python繪製雙Y軸折線圖以及單Y軸雙變數柱狀圖
近來實驗室的師姐要發論文,由於論文交稿時間臨近,有一些雜活兒需要處理,作為實驗室資歷最淺的一批,我這個實習生也就責無旁貸地幫忙當個下手。今天師姐派了一個小活,具體要求是:
給一些訓練模型的迭代次數,訓練精度的資料,讓我做成圖表形式展示出來,一方面幫助檢查模型訓練時的不足,另一方面來看樣本數目和預測精度之間的聯絡,資料具體格式如下:
Iteration 1500
label train test right acc
12 143 24 24 1.0
160 92 16 15 0.9375
100 12 2 0 0.0
142 0 0 0 0.0
152 0 0 0 0.0
110 10 2 0 0.0
170 12 2 2 1.0
42 421 70 63 0.9
31 43 8 5 0.625
22 132 22 18 0.818181818182
60 51 9 8 0.888888888889
51 916 153 143 0.934640522876
131 82 14 11 0.785714285714
53 84 14 10 0.714285714286
70 9 2 2 1.0
21 531 89 89 1.0
120 1 1 1 1.0
11 454 76 71 0.934210526316
90 1 1 1 1.0
32 39 7 6 0.857142857143
41 151 25 14 0.56
132 0 0 0 0.0
151 43 7 6 0.857142857143
43 8 2 1 0.5
80 7 2 1 0.5
141 96 16 16 1.0
44 67 12 2 0.166666666667
right: 509 accuracy:0.883680555556
我的任務就是以label為自變數,繪製出它和train及acc之間的關係。
接到這個任務後,最直觀的感受就是常規的洗資料,於是我先把這些資料放在txt檔案中儲存下來,由於每個資料之間的間隔大於一個空格,我想當然地寫個正則匹配指令碼將資料間的大空格轉換為一個逗號(轉換為逗號的目的是這樣可以直接轉換為CSV表格檔案,然而在本次任務中貌似意義不大….)
#**********************Python 3.6.1***************************#
#* 將txt文字資料中的過長的空格更為一個逗號 *#
#***************** Author LQ ******************************#
#********************** 2018/4/4 ****************************#
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import re
import os #os模組與文字操作直接相關的模組
#*********下面三句程式碼作用不詳,就是為了防止出現編碼問題*********
import importlib
import sys
importlib.reload(sys)
#****************************************************
PATTERN = '\s+'#匹配出文字中的長空格
class Cleaner:
#初始化
def __init__(self):
os.chdir('D:\\Learning\\Machine_Learning\\實習\\師姐論文實驗') #改變工作目錄到txt檔案對應的目錄
self.content = open("acc-onlyRealImage-Iter2500.txt")
def grab_content(self):
line=self.content.readline()
pre=re.compile(PATTERN)
while line:
line_1=pre.sub(',',line) #將文字的長空格轉換為逗號後,利於轉成CSV格式,然後label按照升序排列
self.Write_content(line_1)
line = self.content.readline()
def Write_content(self,line_1):
path='acc-onlyRealImage-Iter2500-after.txt'
f=open(path,'a')
f.write('\n'+line_1)
def run(self):
self.grab_content()
if __name__ == '__main__':
cleaner = Cleaner()
cleaner.run()
資料清洗完成後,自然就是繪圖了,逛了一些部落格後,著手寫個指令碼,第一版是繪製出label和train及acc的雙Y軸折線圖,指令碼較為簡單,就是呼叫別人造的輪子,直接附上程式碼:
#**********************Python 3.6.1***************************#
#* 繪製出雙Y軸折線圖 *#
#***************** Author LQ ******************************#
#********************** 2018/4/4 ****************************#
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import re
import os #os模組與文字操作直接相關的模組
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
#*********下面三句程式碼作用不詳,就是為了防止出現編碼問題*********
import importlib
import sys
importlib.reload(sys)
#****************************************************
font2 = {'family' : 'Times New Roman',
'weight' : 'normal',
'size' : 18,
}
class Drawing:
#初始化
def __init__(self):
os.chdir('D:\\Learning\\Machine_Learning\\實習\\師姐論文實驗') #改變工作目錄到指定檔案目錄
self.content = open("acc-onlyRealImage-Iter2200-after.txt")
self.content1 = open("acc-onlyRealImage-Iter2500-after.txt")
def grab_content(self):
lines=self.content.readlines()
lines_1=self.content1.readlines()
x_1 = [line.strip().split(',')[0] for line in lines ]#欄位以逗號分隔,這裡取得是第4列
y_train_1=[line.strip().split(',')[1] for line in lines ]
y_train_2=[line.strip().split(',')[1] for line in lines_1 ]
y_acc_1=[line.strip().split(',')[4] for line in lines ]
y_acc_2=[line.strip().split(',')[4] for line in lines_1 ]
x = list(range(len(x_1)))
y_acc=[]
y_acc1=[]
y_train=[]
y_train1=[]
for i in range(len(y_acc_1)):
y_acc.append(float(y_acc_1[i]))
y_acc1.append(float(y_acc_2[i]))
y_train.append(int(y_train_1[i]))
y_train1.append(int(y_train_2[i]))
#plt.xticks(x, x_1,rotation=0)
fig,left_axis=plt.subplots()
p1, =left_axis.plot(x, y_train,'ro-')
right_axis = left_axis.twinx()
p2, =right_axis.plot(x, y_acc,'bo-')
plt.xticks(x, x_1,rotation=0) #設定x軸的顯示形式
#設定左座標軸以及右座標軸的範圍、精度
left_axis.set_ylim(0,1201)
left_axis.set_yticks(np.arange(0,1201,200))
right_axis.set_ylim(0,1.01)
right_axis.set_yticks(np.arange(0,1.01,0.20))
#設定座標及標題的大小、顏色
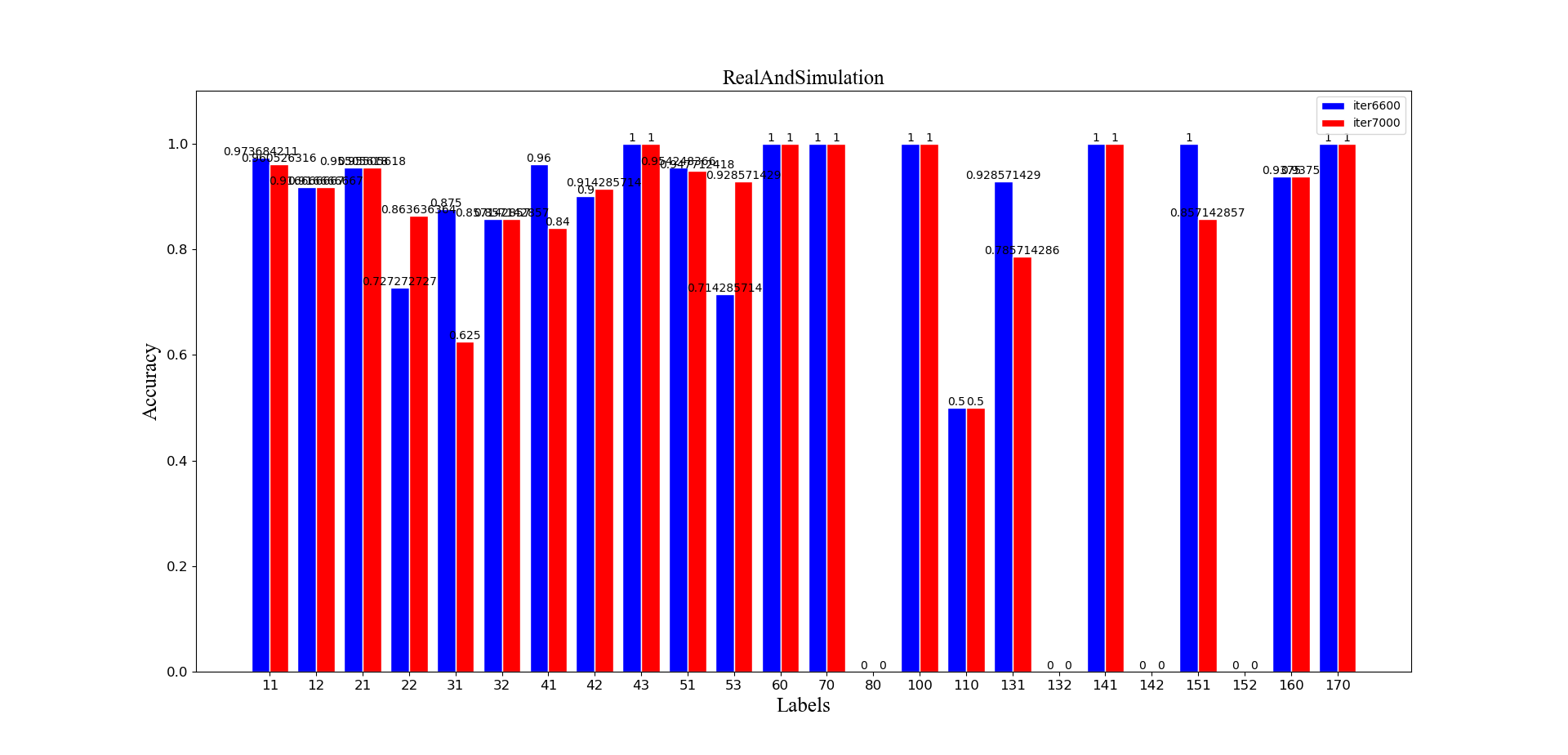
left_axis.set_title('RealAndSimulation-Iter6600',font2)
left_axis.set_xlabel('Labels',font2)
left_axis.set_ylabel('Number of training sets',font2,color='r')
left_axis.tick_params(axis='y', colors='r')
right_axis.set_ylabel('Accuracy',font2,color='b')
right_axis.tick_params(axis='y', colors='b')
plt.show()
def run(self):
self.grab_content()
if __name__ == '__main__':
Drawing = Drawing()
Drawing.run()
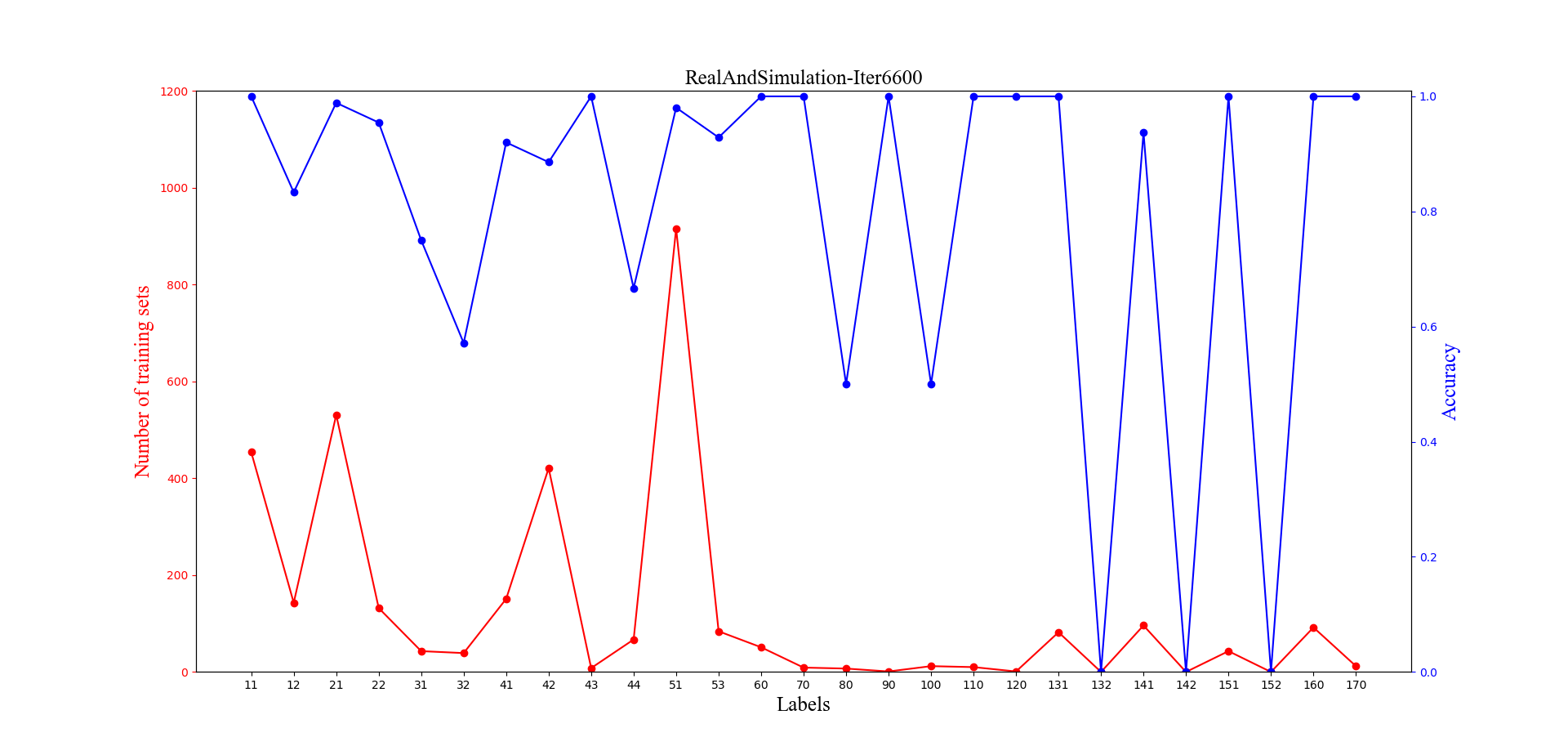
繪製出的圖形如上所示,其實看起來也還不錯,不過師姐表示有點亂,建議做個柱形的看看,於是繼續擼程式碼:
#**********************Python 3.6.1***************************#
#* 繪製單Y軸雙變數柱狀圖 *#
#***************** Author LQ ******************************#
#********************** 2018/4/4 ****************************#
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import re
import os #os模組與文字操作直接相關的模組
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
#*********下面三句程式碼作用不詳,就是為了防止出現編碼問題*********
import importlib
import sys
importlib.reload(sys)
#****************************************************
font2 = {'family' : 'Times New Roman', #設定字型
'weight' : 'normal',
'size' : 18,
}
class Drawing:
#初始化
def __init__(self):
os.chdir('D:\\Learning\\Machine_Learning\\實習\\師姐論文實驗') #改變工作目錄到指定檔案的目錄
self.content = open("acc-onlyRealImage-Iter2200-after.txt")
self.content1 = open("acc-onlyRealImage-Iter2500-after.txt")
def autolabel(self,rects,y): #在柱狀圖上面新增 數值
i=0
for rect in rects:
#讀出列表儲存的value值
value=y[i]
x_1 = rect.get_x() + rect.get_width()/2
y_1 = rect.get_height()
#x_1,y_1對應柱形的橫、縱座標
i+=1
plt.text(x_1, y_1, value, ha='center', va='bottom',fontdict={'size': 8}) #在fontdict中設定字型大小
rect.set_edgecolor('white')
def Pictures(self):
lines=self.content.readlines()
lines_1=self.content1.readlines()
x_1 = [line.strip().split(',')[0] for line in lines ]#欄位以逗號分隔,這裡取得是第1列
y_train_1=[line.strip().split(',')[1] for line in lines ]
y_train_2=[line.strip().split(',')[1] for line in lines_1 ]
y_acc_1=[line.strip().split(',')[4] for line in lines ]
y_acc_2=[line.strip().split(',')[4] for line in lines_1 ]
x = list(range(len(x_1)))
y_acc=[]
y_acc1=[]
y_train=[]
y_train1=[]
for i in range(len(y_acc_1)):
y_acc.append(float(y_acc_1[i]))
y_acc1.append(float(y_acc_2[i]))
y_train.append(int(y_train_1[i]))
y_train1.append(int(y_train_2[i]))
plt.xticks(x, x_1,rotation=0) #設定X軸座標值為label值
for i in range(len(x)): #調整柱狀圖的橫座標,使得打印出來的圖形看起來更加舒服
x[i] = x[i] -0.2
a=plt.bar(x, y_train,width=0.4,label='iter2200',fc = 'b')
#a=plt.bar(x, y_acc,width=0.4,label='iter2200',fc = 'b')
for i in range(len(x)):
x[i] = x[i] + 0.4
b=plt.bar(x, y_train1, width=0.4, label='iter2500',fc = 'r')
#b=plt.bar(x, y_acc1, width=0.4, label='iter2500',fc = 'r')
plt.xlabel('Labels',font2)
#設定Y軸值的範圍
plt.ylim((0, 1000))
#設定Y軸的刻度值
plt.yticks(np.arange(0,1001, 200))
#plt.ylim((0, 1.1))
#plt.yticks(np.arange(0,1.1, 0.2))
#plt.ylabel('Accuracy',font2)
plt.ylabel('Number of training sets',font2) #字型的格式在font2中有設定
self.autolabel(a,y_train_1) #為柱形圖打上數值標籤
self.autolabel(b,y_train_2)
#self.autolabel(a,y_acc_1)
#self.autolabel(b,y_acc_2)
#plt.title("RealAndSimulation",font2)
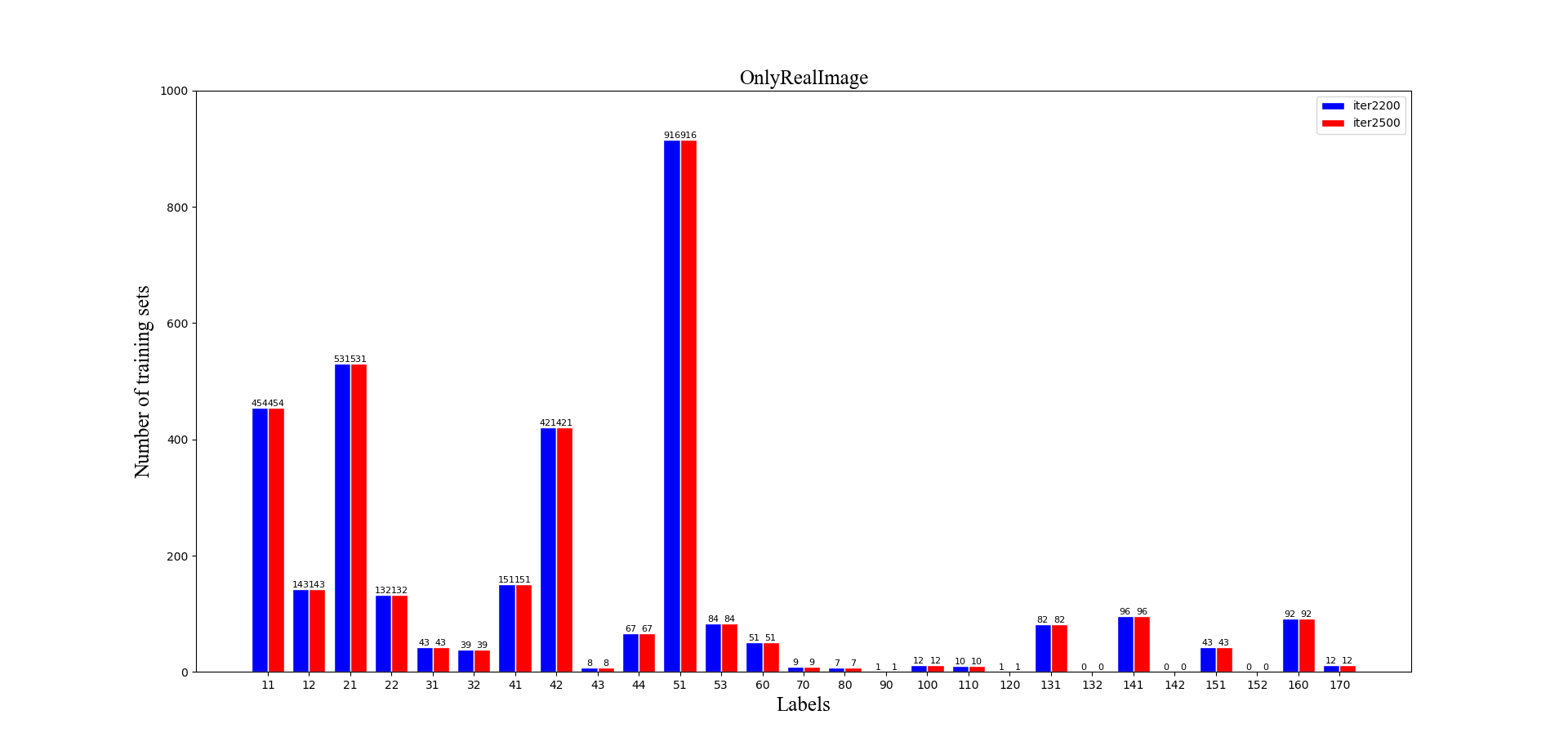
plt.title("OnlyRealImage",font2)
plt.legend()
plt.show()
def run(self):
self.Pictures()
if __name__ == '__main__':
Draw = Drawing()
Draw.run()
呈現的效果如下,此處因為對於雙柱形圖通常採用同一Y軸座標系,所以此處選擇的是比對不同迭代次數:
此處為了方便實驗結果的觀測,在每個柱形上面均打印出了對應的數值,至此,這部分的任務ending,難度不是很大,不過需要自己耐心編寫指令碼,調試出好的結果~