Map集合中value()、keySet()和entrySet()以及效能的分析
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-30
在Map集合中
values():方法是獲取集合中的所有的值----沒有鍵,沒有對應關係,
KeySet():將Map中所有的鍵存入到set集合中。因為set具備迭代器。所有可以迭代方式取出所有的鍵,再根據get方法。獲取每一個鍵對應的值。 keySet():迭代後只能通過get()取keyentrySet():Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() //返回此對映中包含的對映關係的 Set 檢視。 Map.Entry表示對映關係。entrySet():迭代後可以e.getKey(),e.getValue()取key和value。返回的是Entry介面 。
下面通過例項來看看:
說明:public class map { public static void main(String[] args) { Map<String, String> maps = new HashMap<String,String>(); maps.put("10","AA"); maps.put("11","BB"); maps.put("12","CC"); maps.put("13","DD"); maps.put("14","EE"); //①value():方法是獲取集合中的所有的值----沒有鍵,沒有對應關係 Collection<String> collections = maps.values(); System.out.println(collections);//[AA, DD, EE, BB, CC] //②keySet():獲取集合中所有的鍵 Set<String> sets = maps.keySet(); System.out.println(sets);//[10, 13, 14, 11, 12] Iterator<String> iterators = sets.iterator(); while(iterators.hasNext()){ String key = iterators.next(); System.out.print(" "+key);// 10 13 14 11 12 String val = maps.get(key); System.out.print(" "+val);//AA DD EE BB CC } //③entrySet():返回此對映中包含的對映關係的 Set 檢視。 Map.Entry表示對映關係 //通過entrySet()方法將map集合中的對映關係取出(這個關係就是Map.Entry型別) Set<Entry<String, String>> entries = maps.entrySet(); //將關係集合entrySet進行迭代,存放到迭代器中 Iterator<Entry<String, String>> iterator1 = entries.iterator(); while(iterator1.hasNext()){ Entry<String, String> entry = iterator1.next();//獲取Map.Entry關係物件entry String key1 = entry.getKey(); String value1 = entry.getValue(); System.out.println(key1+"--->"+value1); } } }
①Set<K> keySet():返回值是個只存放key值的Set集合(集合中無序存放的),迭代後只能通過get()取key。
②Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet():返回對映所包含的對映關係的Set集合(一個關係就是一個鍵-值對),就是把(key-value)作為一個整體一對一對地存放到Set集合當中的。迭代後可以e.getKey(),e.getValue()取key和value。返回的是Entry介面。
③雖然使用keyset及entryset來進行遍歷能取得相同的結果,但兩者的遍歷速度是有差別的,keySet()的速度比entrySet()慢了很多, 也就是keySet方式遍歷Map的效能不如entrySet效能好,為了提高效能,以後多考慮用entrySet()方式來進行遍歷。
問題:為什麼keySet方式遍歷Map的效能不如entrySet效能?
public class map1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//為什麼keySet效能不如entrySet呢?實驗證明
HashMap<String, String> keySetMap = new HashMap<String, String>();
HashMap<String, String> entrySetMap = new HashMap<String, String>();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) {
keySetMap.put("" + i, "keySet");
}
for (int j = 0; j < 1000000; j++) {
entrySetMap.put("" + j, "entrySet");
}
//keySet實驗:1000000條資料,用時54
long startTimeOne = System.currentTimeMillis();
Iterator<String> keySetIterator = keySetMap.keySet().iterator();
while (keySetIterator.hasNext()) {
String key = keySetIterator.next();
String value = keySetMap.get(key);//效能差距的原因:取得key所對應的value時,此時還要訪問Map的這個方法
System.out.println(value);
}
System.out.println("keyset spent times:"
+ (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTimeOne));//54
//entrySet實驗:1000000條資料,用時28
long startTimeTwo = System.currentTimeMillis();
Iterator<Entry<String, String>> entryKeyIterator = entrySetMap
.entrySet().iterator();
while (entryKeyIterator.hasNext()) {
Entry<String, String> e = entryKeyIterator.next();
System.out.println(e.getValue());
}
System.out.println("entrySet spent times:"
+ (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTimeTwo));//28
}
} 通過檢視原始碼發現,呼叫這個方法keySetMap.keySet()會生成KeyIterator迭代器,其next方法只返回其key值.
Java程式碼
private class KeyIterator extends HashIterator<K> {
public K next() {
return nextEntry().getKey();
}
}Java程式碼
private class EntryIterator extends HashIterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
public Map.Entry<K,V> next() {
return nextEntry();
}
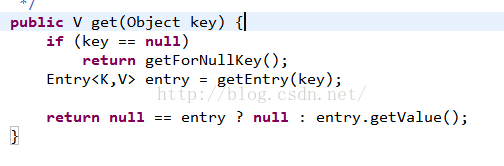
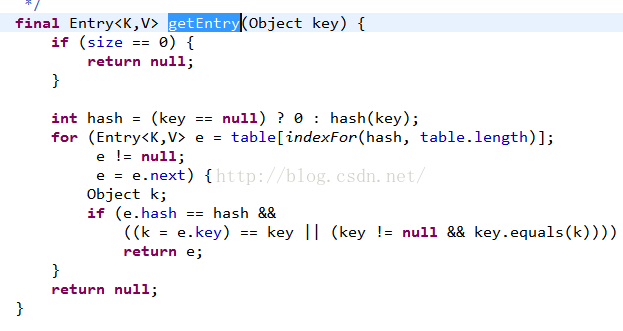
} String value = keySetMap.get(key)檢視原始碼可以看出
這個方法就是二者效能差別的主要原因.