同構樹的判斷 poj 1635
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-23
題目的描述比較長,總的意思就是給出兩棵有根樹,判斷它們是不是同構樹。
所謂的同構樹,定義我也不太知道 。按字面上的意思就是兩棵結構相同的樹。
。按字面上的意思就是兩棵結構相同的樹。
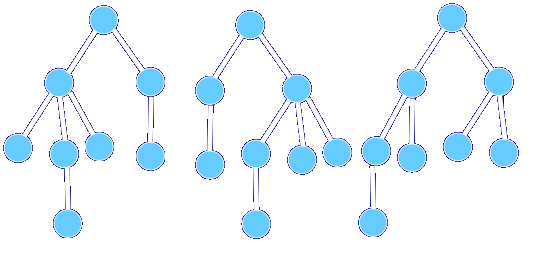
如第一棵樹和第二棵樹就是同構樹,它們和第三棵樹不是同構樹:
並且,同構樹它們有一一對應的點。
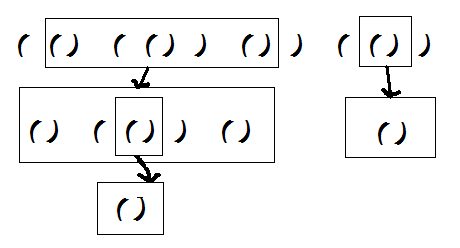
如上面的第一棵樹,既可以表示成(()(())())(()),也可以表示成(())((())()()),有很多的表示方法,為了判斷,我們要用最小表示法,就是字典序最小的一個。第一種括號可以分解成:
每一層都排一下序就可以找到字典樹最小的一個啦 。
。
其實原題就是這樣的一個括號序列,0代表左括號,1代表右括號。這樣問題就很簡單了,把這讀入的兩個字串當做括號處理,如果它們的最小表示法是一樣的,那麼就是同構樹啦。
但是,我們要對字串進行分解,分解完了還要排序,不僅時間複雜度不樂觀,空間處理也比較麻煩。所以,我們可以用雜湊,把一個括號序列雜湊掉。合併的時候將雜湊值從小到大排序,再合成當前的雜湊值。可以去看看《楊弋<Hash在資訊學競賽中的一類應用>》這篇文章。
我看到網上有一種方法,判斷每一層的節點數是否相等,且相同層數子樹大小經過排序後對應相等,那麼就是同構。我不知道這種方法對不對,網上有的說這是錯的。我寫了一下,還真的過了,求證明。
#include <cstdio> #include <cstdlib> #include <time.h> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; int n, P[3007]; bool d[6007]; // 這樣讀入會快些?? int read(int i) { char ch = '*'; do ch = getchar(); while (ch < '0' || ch > '1'); for (; ch == '0' || ch == '1'; ch = getchar()) d[i ++] = ch == '1'; return i; } // 字串的[L, R)的雜湊值 int GetHash(int L, int R) { if (L >= R) return 1; // 只能用vector??我想不到更好的辦法 vector<int> t; t.clear(); int f = 0, cnt = 0; for (int i = L; i < R; i ++) { if (d[i]) f --; else f ++; // 當括號匹配時就可以分解了 if (f == 0) { t.push_back(GetHash(L + 1, i)), cnt ++; L = i + 1; } } // 排序 sort(t.begin(), t.end()); // 求出當前雜湊值 int res = 1; // 這要找個好的雜湊函式, // 一開始我寫得不好,有很多重複 // 後來在網上看到如下的方法 for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i ++) res = (res ^ t[i]) * P[i] % 15237; return res; } int main() { freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin); freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout); srand((int)time(0)); for (int i = 0; i < 3000; i ++) P[i] = rand() % 15237; int T; scanf("%d\n", &T); while (T --) { int n = read(0); int m = read(n); if (GetHash(0, n) == GetHash(n, m)) printf("same\n"); else printf("different\n"); } return 0; }
奇怪的方法(程式碼有點爛, 其實不用構圖的):
#include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; const int N = 3007; struct Tree { int n; int father[N], head[N], to[N], next[N], cnt; struct data { int depth, size; bool operator < (data const &o) const { if (depth != o.depth) return depth < o.depth; return size < o.size; } bool operator == (data const &o) const { return depth == o.depth && size == o.size; } }d[N]; void Insert(int u, int v) { to[++ cnt] = v; next[cnt] = head[u]; head[u] = cnt; } int Q[N]; void Build(char *s) { cnt = 0; memset(head, 0, sizeof(head)); int len = strlen(s); n = 1; int cur = 1; for (int i = 0; i < len; i ++) if (s[i] == '0') { Insert(cur, ++ n); father[n]= cur; cur = n; } else cur = father[cur]; d[1].depth = 1; int lo = 0, hi = 0; Q[0] = 1; for (; lo <= hi; lo ++) { int u = Q[lo]; for (int e = head[u]; e; e = next[e]) { int v = to[e]; d[v].depth = d[u].depth + 1; Q[++ hi] = v; } } for (; hi >= 0; hi --) { int u = Q[hi]; d[u].size = 1; for (int e = head[u]; e; e = next[e]) d[u].size += d[to[e]].size; } sort(d + 1, d + 1 + n); } bool operator == (Tree const &o) const { if (n != o.n) return false; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) if (!(d[i] == o.d[i])) return false; return true; } }a, b; char dat[N]; int main() { int T; scanf("%d\n", &T); while (T --) { scanf("%s\n", dat); a.Build(dat); scanf("%s\n", dat); b.Build(dat); if (a == b) printf("same\n"); else printf("different\n"); } return 0; }