C++之多重繼承
大多數應用程式使用單個基類的公用繼承,但是在某些情況下,單繼承是不夠的,必須使用多繼承。C++允許為一個派生類指定多個基類,這樣的繼承結構被稱做多重繼承.
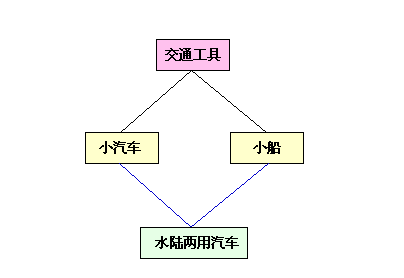
舉個例子,交通工具類可以派生出汽車和船連個子類,但擁有汽車和船共同特性水陸兩用汽車就必須繼承來自汽車類與船類的共同屬性。如下圖示:
程式碼實現:
//多重繼承
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Vehicle
{
public:
Vehicle(int weight = 0)
{
Vehicle::weight = weight;
}
void SetWeight(int weight)
{
cout << "重新設定重量" << endl;
Vehicle::weight = weight;
}
virtual void ShowMe() = 0;//純虛擬函式
protected:
int weight;
private:
};
class car :public Vehicle//汽車
{
public:
car(int weight = 0, int aird = 0) :Vehicle(weight)
{
car::aird = aird;
}
void ShowMe()
{
cout << "我是汽車!" << endl;
}
protected:
int aird;
private:
};
class boat :public Vehicle//船
{
public:
boat(int weight = 0, float tonnage = 0) :Vehicle(weight)
{
boat::tonnage = tonnage;
}
void ShowMe()
{
cout << "我是船!" << endl;
}
protected:
float tonnage;
private:
};
class AmphibianCar :public car, public boat//水陸兩用汽車,多重繼承的體現
{
public:
AmphibianCar(int weight, int aird, float tonnage)
:Vehicle(weight), car(weight, aird), boat(weight, tonnage)
//多重繼承要注意呼叫基類建構函式
{
}
void ShowMe()
{
cout << "我是水陸兩用汽車!" << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
AmphibianCar a(4, 200, 1.35f);//錯誤
a.SetWeight(3);//錯誤
system("pause");
}
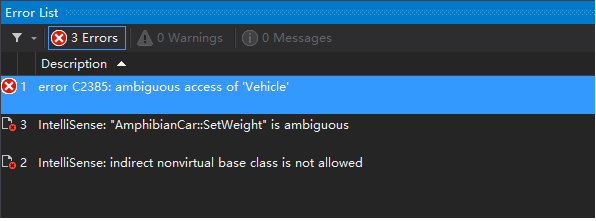
上面的程式碼從表面看,看不出有明顯的語發錯誤,但是它是不能夠通過編譯的。錯誤如下:
這有是為什麼呢? 這是由於多重繼承帶來的繼承的模糊性帶來的問題。
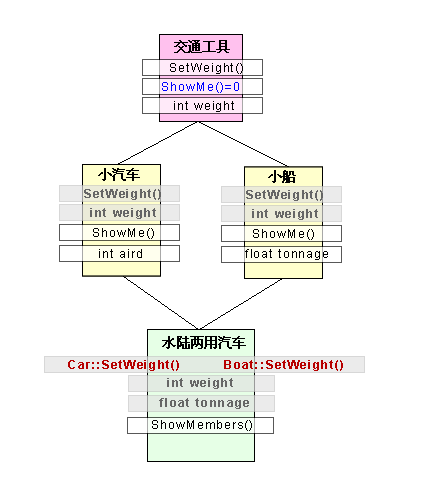
先看如下的圖示:
在圖中深紅色標記出來的地方正是主要問題所在,水陸兩用汽車類繼承了來自Car類與Boat類的屬性與方法,Car類與Boat類同為AmphibianCar類的基類,在記憶體分配上AmphibianCar獲得了來自兩個類的SetWeight()成員函式,當我們呼叫a.SetWeight(3)的時候計算機不知道如何選擇分別屬於兩個基類的被重複擁有了的類成員函式SetWeight()。
以上面的程式碼為例,我們要想讓AmphibianCar類既獲得一個Vehicle的拷貝,而且又同時共享用Car類與Boat類的資料成員與成員函式就必須通過C++所提供的虛擬繼承技術來實現。
在Car類和Boat類繼承Vehicle類時前面加上virtual關鍵字就可以實現虛擬繼承,使用虛擬繼承後,當系統碰到多重繼承的時候就會自動先加入一個Vehicle的拷貝,當再次請求一個Vehicle的拷貝的時候就會被忽略,保證繼承類成員函式的唯一性。
修改後的程式碼:
//加virtual後的正確程式碼
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Vehicle
{
public:
Vehicle(int weight = 0)
{
Vehicle::weight = weight;
cout << "載入Vehicle類建構函式" << endl;
}
void SetWeight(int weight)
{
cout << "重新設定重量" << endl;
Vehicle::weight = weight;
}
virtual void ShowMe() = 0;
protected:
int weight;
};
class Car :virtual public Vehicle//汽車,這裡是虛擬繼承
{
public:
Car(int weight = 0, int aird = 0) :Vehicle(weight)
{
Car::aird = aird;
cout << "載入Car類建構函式" << endl;
}
void ShowMe()
{
cout << "我是汽車!" << endl;
}
protected:
int aird;
};
class Boat :virtual public Vehicle//船,這裡是虛擬繼承
{
public:
Boat(int weight = 0, float tonnage = 0) :Vehicle(weight)
{
Boat::tonnage = tonnage;
cout << "載入Boat類建構函式" << endl;
}
void ShowMe()
{
cout << "我是船!" << endl;
}
protected:
float tonnage;
};
class AmphibianCar :public Car, public Boat//水陸兩用汽車,多重繼承的體現
{
public:
AmphibianCar(int weight, int aird, float tonnage)
:Vehicle(weight), Car(weight, aird), Boat(weight, tonnage)
//多重繼承要注意呼叫基類建構函式
{
cout << "載入AmphibianCar類建構函式" << endl;
}
void ShowMe()
{
cout << "我是水陸兩用汽車!" << endl;
}
void ShowMembers()
{
cout << "重量:" << weight << "頓," << "空氣排量:" << aird << "CC," << "排水量:" << tonnage << "頓" << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
AmphibianCar a(4, 200, 1.35f);
a.ShowMe();
a.ShowMembers();
a.SetWeight(3);
a.ShowMembers();
system("pause");
}
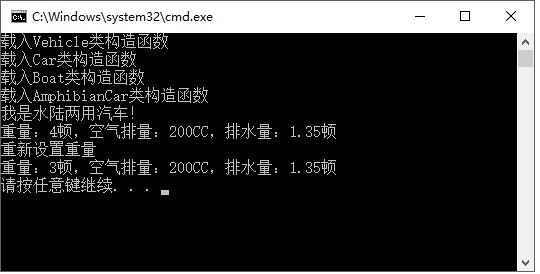
輸出:
雖然說虛擬繼承與虛擬函式有一定相似的地方,但務必要記住,他們之間是絕對沒有任何聯絡的!
************************************************************************************************************************
************************************************************************************************************************
總結多繼承的一些要點和注意事項:
- 多重繼承的情況下,遇到二義性的可能將會更大,編譯器不會試圖根據派生類轉換區別基類間的轉換,轉換成每個基類都一樣好,有如下程式碼:
class ZooAnimal
{
};
class Bear : public ZooAnimal
{
};
class Endangered
{
};
class Panda : public Bear, public Endangered
{
};
如果有print函式的兩個過載版本:
void print(const Bear&);
void print(const Endangered&);
這個呼叫將會出錯,編譯器將指出改掉用有二義性。
- 假定在類的多個基類中定義了相同的成員,將會導致二義性,如果定義了同名的成員函式,即使是函式引數不同,也會導致二義性,程式碼如下:
class ZooAnimal
{
};
class Bear : public ZooAnimal
{
public:
void print(int x) { cout << "print Bear" << endl; }
};
class Endangered
{
public:
void print() { cout << "print Endangered" << endl; };
};
class Panda : public Bear, public Endangered
{
};
int main()
{
Panda p;
p.Bear::print(1); //產生二義 p.print(1);
p.Endangered::print();
return 0;
}
輸出結果
如果在ZooAnimal中定義了print 而Bear中沒有定義,同樣會出現二義性。避免二義性的最好方法就是指定函式的作用域,同上示例比如:
Bear::print(x);