利用python求解八數碼難題
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-26
實驗目的
- 實驗內容
八數碼問題也稱為九宮問題。在3×3的棋盤,擺有八個棋子,每個棋子上標有1至8的某一數字,不同棋子上標的數字不相同。棋盤上還有一個空格,與空格相鄰的棋子可以移到空格中。要求解決的問題是:給出一個初始狀態和一個目標狀態,找出一種從初始狀態轉變成目標狀態的移動棋子步數最少的移動步驟。 - 實驗要求
分別利用寬度優先搜尋和有序搜尋演算法求解八數碼難題,給出搜尋樹,並給出從初始節點到目標節點的路徑。
實驗裝置及軟體環境
1. 電腦配置:
(1)處理器 : Intel i5-4210U CPU @ 1.70GHz, 2.40GHz
(2)安裝記憶體: 8.00GB
(3)作業系統: Windows 10
(4)程式語言: Python
(5)軟體環境: python 3.5 、numpy、matplotlib、scipy、Axure 7.0
(6)IDE : PyCharm 5.0.1
實驗方法
演算法描述
(1) 寬度優先搜尋
如果搜尋是以接近起始節點的程度依次擴充套件節點的,那麼這種搜尋就叫做寬度優先搜尋。這種搜尋是逐層進行的,在對下一層的任一節點進行搜尋之前,必須搜尋完本層的所有節點。
(2) 有序搜尋
令f(n) 表示節點n 的估價函式值,估算節點希望程度的量度。本次實驗選擇的f(n) 的函式形式為:
f(n)=g(n)+h(n)
其中,g(n) 為初始節點到當前節點的路徑長度(深度),h(n) 為當前節點“不在位”的將牌數。
有序搜尋(ordered search),即最好優先搜尋, 選擇Open表上具有最小f值的節點作為下一個要擴充套件的節點。- 流程圖
(1) 寬度優先搜尋
(2) 有序搜尋
- 程式程式碼 (python)
(1) 寬度優先搜尋
__author__ = 'ysc'
import numpy as np
class State:
def __init__(self, state, directionFlag=None, parent=None):
self.state = state
# state is a ndarray with a shape(3,3) to storage the state
self.direction = ['up', 'down', 'right', 'left']
if directionFlag:
self.direction.remove(directionFlag)
# record the possible directions to generate the sub-states
self.parent = parent
self.symbol = ' '
def getDirection(self):
return self.direction
def showInfo(self):
for i in range(3):
for j in range(3):
print(self.state[i, j], end=' ')
print("\n")
print('->')
return
def getEmptyPos(self):
postion = np.where(self.state == self.symbol)
return postion
def generateSubStates(self):
if not self.direction:
return []
subStates = []
boarder = len(self.state) - 1
# the maximum of the x,y
row, col = self.getEmptyPos()
if 'left' in self.direction and col > 0:
#it can move to left
s = self.state.copy()
temp = s.copy()
s[row, col] = s[row, col-1]
s[row, col-1] = temp[row, col]
news = State(s, directionFlag='right', parent=self)
subStates.append(news)
if 'up' in self.direction and row > 0:
#it can move to upper place
s = self.state.copy()
temp = s.copy()
s[row, col] = s[row-1, col]
s[row-1, col] = temp[row, col]
news = State(s, directionFlag='down', parent=self)
subStates.append(news)
if 'down' in self.direction and row < boarder: #it can move to down place
s = self.state.copy()
temp = s.copy()
s[row, col] = s[row+1, col]
s[row+1, col] = temp[row, col]
news = State(s, directionFlag='up', parent=self)
subStates.append(news)
if self.direction.count('right') and col < boarder: #it can move to right place
s = self.state.copy()
temp = s.copy()
s[row, col] = s[row, col+1]
s[row, col+1] = temp[row, col]
news = State(s, directionFlag='left', parent=self)
subStates.append(news)
return subStates
def solve(self):
# generate a empty openTable
openTable = []
# generate a empty closeTable
closeTable = []
# append the origin state to the openTable
openTable.append(self)
steps = 1
# start the loop
while len(openTable) > 0:
n = openTable.pop(0)
closeTable.append(n)
subStates = n.generateSubStates()
path = []
for s in subStates:
if (s.state == s.answer).all():
while s.parent and s.parent != originState:
path.append(s.parent)
s = s.parent
path.reverse()
return path, steps+1
openTable.extend(subStates)
steps += 1
else:
return None, None
if __name__ == '__main__':
# the symbol representing the empty place
# you can change the symbol at here
symbolOfEmpty = ' '
State.symbol = symbolOfEmpty
# set the origin state of the puzzle
originState = State(np.array([[2, 8, 3], [1, 6 , 4], [7, symbolOfEmpty, 5]]))
# and set the right answer in terms of the origin
State.answer = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [8, State.symbol, 4], [7, 6, 5]])
s1 = State(state=originState.state)
path, steps = s1.solve()
if path: # if find the solution
for node in path:
# print the path from the origin to final state
node.showInfo()
print(State.answer)
print("Total steps is %d" % steps)(2)有序搜尋演算法
__author__ = 'ysc'
import numpy as np
class State:
def __init__(self, state, directionFlag=None, parent=None, depth=1):
self.state = state
# state is a ndarray with a shape(3,3) to storage the state
self.direction = ['up', 'down', 'right', 'left']
if directionFlag:
self.direction.remove(directionFlag)
# record the possible directions to generate the sub-states
self.parent = parent
self.symbol = ' '
self.answer = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [8, State.symbol, 4], [7, 6, 5]])
self.depth = depth
# calculate the num of elements which are not in the proper position
num = 0
for i in range(len(state)):
for j in range(len(state)):
if self.state[i, j] != ' 'and self.state[i, j] != self.answer[i, j]:
num += 1
self.cost = num + self.depth
def getDirection(self):
return self.direction
def showInfo(self):
for i in range(3):
for j in range(3):
print(self.state[i, j], end=' ')
print("\n")
print('->')
return
def getEmptyPos(self):
postion = np.where(self.state == self.symbol)
return postion
def generateSubStates(self):
if not self.direction:
return []
subStates = []
# the maximum of the x,y
row, col = self.getEmptyPos()
if 'left' in self.direction and col > 0:
#it can move to left place
s = self.state.copy()
temp = s.copy()
s[row, col] = s[row, col-1]
s[row, col-1] = temp[row, col]
news = State(s, directionFlag='right', parent=self, depth=self.depth+1)
subStates.append(news)
if 'up' in self.direction and row > 0:
#it can move to upper place
s = self.state.copy()
temp = s.copy()
s[row, col] = s[row-1, col]
s[row-1, col] = temp[row, col]
news = State(s, directionFlag='down', parent=self, depth=self.depth+1)
subStates.append(news)
if 'down' in self.direction and row < boarder:
#it can move to down place
s = self.state.copy()
temp = s.copy()
s[row, col] = s[row+1, col]
s[row+1, col] = temp[row, col]
news = State(s, directionFlag='up', parent=self, depth=self.depth+1)
subStates.append(news)
if self.direction.count('right') and col < boarder:
#it can move to right place
s = self.state.copy()
temp = s.copy()
s[row, col] = s[row, col+1]
s[row, col+1] = temp[row, col]
news = State(s, directionFlag='left', parent=self, depth=self.depth+1)
subStates.append(news)
return subStates
def solve(self):
# generate a empty openTable
openTable = []
# generate a empty closeTable
closeTable = []
# append the origin state to the openTable
openTable.append(self)
# denote the steps it travels
steps = 0
while len(openTable) > 0: # start the loop
n = openTable.pop(0)
closeTable.append(n)
subStates = n.generateSubStates()
path = []
for s in subStates:
if (s.state == s.answer).all():
while s.parent and s.parent != originState:
path.append(s.parent)
s = s.parent
path.reverse()
return path, steps+1
openTable.extend(subStates)
# sort the openTable in terms of the cost
openTable.sort(key=lambda x: x.cost)
steps += 1
else:
return None, None
if __name__ == '__main__':
# the symbol representing the empty place
symbolOfEmpty = ' '
# you can change the symbol at here
State.symbol = symbolOfEmpty
# set the origin state of the puzzle
originState = State(np.array([[2, 8, 3], [1, 6 , 4], [7, symbolOfEmpty, 5]]))
State.answer = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [8, State.symbol, 4], [7, 6, 5]])
s1 = State(state=originState.state)
path, steps = s1.solve()
if path: # if find the solution
for node in path:
# print the path from the origin to final state
node.showInfo()
print(State.answer)
print("Total steps is %d" % steps)
實驗結果
繪圖軟體為:Axure 7.0
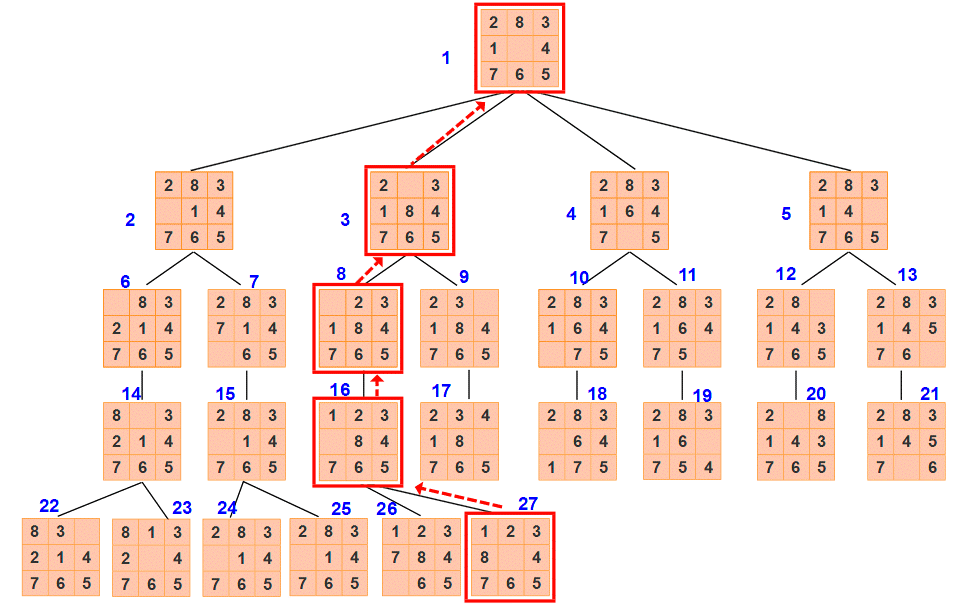
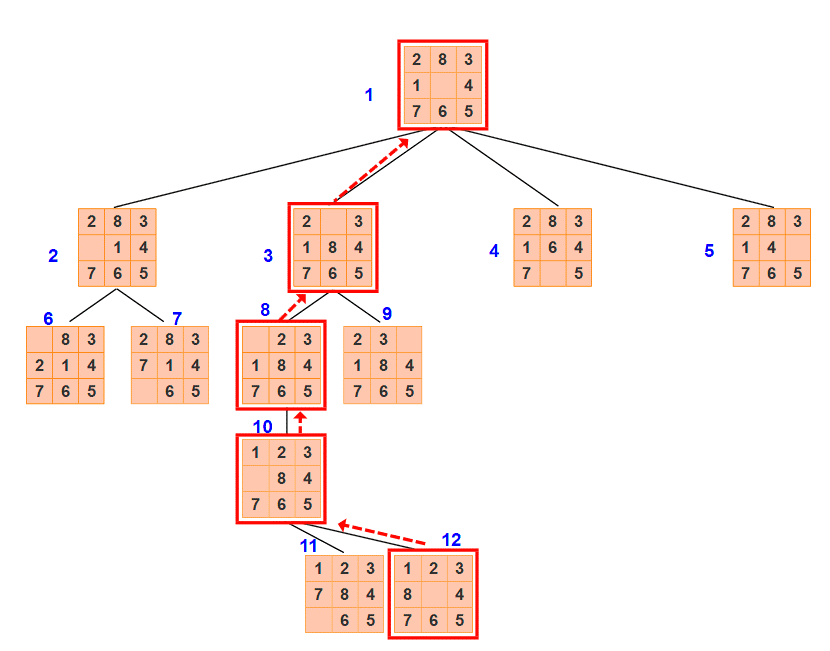
- 搜尋樹
(1)DFS
(2) 有序搜尋
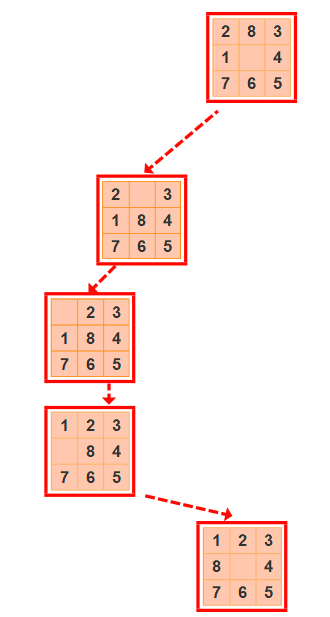
- 搜尋路徑
實驗分析
- 結果分析
(1) 寬度優先搜尋
由實驗結果可知,寬度優先搜尋擴充套件節點個數為4,生成節點個數為26。
(擴充套件節點:路徑中的節點數-1;生成節點:搜尋樹中節點數目-1)
(2) 有序搜尋
由實驗結果可知,有序搜尋擴充套件節點個數為4,生成節點個數為12。
(擴充套件節點:路徑中的節點數-1;生成節點:搜尋樹中節點數目-1)
2. 方法特點
(1) 寬度優先搜尋 - 寬度優先搜尋又稱廣度優先搜尋,“廣度”一詞形象地揭示了這種搜尋是逐層進行的:在對下一層的任一節點進行搜尋之前,必須搜尋完本層的所有節點。
- 不需要重排Open表
- 一般只適用於求解比較簡單的問題。
- 若問題有解,寬度優先搜尋一定可以求得,並且求出的是最優解。
(2) 有序搜尋
有序搜尋利用到啟發式資訊,對Open表中元素進行了重排,選擇最有希望的節點加以擴充套件,搜尋效率較盲目搜尋大為提高。
3. 區別
寬度優先搜尋屬於盲目搜尋,沒有利用到啟發資訊,故效率較低;而有序搜尋利用到節點本身的特性,將其作為啟發式資訊,對Open表進行重排,每一次選擇都是最優的,具有貪心性質,搜尋效率大為提高。
結論
綜上所述,可以明顯看出寬度優先搜尋與有序搜尋的效率差異。這啟示我們在解決生活問題時,不僅僅是需要找到一個通用的(general)演算法框架,因為雖然可以求出解,但是效率很低,我們更需要根據實際問題具體分析,通過問題本身,提煉出更有效的啟發式資訊,這樣才能提高解的效率。