關注校招求職,微訊號:job_campus
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-31
導言:
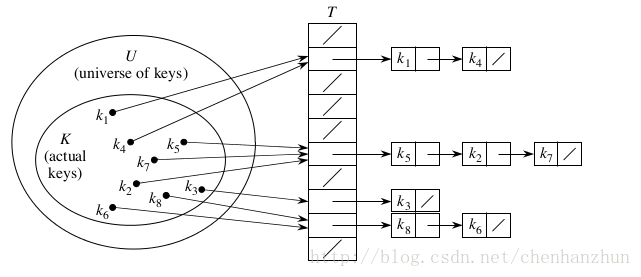
陣列的特點是:定址容易,插入和刪除困難;而連結串列的特點是:定址困難,插入和刪除容易。那麼我們能不能綜合兩者的特性,做出一種定址容易,插入刪除也容易的資料結構?答案是肯定的,這就是我們要提起的雜湊表,雜湊表有多種不同的實現方法,我接下來解釋的是最常用的一種方法——拉鍊法,我們可以理解為“連結串列的陣列”,拉接法的思路是:如果多個關鍵字對映到了雜湊表的同一個位置處,則將這些關鍵字記錄在同一個線性連結串列中。結構如下圖所示:(注:以下是單鏈表實現,若為了方便刪除資料,也可以使用雙向連結串列實現)
直接定址表:
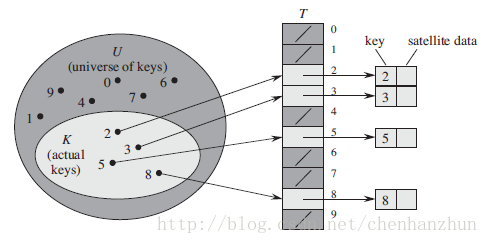
當關鍵字的全域U比較小時,直接定址是一種簡單有效的技術。關鍵字大小直接與元素所在的位置序號相等,不會出現衝突的情況。其結構圖如下所示:
雜湊表:
如果全域U很大時,直接定址表存在的很明顯的缺點。這時採用一種對映關係得到由雜湊值組成的雜湊表,使儲存空間利用率更高。但是,雜湊表存在的衝突情況,即不同的關鍵字在雜湊函式的對映下得到相同的雜湊值。為了解決這種衝突,可以採用一些有用的方法,例如:拉鍊法,開放定址等。雜湊表的確定主要是雜湊函式的選擇。
雜湊函式:
除法雜湊法
雜湊函式如下:
式中表示在基數m中對關鍵字k取餘,其中m的取值最好為一個不太接近2的整數冪的素數。
乘法雜湊法
雜湊函式如下:
式中,m一般取2的某個次冪,k為關鍵字,A為某個引數一般取黃金分割值,kA(mod)1表示取kA的小數部分。
單鏈表實現的源程式:
函式定義:#ifndef HASHTABLE_LINKLIST_H_INCLUDE #define HASHTABLE_LINKLIST_H_INCLUDE #define M 5 typedef int Elemtype; typedef struct Node { Elemtype data; struct Node *next; }Node,*pNode; typedef struct HashNode { pNode head; }HashNode,*HashTable; //建立雜湊表 HashTable Creat_HashTable(int n); //插入資料 void Insert_HashTable(HashTable HT,Elemtype data); //查詢資料 pNode Search_HashTable(HashTable HT,Elemtype key); //刪除資料 void Delete_HashTable(HashTable HT,Elemtype key); #endif
/*****************************************
****該雜湊表是利用單鏈表解決衝突問題的****
*****************************************/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "HashTable_LinkList.h"
//建立雜湊表
HashTable Creat_HashTable(int n)
{
//分配雜湊表所需的地址空間
HashTable HT = (HashTable)malloc(n*sizeof(HashNode));
if (!HT)
{
printf("malloc the HashTable is failed.\n");
exit(1);
}
//初始化空雜湊表
int i;
for (i = 0;i < n;i++)
{
HT[i].head = NULL;
}
return HT;
}
//插入資料
void Insert_HashTable(HashTable HT,Elemtype data)
{
//查詢雜湊表是否存在要插入的資料
//若存在則插入不成功,並退出
if (Search_HashTable(HT,data))
{
printf("the data of %d you want to insert is exist.\n",data);
exit(1);
}
else
{
pNode pNew = (pNode)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if (!pNew)
{
printf("malloc the memory is failed.\n");
exit(1);
}
//把資料插入到連結串列尾部
pNew->data = data;
pNew->next = NULL;
//雜湊函式採用除法雜湊法
int h = data%M;
pNode pCur = HT[h].head;
if (NULL == pCur)
{
HT[h].head = pNew;
}
else
{
while (pCur->next)
{
pCur = pCur->next;
}
pCur->next = pNew;
}
printf("Insert the data of %d is success.\n",data);
}
}
//查詢資料
pNode Search_HashTable(HashTable HT,Elemtype key)
{
if(!HT)
return NULL;
int h = key%M;
pNode pCur = HT[h].head;
while(pCur && pCur->data != key)
pCur = pCur->next;
return pCur;
}
//刪除資料
void Delete_HashTable(HashTable HT,Elemtype key)
{
if (!Search_HashTable(HT,key))
{
printf("the data is not exist");
exit(1);
}
else
{
int h = key%M;
pNode pCur = HT[h].head;
if(pCur->data == key)//該資料為第一個節點
HT[h].head = pCur->next;
else
{
pNode pre = pCur;//當前節點的前一個節點;
while (pCur && pCur->data != key)
{
pre = pCur;
pCur = pCur->next;
}
pre->next = pCur->next;
}
free(pCur);
printf("delete the data of %d is success.\n",key);
}
}#include <stdio.h>
#include "HashTable_LinkList.h"
int main()
{
int n_len = 10;
int Array[]={1,5,8,10,15,17};
//建立雜湊表並插入資料
HashTable HT = Creat_HashTable(n_len);
int i;
for (i=0;i<6;i++)
{
Insert_HashTable(HT,Array[i]);
}
//查詢資料
pNode p = Search_HashTable(HT,8);
if (p)
{
printf("the data is exist.\n");
}
else
{
printf("the data is not exist.\n");
}
//刪除資料
Delete_HashTable(HT,15);
p = Search_HashTable(HT,15);
if (p)
{
printf("the data is exist.\n");
}
else
{
printf("the data is not exist.\n");
}
return 0;
}
開放定址法:
開放定址法是解決衝突的另一種辦法。
定義:將雜湊函式擴充套件定義成探查序列,即每個關鍵字有一個探查序列h(k,0)、h(k,1)、...、h(k,m-1),這個探查序列一定是0....m-1的一個排列(一定要包含散列表全部的下標,不然可能會發生雖然散列表沒滿,但是元素不能插入的情況),如果給定一個關鍵字k,首先會看h(k,0)是否為空,如果為空,則插入;如果不為空,則看h(k,1)是否為空,以此類推。 特點:散列表的每個槽只能放一個元素,因此當n==m時,最終會發生不能再插入元素的情況,n/m<=1。 一致雜湊:每個關鍵字所對應的探查序列是0...m-1的m!種排列的每個可能性都相同,並且和其他關鍵字獨立無關。開放定址法好效能的前提是一致雜湊。 缺點:不支援刪除操作,只支援INSERT、SEARCH操作,因此如果有刪除操作,就用連結法。演算法導論11.4-2要求實現DELETE操作。 生成探查序列的方法有:(1)線性探查:h(k,i)=(h'(k)+i) mod m,可能有“一次群集”問題,即隨著插入的元素越來越多,操作時間越來越慢。
(2)二次探查:h(k,i)=(h'(k)+ai+bi^2) mod m,可能有“二次群集”問題,即如果h(k1,0)=h(k2,0),則探查序列就一致。
(3)二次雜湊:h(k,i)=(h1(k)+ih2(k)) mod m ,要求m和h2(k)互質,不然探查序列不能覆蓋到整個下標。演算法導論11.4-3證明了這點。其中二次雜湊最好,因為他能夠生成m^2種(離m!最接近)排列,而線性探查、二次探查只能生成m種排列,而理想中如果滿足一致雜湊的話,則會生成m!種排列。
參考資料: