學習記錄:一個試卷批改系統
本文程式設計採用Python語言,結合opencv庫對影象進行處理,再利用TensorFlow框架下卷積神經網路 實現一個初步的簡易試卷批改系統。
實現一個試卷批改系統,我將它主要分成倆個模組,第一個模組是影象識別,第二個模組是利用機器學習訓練模型。
先說我們是如何訓練模型的,對於一般的影象分類問題,利用卷積神經網路是一個不錯的選擇,卷積神經網路在影象分類的應用十分廣泛,具體程式碼如下:
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
mnist=input_data.read_data_sets('MNIST_data' - 測試下我們訓練的準確率情況:訓練10000次,每隔100次列印一次,最後的訓練準確率大概是99%左右。
程式碼中使用的是mnist手寫數字資料集,將影象分成10個類別,分別代表數字0-9,訓練好的模型儲存在my_net/save_net.ckpt裡面,檔案格式是.ckpt。
下一步工作是如何呼叫訓練的模型。呼叫模型的方法很簡單,首先需要重構一個和訓練集一樣的神經網路架構,注意這裡不需要再訓練資料了,直接呼叫模型就可以了,然後輸入和mnist資料集相同格式的圖片就能實現數字識別。如下程式碼 是如何重構模型以及呼叫模型的方法。(注意在儲存和呼叫模型的程式碼中均有saver.restore(sess, “my_net/save_net.ckpt”)這段程式碼,唯一不同的是,儲存程式碼用的是saver.save(sess, “my_net/save_net.ckpt”),呼叫程式碼用的是saver.restore(sess, “my_net/save_net.ckpt”)。)
import tensorflow as tf
import cv2
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
def weight_variable(shape):
initial=tf.truncated_normal(shape,stddev=0.1)
return tf.Variable(initial,dtype=tf.float32,name='weight')
def bias_variable(shape):
initial=tf.constant(0.1,shape=shape)
return tf.Variable(initial,dtype=tf.float32,name='biases')
def conv2d(x,W):
return tf.nn.conv2d(x,W,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding='SAME')
def max_pool_2x2(x):
return tf.nn.max_pool(x,ksize=[1,2,2,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],padding='SAME')
xs=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,784])#輸入是一個28*28的畫素點的資料
keep_prob=tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
x_image=tf.reshape(xs,[-1,28,28,1])#xs的維度暫時不管,用-1表示,28,28表示xs的資料,1表示該資料是一個黑白照片,如果是彩色的,則寫成3
#卷積層1
W_conv1=weight_variable([5,5,1,32])#抽取一個5*5畫素,高度是32的點,每次抽出原影象的5*5的畫素點,高度從1變成32
b_conv1=bias_variable([32])
h_conv1=tf.nn.relu(conv2d(x_image,W_conv1)+b_conv1)#輸出 28*28*32的影象
h_pool1=max_pool_2x2(h_conv1)##輸出14*14*32的影象,因為這個函式的步長是2*2,影象縮小一半。
#卷積層2
W_conv2=weight_variable([5,5,32,64])#隨機生成一個5*5畫素,高度是64的點,抽出原影象的5*5的畫素點,高度從32變成64
b_conv2=bias_variable([64])
h_conv2=tf.nn.relu(conv2d(h_pool1,W_conv2)+b_conv2)#輸出14*14*64的影象
h_pool2=max_pool_2x2(h_conv2)##輸出7*7*64的影象,因為這個函式的步長是2*2,影象縮小一半。
#fully connected 1
W_fc1=weight_variable([7*7*64,1024])
b_fc1=bias_variable([1024])
h_pool2_flat=tf.reshape(h_pool2,[-1,7*7*64])#將輸出的h_pool2的三維資料變成一維資料,平鋪下來,(-1)代表的是有多少個例子
h_fc1=tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_pool2_flat,W_fc1)+b_fc1)
h_fc1_drop=tf.nn.dropout(h_fc1,keep_prob)
#fully connected 2
W_fc2=weight_variable([1024,10])
b_fc2=bias_variable([10])
prediction=tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(h_fc1_drop,W_fc2)+b_fc2)#輸出層
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
saver = tf.train.Saver()
saver.restore(sess, "my_net/save_net.ckpt")
result= tf.argmax(prediction, 1)
#result= result.eval(feed_dict={xs:img, keep_prob: 1.0}, session=sess)
result=sess.run(prediction, feed_dict={xs:img,keep_prob: 1.0})
result1 =np.argmax(result,1)
print(result1)
# result = sess.run(prediction, feed_dict={x: data})
# print(result)- 接下來我們來做一個測試,測試圖片如下:

對於上面的圖片,我們先對影象進行一系列處理,讓它符合我們的格式,程式碼如下:
import tensorflow as tf
import cv2
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
img = cv2.imread("D:\\opencv_camera\\digits\\10.jpg")
res=cv2.resize(img,(28,28),interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
#cv2.namedWindow("Image")
#print(img.shape)
#灰度化
emptyImage3=cv2.cvtColor(res,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
cv2.imshow("a",emptyImage3)
cv2.waitKey(0)
#二值化
ret, bin = cv2.threshold(emptyImage3, 140, 255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
cv2.imshow("a",bin)
cv2.waitKey(0)
print(bin)
def normalizepic(pic):
im_arr = pic
im_nparr = []
for x in im_arr:
x=1-x/255
im_nparr.append(x)
im_nparr = np.array([im_nparr])
return im_nparr
#print(normalizepic(bin))
img=normalizepic(bin).reshape((1,784))
#print(img)
img= img.astype(np.float32)灰度化的圖片如下: 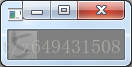
二值化的圖片如下: 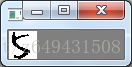
然後呼叫模型結果如下: 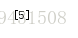
結果是5,預測準確。
上面的是做測試結果,關於試卷識別,我們有下面的例子,圖片如下: 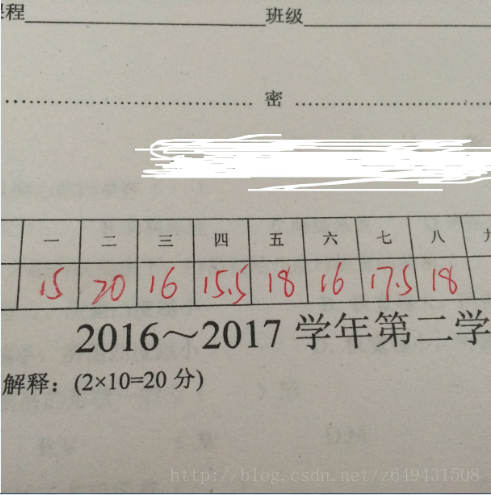
對這個圖片我們要做的是提取方框內的分數,然後識別出來數字,進行統計,最後得出分數總和,儲存起來,這就是整體思路。具體操作程式碼如下:
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import cv2
from PIL import Image
from skimage import data, util,measure,color
from skimage.measure import label
image = cv2.imread('D:\opencv_camera\digits\\12.jpg')
lower=np.array([50,50,150])
upper=np.array([140,140,250])
mask = cv2.inRange(image, lower, upper)
output1 = cv2.bitwise_and(image, image, mask=mask)
output=cv2.cvtColor(output1,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
th2 = cv2.adaptiveThreshold(output,255,cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_GAUSSIAN_C,cv2.THRESH_BINARY,11,0)
# cv2.imshow("images",th2)
# cv2.waitKey(0)
roi=[]
for i in range(8):
img_roi = output1[260:310,35+55*i:80+58*i]
roi.append(img_roi)
#歸一化
def normalizepic(pic):
im_arr = pic
im_nparr = []
for x in im_arr:
x=1-x/255
im_nparr.append(x)
im_nparr = np.array([im_nparr])
return im_nparr
########圖片預處理##########
def weight_variable(shape):
initial=tf.truncated_normal(shape,stddev=0.1)
return tf.Variable(initial,dtype=tf.float32,name='weight')
def bias_variable(shape):
initial=tf.constant(0.1,shape=shape)
return tf.Variable(initial,dtype=tf.float32,name='biases')
def conv2d(x,W):
return tf.nn.conv2d(x,W,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding='SAME')
def max_pool_2x2(x):
return tf.nn.max_pool(x,ksize=[1,2,2,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],padding='SAME')
xs=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,784])#輸入是一個28*28的畫素點的資料
keep_prob=tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
x_image=tf.reshape(xs,[-1,28,28,1])#xs的維度暫時不管,用-1表示,28,28表示xs的資料,1表示該資料是一個黑白照片,如果是彩色的,則寫成3
#卷積層1
W_conv1=weight_variable([5,5,1,32])#抽取一個5*5畫素,高度是32的點,每次抽出原影象的5*5的畫素點,高度從1變成32
b_conv1=bias_variable([32])
h_conv1=tf.nn.relu(conv2d(x_image,W_conv1)+b_conv1)#輸出 28*28*32的影象
h_pool1=max_pool_2x2(h_conv1)##輸出14*14*32的影象,因為這個函式的步長是2*2,影象縮小一半。
#卷積層2
W_conv2=weight_variable([5,5,32,64])#隨機生成一個5*5畫素,高度是64的點,抽出原影象的5*5的畫素點,高度從32變成64
b_conv2=bias_variable([64])
h_conv2=tf.nn.relu(conv2d(h_pool1,W_conv2)+b_conv2)#輸出14*14*64的影象
h_pool2=max_pool_2x2(h_conv2)##輸出7*7*64的影象,因為這個函式的步長是2*2,影象縮小一半。
#fully connected 1
W_fc1=weight_variable([7*7*64,1024])
b_fc1=bias_variable([1024])
h_pool2_flat=tf.reshape(h_pool2,[-1,7*7*64])#將輸出的h_pool2的三維資料變成一維資料,平鋪下來,(-1)代表的是有多少個例子
h_fc1=tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_pool2_flat,W_fc1)+b_fc1)
h_fc1_drop=tf.nn.dropout(h_fc1,keep_prob)
#fully connected 2
W_fc2=weight_variable([1024,10])
b_fc2=bias_variable([10])
prediction=tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(h_fc1_drop,W_fc2)+b_fc2)#輸出層
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
saver = tf.train.Saver()
saver.restore(sess, "my_net/save_net.ckpt")
result= tf.argmax(prediction, 1)
SUM=[]
for i in range(8):
output = cv2.cvtColor(roi[i], cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
th2 = cv2.adaptiveThreshold(output, 255, cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_GAUSSIAN_C, cv2.THRESH_BINARY, 11, 0)
# cv2.imshow("images", th2)
# cv2.waitKey(0)
labels = label(th2, connectivity=2)
dst = color.label2rgb(labels)
a=[]
for region in measure.regionprops(labels):
minr, minc, maxr, maxc = region.bbox
# img = cv2.rectangle(dst, (minc -10 , minr - 10), (maxc + 10, maxr + 10), (0, 255, 0), 1)
ROI = th2[minr - 2:maxr + 2, minc - 2:maxc + 2]
if ROI.shape[1] < 10:
kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (2, 2))
ROI = cv2.erode(ROI, kernel, iterations=1)
ret, thresh2 = cv2.threshold(ROI, 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV)
res = cv2.resize(thresh2, (28, 28), interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
cv2.imshow("images", res)
cv2.waitKey(0)
img = normalizepic(res).reshape((1, 784))
img = img.astype(np.float32)
result=sess.run(prediction, feed_dict={xs:img,keep_prob: 1.0})
result1 =np.argmax(result,1)
print(result1)
a.append(result1)
if len(a)==2:
#print(a[1]*10+a[0])
SUM.append(a[1]*10+a[0])
else:
#print(a[0])
SUM.append(a[0])
print(sum(SUM))將最後的結果儲存在列表中,得出結果。整個程式碼寫到這裡基本上就完成了,在影象處理過程中,需要掌握opencv的一些具體的操作,包括影象二值化,特定區域ROI提取,在對影象進行分割的時候用到了skimage庫,這個庫可以對不同連通區域的影象進行分割,非常方便實用。整個過程還存在一些問題需要完善,包括對於粘連的數字如何處理,之前查過一篇文獻光學手寫數字字元識別技術的研究,裡面提到了一種用水滴法分割粘連字元,整個識別過程還存在一些不足,後續還有很大的改善空間。
