Python實現二叉樹及其4種遍歷
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-26
Python & BinaryTree
1. BinaryTree (二叉樹)
二叉樹是有限個元素的集合,該集合或者為空、或者有一個稱為根節點(root)的元素及兩個互不相交的、分別被稱為左子樹和右子樹的二叉樹組成。
- 二叉樹的每個結點至多隻有二棵子樹(不存在度大於2的結點),二叉樹的子樹有左右之分,次序不能顛倒。
- 二叉樹的第i層至多有2^{i-1}個結點
- 深度為k的二叉樹至多有2^k-1個結點;
- 對任何一棵二叉樹T,如果其終端結點數為N0,度為2的結點數為N2,則N0=N2+1
2. 二叉樹
- 生成二叉樹
# init a tree
def InitBinaryTree(dataSource, length):
root = BTNode(dataSource[0])
for x in xrange(1,length):
node = BTNode(dataSource[x])
InsertElementBinaryTree(root, node)
return root
print 'Done...'
- 前根遍歷
# pre-order
def PreorderTraversalBinaryTree
- 中根遍歷
# in-order
def InorderTraversalBinaryTree(root):
if root:
InorderTraversalBinaryTree(root.leftChild)
print
- 後根遍歷
# post-order
def PostorderTraversalBinaryTree(root):
if root:
PostorderTraversalBinaryTree(root.leftChild)
PostorderTraversalBinaryTree(root.rightChild)
print '%d | ' % root.data,
- 按層遍歷
# layer-order
def TraversalByLayer(root, length):
stack = []
stack.append(root)
for x in xrange(length):
node = stack[x]
print '%d | ' % node.data,
if node.leftChild:
stack.append(node.leftChild)
if node.rightChild:
stack.append(node.rightChild)
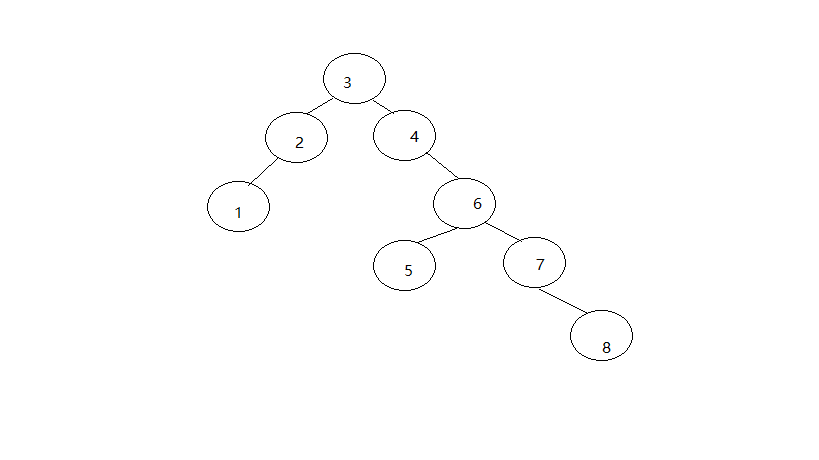
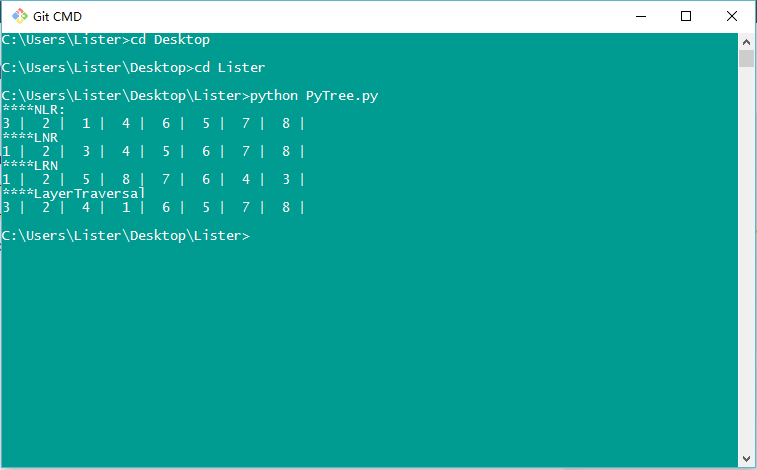
- Result
二叉樹的思想重在“遞迴”, 並不是非要用遞迴處理,而是去理解二叉樹遞迴的思想
- 完整程式碼段
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
#################
### implement Binary Tree using python
### Hongwing
### 2016-9-4
#################
import math
class BTNode(object):
"""docstring for BTNode"""
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.leftChild = None
self.rightChild = None
# insert element
def InsertElementBinaryTree(root, node):
if root:
if node.data < root.data:
if root.leftChild:
InsertElementBinaryTree(root.leftChild, node)
else:
root.leftChild = node
else:
if root.rightChild:
InsertElementBinaryTree(root.rightChild, node)
else:
root.rightChild = node
else:
return 0
# init a tree
def InitBinaryTree(dataSource, length):
root = BTNode(dataSource[0])
for x in xrange(1,length):
node = BTNode(dataSource[x])
InsertElementBinaryTree(root, node)
return root
print 'Done...'
# pre-order
def PreorderTraversalBinaryTree(root):
if root:
print '%d | ' % root.data,
PreorderTraversalBinaryTree(root.leftChild)
PreorderTraversalBinaryTree(root.rightChild)
# in-order
def InorderTraversalBinaryTree(root):
if root:
InorderTraversalBinaryTree(root.leftChild)
print '%d | ' % root.data,
InorderTraversalBinaryTree(root.rightChild)
# post-order
def PostorderTraversalBinaryTree(root):
if root:
PostorderTraversalBinaryTree(root.leftChild)
PostorderTraversalBinaryTree(root.rightChild)
print '%d | ' % root.data,
# layer-order
def TraversalByLayer(root, length):
stack = []
stack.append(root)
for x in xrange(length):
node = stack[x]
print '%d | ' % node.data,
if node.leftChild:
stack.append(node.leftChild)
if node.rightChild:
stack.append(node.rightChild)
if __name__ == '__main__':
dataSource = [3, 4, 2, 6, 7, 1, 8, 5]
length = len(dataSource)
BTree = InitBinaryTree(dataSource, length)
print '****NLR:'
PreorderTraversalBinaryTree(BTree)
print '\n****LNR'
InorderTraversalBinaryTree(BTree)
print '\n****LRN'
PostorderTraversalBinaryTree(BTree)
print '\n****LayerTraversal'
TraversalByLayer(BTree, length)