10.SpringMVC 請求處理
基本概念
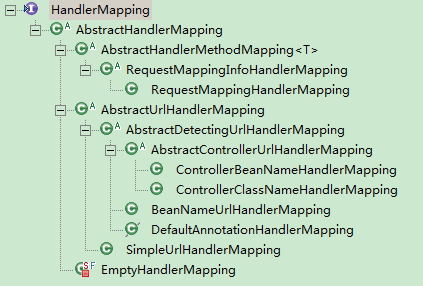
即處理器對映,它的主要作用就是根據 reqeust 獲取 HandlerExecutionChain。
下面來看它的原始碼:
public interface HandlerMapping {
// 省略部分程式碼...
HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception;
}再來看它的繼承關係:
AbstractHandlerMapping
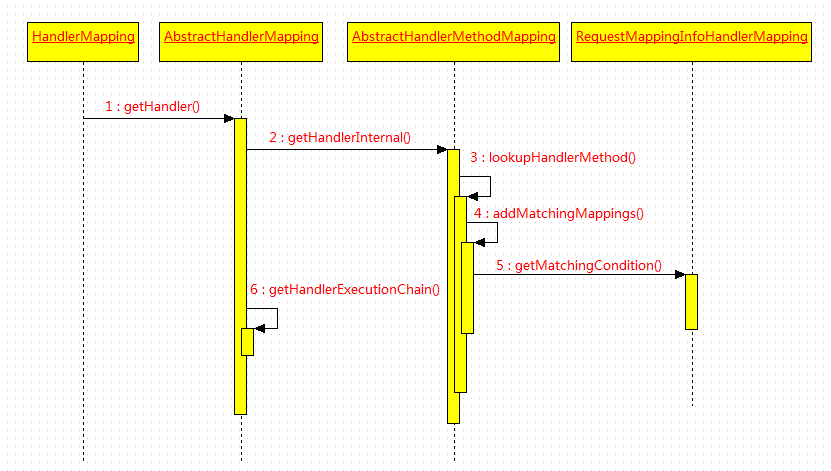
AbstractHandlerMapping 是該介面的抽象實現類,該類實現了 getHandler 方法。
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
// 關鍵 -> 取得處理器,留給子類
Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);
// 取得預設處理器
if (handler == null) {
handler = getDefaultHandler();
}
if (handler == null) {
return 繼續追蹤到 getHandlerExecutionChain 方法
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandlerExecutionChain(Object handler, HttpServletRequest request) {
// 1.取得 HandlerExecutionChain ,包含了處理器和攔截器,下面會詳細分析
HandlerExecutionChain chain = (handler instanceof HandlerExecutionChain ?
(HandlerExecutionChain) handler : newHandlerExecutionChain(handler));
// 2.獲取請求路徑
// 若完整請求地址為 http://localhost:8080/Demo/hello,則 lookupPath = /hello
String lookupPath = this.urlPathHelper.getLookupPathForRequest(request);
// 3.新增攔截器到 HandlerExecutionChain
// 遍歷 SpringMVC 容器的所有攔截器
for (HandlerInterceptor interceptor : this.adaptedInterceptors) {
// 判斷攔截器型別,屬於 MappedInterceptor,則先匹配路徑,否則直接新增
if (interceptor instanceof MappedInterceptor) {
MappedInterceptor mappedInterceptor = (MappedInterceptor) interceptor;
if (mappedInterceptor.matches(lookupPath, this.pathMatcher)) {
chain.addInterceptor(mappedInterceptor.getInterceptor());
}
}else {
chain.addInterceptor(interceptor);
}
}
return chain;
}分析程式碼可知, HandlerMapping 的主要職責是取得 HandlerExecutionChain,具體步驟如下:
- 取得 HandlerExecutionChain 的處理器,由不同子類作實現。
- 取得 HandlerExecutionChain 的攔截器
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping
在介紹該類之前,先來看幾個類:
RequestMapingInfo ,該類包含了 @ReuestMaping 的所有註解內容,包括 value,method,param,header,consumes,produces 等屬性定義的內容 。
// 註解的所有內容被封裝到它的成員變數中 // 包含了註解屬性 value 的內容,如 "/hello" private final PatternsRequestCondition patternsCondition; // 包含了註解屬性 method 的內容,如 GET private final RequestMethodsRequestCondition methodsCondition; // 省略部分程式碼...
MappingRegistry,它是 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping 的內部類。它內有一個 Map,維護著 SpringMVC 中所有的 RequestMapingInfo 與 HandlerMethod 的對映關係。
// T 實際就是 RequestMapingInfo private final Map<T, HandlerMethod> mappingLookup = new LinkedHashMap<T, HandlerMethod>(); // 取得對映 public Map<T, HandlerMethod> getMappings() { return this.mappingLookup; }
Match,它是 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping 的私有內部類,也稱匹配者,封裝了一個RequestMappingInfo ,以及對應的 HandlerMethod 。
private class Match { private final T mapping; private final HandlerMethod handlerMethod; public Match(T mapping, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) { this.mapping = mapping; this.handlerMethod = handlerMethod; } }
該類是 AbstractHandlerMapping 類的子類,也是個抽象類。它實現了取得處理器的具體過程,也就是對 getHandlerInternal 作了具體實現。
protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
// 省略部分程式碼...
// 1.取得請求路徑
String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request);
// 新增讀鎖,其他執行緒只能讀不能寫
this.mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock();
try {
// 關鍵 -> 2.取得 HandlerMethod
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request);
// 建立控制器並返回
return (handlerMethod != null ?
handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null);
}finally {
// 釋放讀鎖
this.mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock();
}
}繼續追蹤到 lookupHandlerMethod 方法。
protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
List<Match> matches = new ArrayList<Match>();
// 1.取得 RequestMappingInfo,根據路徑進行匹配
List<T> directPathMatches =
this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByUrl(lookupPath);
if (directPathMatches != null) {
// 2.構建 Match 並加入集合
addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request);
}
if (matches.isEmpty()) {
addMatchingMappings(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(),
matches, request);
}
// 3.選出最佳的 Match
if (!matches.isEmpty()) {
// 利用比較器進行排序
Comparator<Match> comparator =
new MatchComparator(getMappingComparator(request));
Collections.sort(matches, comparator);
// 省略部分程式碼...
Match bestMatch = matches.get(0);
// 存在多個 Match 時,對前兩個匹配者再比較,若相同則丟擲異常
if (matches.size() > 1) {
// 省略部分程式碼...
Match secondBestMatch = matches.get(1);
if (comparator.compare(bestMatch, secondBestMatch) == 0) {
// 丟擲異常...
}
}
// 將 相關資訊新增到 reqeust 的屬性。
handleMatch(bestMatch.mapping, lookupPath, request);
return bestMatch.handlerMethod;
} else {
// 處理沒有 Match 的情況
return handleNoMatch(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(),
lookupPath, request);
}
}再來看看 addMatchingMappings 的實現過程:
private void addMatchingMappings(Collection<T> mappings, List<Match> matches, HttpServletRequest request) {
for (T mapping : mappings) {
// 關鍵 -> 取得匹配的 RequetMapingInfo,留給子類實現
T match = getMatchingMapping(mapping, request);
// 建立 Match 並加入集合
if (match != null) {
matches.add(new Match(match,
this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().get(mapping)));
}
}
}綜上所述,該類的主要作用是負責找到相應的處理器,也就是 HandlerMethod。它的具體步驟如下:
1.取得 RequestMappingInfo。根據請求路徑進行匹配。
2.構建 Match 並加入集合。過濾 RequestMappingInfo 與 rqeust 請求不符的內容,再從 MappingRegistry 找到對應的 HandlerMethod,最後新增進集合。
3.選出最佳的 Match。利用比較器篩選中最佳的 Match,再返回 Match 中的 HandlerMethod。
RequestMappingHandlerMapping
該類是 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping 的子類。
若控制器採用了註解方法實現,則就會採用 RequestMappingHandlerMapping 來處理。在其內部實現了 getMatchingMapping 方法:
protected RequestMappingInfo getMatchingMapping(RequestMappingInfo info, HttpServletRequest request) {
// 將 info 的內容 rqeust 的內容進行匹配
// 假設 @RquestMapping 中 method 為 GET、POST
// 而 reqeuest 的請求類為 GET
// 經過匹配,RequestMappingInfo 中關於 method 的內容只剩下 GET
return info.getMatchingCondition(request);
}總結
整個 HandlerMapping 的工作流程如下:
根據目的就是通過 reqeust 獲取 HandlerExecutionChain 的 HandlerMethod、Interceptor。
而實現的重點又在獲取 HandlerMethod 的過程,即根據請求獲取 Controller 中處理方法的過程。