原來可以這樣二分 -_-
The determinant of a matrix 2 × 2 is defined as follows:
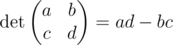
A matrix is called degenerate if its determinant is equal to zero.
The norm ||A|| of a matrix A is defined as a maximum of absolute values of its elements.
You are given a matrix 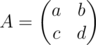 .
Consider any degenerate matrix B such that norm ||A - B
.
Consider any degenerate matrix B such that norm ||A - B
The first line contains two integers a and b (|a|, |b| ≤ 109), the elements of the first row of matrix A.
The second line contains two integers c and d (|c|, |d| ≤ 109) the elements of the second row of matrix A.
Output
Output a single real number, the minimum possible value of ||A
1 2 3 4output
0.2000000000input
1 0 0 1output
0.5000000000Note
In the first sample matrix B is 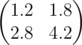
In the second sample matrix B is 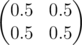
題意:
給你一個2*2的矩陣A,讓你構造一個矩陣B,矩陣B要滿足兩條對角線元素相乘結果相等,使得 ||A-B|| 值最小。||X||表示矩陣X中的4個元素中值最大的元素。
分析:
列舉增量(發現有很多二分都是列舉增量的),判斷是否符合條件,然後縮小範圍。
code:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long double LD;
int a, b, c, d;
LD f1(int m1, int m2, LD x)
{
return max(max((m1+x)*(m2+x),(m1+x)*(m2-x)),max((m1-x)*(m2+x),(m1-x)*(m2-x)));
}
LD f2(int m1, int m2, LD x)
{
return min(min((m1+x)*(m2+x),(m1+x)*(m2-x)),min((m1-x)*(m2+x),(m1-x)*(m2-x)));
}
int Check(LD x)
{
LD pr = f1(a,d,x); //(a..)*(d..) 與 (c..)*(b..) 比較,把它比作第一段和第二段,然後進行比較,是否會有等值情況
LD pl = f2(a,d,x);
LD qr = f1(c,b,x);
LD ql = f2(c,b,x);
if(pr < ql || qr < pl) return 0; //如果第一段與第二段不相交,則擴大兩邊使其可能相交
else return 1; //如果已經相交,那麼減小增量x使得兩邊縮小,更靠近結果
} //這裡我說得相交是將最大值與最小值看做兩個點,連成的一條線段,最後兩條線段的位置關係(yy的。。)
//相交的部分代表值相等
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d%d%d", &a,&b,&c,&d);
LD l=0, r=1e10;
for(int i=0; i<200; i++)
{
LD mid = 0.5*(l+r);
if(Check(mid)) r = mid;
else l = mid; //增量x增大,那麼結果的兩邊(最大值與最小值)會相應往兩邊擴(更大、更小)
}
printf("%.10f\n", (double)(0.5*(l+r)));
return 0;
}做完上面這道題後,把本來一直不會做的下面這道題給秒了。。
序列變換
Time Limit: 4000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 625 Accepted Submission(s): 305
Problem Description 給定序列A={A1,A2,...,An}, 要求改變序列A中的某些元素,形成一個嚴格單調的序列B(嚴格單調的定義為:Bi<Bi+1,1≤i<N)。
我們定義從序列A到序列B變換的代價為cost(A,B)=max(|Ai−Bi|)(1≤i≤N)。
請求出滿足條件的最小代價。
注意,每個元素在變換前後都是整數。
Input 第一行為測試的組數T(1≤T≤10).
對於每一組:
第一行為序列A的長度N(1≤N≤105),第二行包含N個數,A1,A2,...,An.
序列A中的每個元素的值是正整數且不超過106。
Output 對於每一個測試樣例,輸出兩行:
第一行輸出:"Case #i:"。i代表第 i 組測試資料。
第二行輸出一個正整數,代表滿足條件的最小代價。
Sample Input 2 2 1 10 3 2 5 4
Sample Output Case #1: 0 Case #2: 1 code:
#include<stdio.h>
int T, n, a[100010], b[100010];
bool Check(int x)
{
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) b[i] = a[i];
b[0] -= x;
for(int i=1; i<n; i++)
{
int temp1 = b[i-1]-b[i]+1;
int temp2 = b[i]-b[i-1]-1;
if(b[i] <= b[i-1])
{
if(temp1 > x) return false;
else b[i] = b[i-1]+1;
}
else
{
if(temp2 <= x) b[i] = b[i-1]+1;
else b[i] -= x;
}
}
return true;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d", &T);
for(int t=1; t<=T; t++)
{
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
scanf("%d", a+i);
int l = 0, r = 1e6, mid;
for(int i=0; i<20; i++)
{
mid = (l+r)/2;
if(Check(mid)) r = mid;
else l = mid;
}
printf("Case #%d:\n%d\n", t,r);
}
return 0;
}