【CodeForces 686 D. 】 【樹的重心性質】
D. Kay and Snowflake
time limit per test 3 seconds
memory limit per test 256 megabytes
input standard input
output standard output
After the piece of a devilish mirror hit the Kay’s eye, he is no longer interested in the beauty of the roses. Now he likes to watch snowflakes.
Once upon a time, he found a huge snowflake that has a form of the tree (connected acyclic graph) consisting of n nodes. The root of tree has index 1. Kay is very interested in the structure of this tree.
After doing some research he formed q queries he is interested in. The i-th query asks to find a centroid of the subtree of the node vi. Your goal is to answer all queries.
Subtree of a node is a part of tree consisting of this node and all it’s descendants (direct or not). In other words, subtree of node v is formed by nodes u, such that node v is present on the path from u to root.
Centroid of a tree (or a subtree) is a node, such that if we erase it from the tree, the maximum size of the connected component will be at least two times smaller than the size of the initial tree (or a subtree).
Input
The first line of the input contains two integers n and q (2 ≤ n ≤ 300 000, 1 ≤ q ≤ 300 000) — the size of the initial tree and the number of queries respectively.
The second line contains n - 1 integer p2, p3, …, pn (1 ≤ pi ≤ n) — the indices of the parents of the nodes from 2 to n. Node 1 is a root of the tree. It’s guaranteed that pi define a correct tree.
Each of the following q lines contain a single integer vi (1 ≤ vi ≤ n) — the index of the node, that define the subtree, for which we want to find a centroid.
Output
For each query print the index of a centroid of the corresponding subtree. If there are many suitable nodes, print any of them. It’s guaranteed, that each subtree has at least one centroid.
Example
input
7 4
1 1 3 3 5 3
1
2
3
5
output
3
2
3
6
Note
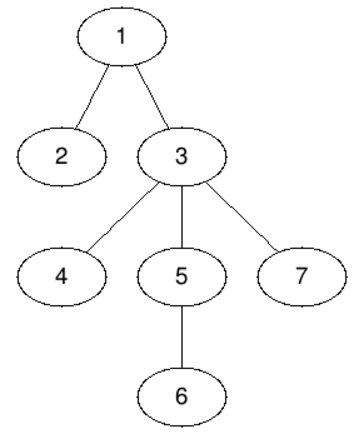
The first query asks for a centroid of the whole tree — this is node 3. If we delete node 3 the tree will split in four components, two of size1 and two of size 2.
The subtree of the second node consists of this node only, so the answer is 2.
Node 3 is centroid of its own subtree.
The centroids of the subtree of the node 5 are nodes 5 and 6 — both answers are considered correct.
題意 給一顆有向邊的樹,根節點為 1,q次詢問,詢問以該點為根節點的子樹的重心編號。
補充知識點 :
樹的重心
定義 以這個點為根,那麼所有的子樹(不算整個樹自身)的大小都不超過整個樹大小的一半。
性質 1 :樹中所有點到某個點的距離和中,到重心的距離和是最小的,如果有多個重心,他們的距離和一樣。
性質 2 :把兩棵樹通過某一點相連得到一顆新的樹,新的樹的重心必然在連線原來兩棵樹重心的路徑上。
性質 3 :一棵樹新增或者刪除一個節點,樹的重心最多隻移動一條邊的位置。
程式碼
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std 