Linux訊號(一)——子程序的非同步等待方式
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-29
1.訊號
訊號(是一種軟體中斷)是由使用者、系統或者程序傳送給目標程序的資訊,以通知目標程序某個狀態的改變或系統異常。2.訊號的產生
(1)前臺程序,使用者可以通過輸入特殊終端字元來給它傳送訊號。比如Ctrl+C通常給程序傳送一箇中斷訊號——2號訊號(SIGINT),只能終止前臺程序(後臺程序一般在執行後面加&,就可以使得程序在後臺執行)。 (2)系統異常。比如浮點異常——8號訊號(SIGFPE)。 (3)系統狀態變化。比如alarm函式定時器到期引起14號訊號——SIGALRM訊號。 (4)執行kill命令呼叫kill函式。產生9號訊號——SIGKILL(該訊號不能被定義或捕捉,該訊號用來殺死程序)。3.訊號的分類
列表中,編號為1~31號訊號為普通訊號,也稱為不可靠訊號;編號34~64為後來擴充的,被稱作可靠 訊號(實時訊號);不可靠訊號和可靠訊號二者的區別是前者不支援排隊,可能會造成訊號丟失, 後者不會。
4.Linux訊號處理方式
(1)忽略此訊號。大多數訊號都可以使用這種方式進行處理,除了9)SIGKILL和19)SIGSTOP。這兩種訊號不能被忽略的原因:它們是用來終止程序的一種可靠的方法。如果忽略某些由硬體異常所產生的訊號(例如非法儲存訪問或除以0),則程序的行為是未定義的。 (2)執行預設動作(大部分的預設動作就是終止該程序(Term)),還有比如:忽略訊號(Ign)、結束程序並生成核心轉儲檔案(Core)、暫停程序(Stop)、以及繼續程序(Cont)。5.訊號相關函式
(1)signal函式#include<signal.h>
void(*signal (int signo ,void (*func)(int))) (int);
//返回則為以前的訊號處理配置,若出錯則為SIG_ERR#include <sys/types.h>
#include <signal.h>
int kill (pid_t pid, int signo);
int raise(int signo);
//兩個函式返回:成功則為0,若出錯則為-1kill命令呼叫kill函式實現,kill函式給一個指定的程序傳送指定的訊號 raise函式只允許程序向自身傳送訊號
6.驗證子程序退出會給父程序傳送訊號
測試程式碼:#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <error.h>
void catchsignal(int sig)
{
printf("I am a father my pid is:%d , receive signal is %d\n",getpid(),sig);
}
int main()
{
signal(SIGCHLD,catchsignal);
pid_t id=fork();
if(id==0){
//child
int count=0;
while(count<4){
printf("I am a child,my pid is: %d ,my father's pid is: %d \n",getpid(),getppid());
sleep(1);
count++;
}
exit(0);
}
else if(id>0){
//father
waitpid(id,NULL,0);
}
else{
perror("fork error\n");
}
return 0;
}
執行結果:
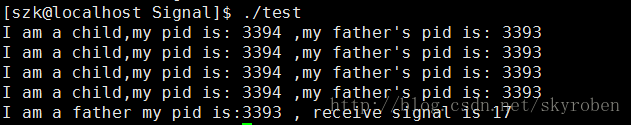
很明顯子程序退出時父程序收到了17號訊號——17)SIGCHLD。
7.編寫父程序等待子程序的非同步版本
非同步:父子程序互不干擾(非阻塞式等待),繼續執行各自任務。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <error.h>
void catchsignal(int sig)
{
printf("I am a father my pid is:%d , receive signal is %d\n",getpid(),sig);
}
int main()
{
signal(SIGCHLD,catchsignal);
pid_t id=fork();
if(id==0){
//child
int count=0;
while(count<4){
printf("I am a child,my pid is: %d ,my father's pid is: %d \n",getpid(),getppid());
sleep(1);
count++;
}
exit(0);
}
else if(id>0){
//father
while(1){
sleep(2);
printf("I am a father,running\n");
}
}
else{
perror("fork error\n");
}
return 0;
}
執行結果:

