java-集合類(二)-迭代器-Iterator-Collections類自然排序
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-31
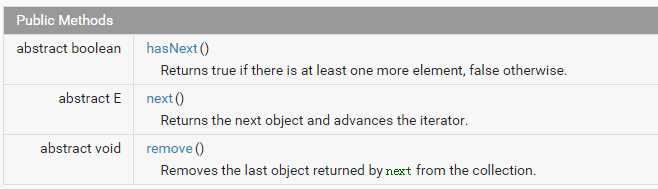
迭代器方法:
迭代器的工作原理:
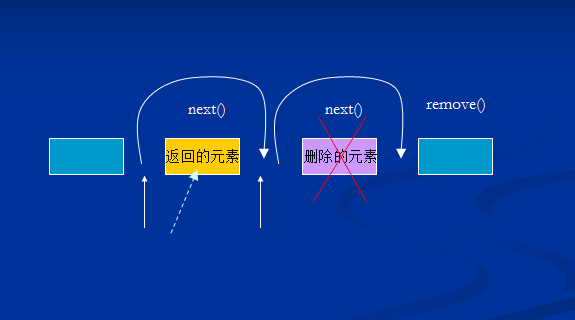
注意:迭代器是指向兩個元素之間的位置,如果後面有元素則hasNext()返回真,當我們呼叫next()方法時,返回黃色的元素,如上圖,當我們呼叫remove方法是要先呼叫一次next(),呼叫remove將返回的元素刪除.
容器的最大作用例項:
package ArrayList;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
class ArrayListTest {
//容器的最大作用 Collections類
排序:Collections.sort()
(1)自然排尋(natural ordering );
(2)實現比較器(Comparator)介面。
package ArrayList;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
class ArrayListTest {
public static void printElements(Collection<?> c) {
Iterator<?> it = c.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
System.out.println(it.next());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1 = new Student(5, "xiaoxi");
Student s2 = new Student(2, "xiaohong");
Student s3 = new Student(3, "xiaozhu");
ArrayList<Student> al = new ArrayList<Student>();
al.add(s1);
al.add(s2);
al.add(s3);
//Collections類進行排序,自然排序
Collections.sort(al);
printElements(al);
}
}
class Student implements Comparable<Object> {
int num;
String name;
Student(int num, String name) {
this.name = name;
this.num = num;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Object arg0) {
Student s = (Student) arg0;
//如果當前數比你要比較的數大返回1,小,返回負數
return num > s.num ? 1 : (num == s.num ? 0 : -1);
}
public String toString() {
return "num=" +num + ", name=" + name;
}
}
結果
num=2, name=xiaohong
num=3, name=xiaozhu
num=5, name=xiaoxi