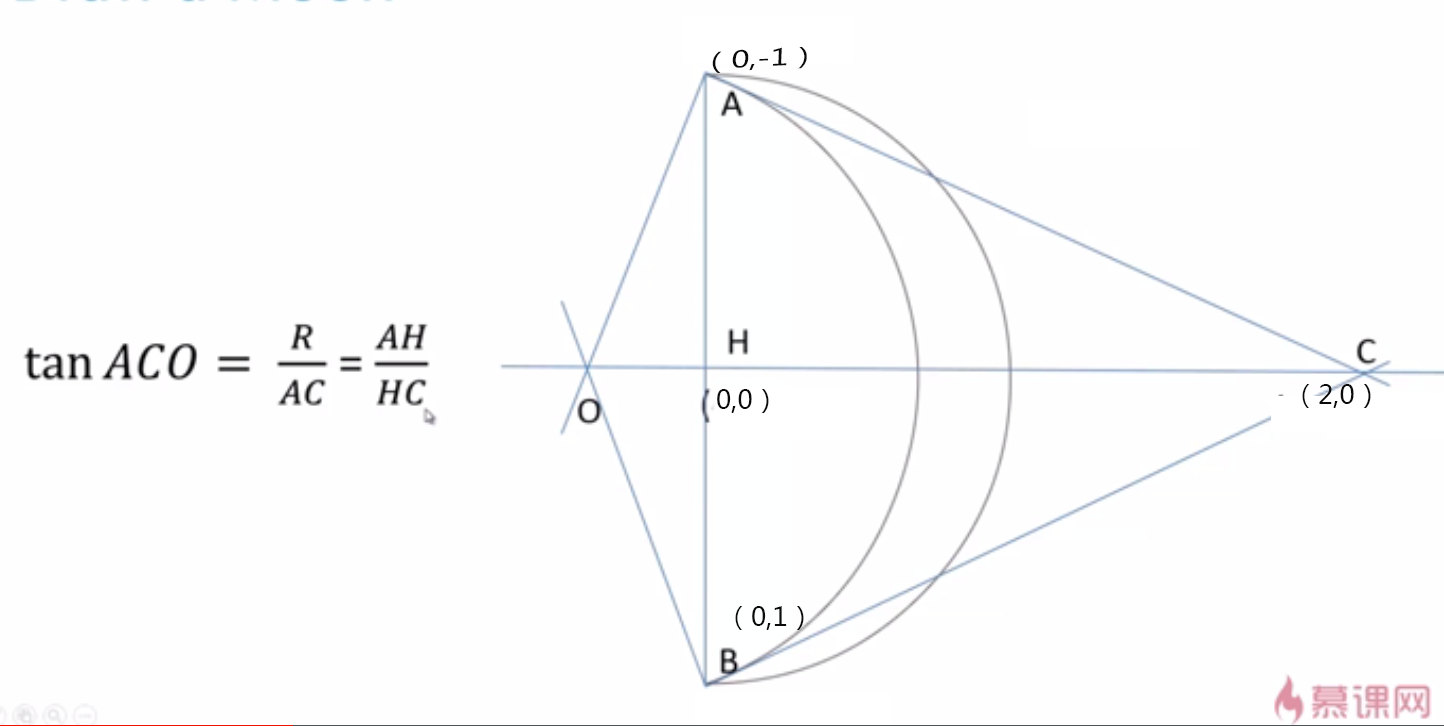
</script>正則環境下繪製彎月
在正則的環境下繪製,即以0,0點為圓心,1位半徑的環境下繪製,這樣的話
控制點d的值也應該在這個範圍內進行取值
通過translate(),rotate(),scale()對正則環境下的彎月進行位移,旋轉,縮放
/**
* [fillMoon 繪製帶有填充顏色的彎月
* 在正則的環境下繪製,即以0,0點為圓心,1位半徑的環境下繪製,這樣的話
* 控制點d的值也應該在這個範圍內進行取值
*
* 通過translate(),rotate(),scale()對正則環境下的彎月進行位移,旋轉,縮放
* ]
* @param {[type]} cxt [description]
* @param {[type]} d [arcTo控制點的x座標]
* @param {[type]} x [彎月的位置]
* @param {[type]} y [彎月的位置]
* @param {[type]} R [彎月的半徑]
* @param {[type]} rot [彎月旋轉的角度]
* @param {[type]} fillColor [用什麼顏色填充,可選]
* @return {[type]} [description]
*/
function fillMoon(cxt,d,x,y,R,rot,fillColor){
cxt.save();
cxt.translate(x,y);
cxt.rotate(rot * Math.PI /180);
cxt.scale(R,R);
pathMoon(cxt,d);
cxt.fillStyle = fillColor || '#fd5';
cxt.fill();
cxt.restore();
}
//以0,0點為圓心,1位半徑的單位圓進行路徑規劃
function pathMoon(cxt,d){
cxt.beginPath();
cxt.arc(0,0,1,0.5 * Math.PI,1.5 * Math.PI ,true);
cxt.moveTo(0,-1);
cxt.arcTo(d,0,0,1,dis(d,0,0,-1) /d );
cxt.closePath();
}
fillMoon(context,2,400,400,300,0);貝塞爾曲線
二次貝塞爾曲線
context.moveTo(x0,y0);
context.quadraticCurveTo(x1,y1,x2,y2);
和arcTo不同的是moveTo的x0,y0就是曲線的起始點,x2,y2就是曲線的終止點,x1,y1是控制點
不會是一個標準的圓弧,會扭曲,扭曲成什麼樣子,那就要根據幾個座標的位置了
在上面arcTo繪製彎月的基礎上,講pathMoon(cxt,d)方法進行更改
//使用貝塞爾曲線進行規劃彎月路徑
function pathMoon(cxt,d){
cxt.beginPath();
cxt.arc(0,0,1,0.5 * Math.PI,1.5 * Math.PI ,true);
cxt.moveTo(0,-1);
//cxt.arcTo(d,0,0,1,dis(d,0,0,-1) /d );
cxt.quadraticCurveTo(1.2,0,0,1);
cxt.closePath();
}
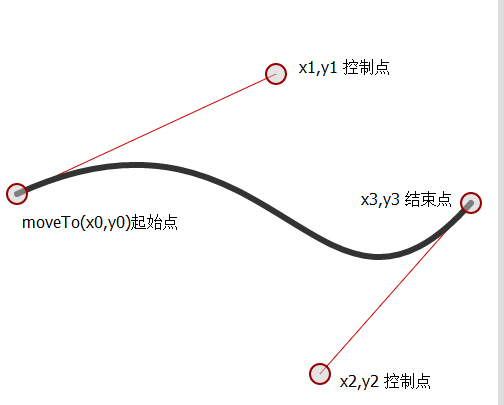
fillMoon(context,2,400,400,300,0);三次貝塞爾曲線
context.moveTo(x0,y0);
context.bezierCurveTo(x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3);
三次貝塞爾曲線可以畫出波浪形的曲線,而二次貝塞爾曲線是畫不出來的
和二次曲線不同的是,三次貝塞爾曲線有兩個控制點
(x1,y1)、(x2,y2)為控制點,(x3,y3)是曲線的終止點