linux下動態庫的使用
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-30
編譯時與執行時庫的路徑
執行時動態庫的路徑搜尋順序
LD_PRELOAD環境變數,一般用於hack
編譯目的碼時指定的動態庫搜尋路徑(指的是用-wl,rpath或-R選項而不是-L),
readelf -d命令可以檢視編譯的目標檔案中rpath引數;gcc -Wl,-rpath,/home/arc/test,-rpath,/usr/local/lib test.c環境變數LD_LIBRARY_PATH指定的動態庫搜尋路徑;
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/root/test/env/lib ./main或者
LD_LIBRARY_PATH=.:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH ./main配置檔案/etc/ld.so.conf中指定的動態庫搜尋路徑;
更改/etc/ld.so.conf檔案後記得一定要執行命令:ldconfig!該命令會將/etc/ld.so.conf檔案中所有路徑下的庫載入記憶體中
預設的動態庫搜尋路徑/lib;
預設的動態庫搜尋路徑/usr/lib。
編譯時查詢庫的搜尋路徑
- 編譯時使用-L指定庫的路徑;
gcc main.c -o main -L./ -lcac 通過環境變數LIBRARY_PATH指定搜尋路徑
LIBRARY_PATH=.:$LIBRARY_PATH gcc main.c -o main -lcac- 系統標準路徑/lib /usr/lib /usr/local/lib
比較
- 編譯時查詢的是靜態庫或動態庫,而執行時查詢的只是動態庫;
- gcc引數-L指定編譯時的連結路徑,-Wl,-rpath指定執行時連結路徑;
- 編譯時使用環境變數LIBRARY_PATH指定庫的路徑,執行時使用環境變數LD_LIBRARY_PATH或/etc/ld.so.conf指定庫的路徑;
- 編譯時用的連結器是ld,而執行時用的連結器是/lib/ld-linux.so.2;
- 編譯時與執行時都會查詢預設路徑:/lib /usr/lib;
- 編譯時還有一個預設路徑:/usr/local/lib,而執行時不會預設找查該路徑。
動態庫使用例項
定義庫的標頭檔案
/*caculate.h*/
#ifndef CACULATE_HEAD_ 庫中函式的實現
/*caculate.c檔案*/
#include "caculate.h"
//求兩個數的和
int add(int a, int b)
{
return (a + b);
}
//減法
int sub(int a, int b)
{
return (a - b);
}
//除法
int div(int a, int b)
{
return (int)(a / b);
}
//乘法
int mul(int a, int b)
{
return (a * b);
}編譯生產libcac.so檔案如下: gcc -shared -fPIC caculate.c -o libcac.so
動態庫的使用方法1
#include <stdio.h>
#include "caculate.h"
int main()
{
int a = 20;
int b = 10;
printf("%d + %d = %d\n", a, b, add(a, b));
printf("%d - %d = %d\n", a, b, sub(a, b));
printf("%d / %d = %d\n", a, b, div(a, b));
printf("%d * %d = %d\n", a, b, mul(a, b));
return 0;
}編譯執行:
gcc main.c -o main -L ./ -lcac
LD_LIBRARY_PATH=.:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH ./main
動態庫的使用方法2
#include <stdio.h>
#include <dlfcn.h>
#define DLL_FILE_NAME "libcac.so"
int main()
{
void *handle;
int (*func)(int, int);
char *error;
int a = 30;
int b = 5;
handle = dlopen(DLL_FILE_NAME, RTLD_NOW);
if (handle == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to open libaray %s error:%s\n", DLL_FILE_NAME, dlerror());
return -1;
}
func = dlsym(handle, "add");
printf("%d + %d = %d\n", a, b, func(a, b));
func = dlsym(handle, "sub");
printf("%d + %d = %d\n", a, b, func(a, b));
func = dlsym(handle, "div");
printf("%d + %d = %d\n", a, b, func(a, b));
func = dlsym(handle, "mul");
printf("%d + %d = %d\n", a, b, func(a, b));
dlclose(handle);
return 0;
}編譯執行
gcc call_main.c -o call_main -ldl -Wl,-rpath,./
./main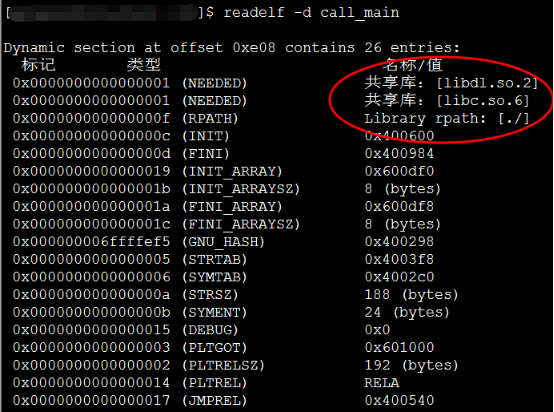
參考:
