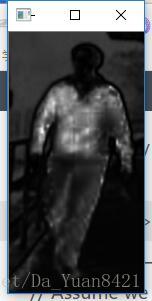
【OpenCV】顯著區域檢測
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-02-01
寫在前面
最近在做畢設,題目是行人再識別。目前只是用行人區域的顏色直方圖進行匹配,效果比較不理想。老闆推薦加入顯著性檢測,然後就搞了搞。
環境
- VS2015
- OpenCV3.2
程式碼
Saliency_h
// Saliency.h: interface for the Saliency class.
//
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//===========================================================================
// Copyright (c) 2009 Radhakrishna Achanta [EPFL]
//=========================================================================== Saliency_cpp
// Saliency.cpp: implementation of the Saliency class.
//
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//===========================================================================
// Copyright (c) 2009 Radhakrishna Achanta [EPFL]
//===========================================================================
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "Saliency.h"
#include <cmath>
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Construction/Destruction
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
Saliency::Saliency()
{
}
Saliency::~Saliency()
{
}
//===========================================================================
/// RGB2LAB
//===========================================================================
void Saliency::RGB2LAB(
const vector<unsigned int>& ubuff,
vector<double>& lvec,
vector<double>& avec,
vector<double>& bvec)
{
int sz = int(ubuff.size());
lvec.resize(sz);
avec.resize(sz);
bvec.resize(sz);
for (int j = 0; j < sz; j++)
{
int r = (ubuff[j] >> 16) & 0xFF;
int g = (ubuff[j] >> 8) & 0xFF;
int b = (ubuff[j]) & 0xFF;
double xval = 0.412453 * r + 0.357580 * g + 0.180423 * b;
double yval = 0.212671 * r + 0.715160 * g + 0.072169 * b;
double zVal = 0.019334 * r + 0.119193 * g + 0.950227 * b;
xval /= (255.0 * 0.950456);
yval /= 255.0;
zVal /= (255.0 * 1.088754);
double fX, fY, fZ;
double lval, aval, bval;
if (yval > 0.008856)
{
fY = pow(yval, 1.0 / 3.0);
lval = 116.0 * fY - 16.0;
}
else
{
fY = 7.787 * yval + 16.0 / 116.0;
lval = 903.3 * yval;
}
if (xval > 0.008856)
fX = pow(xval, 1.0 / 3.0);
else
fX = 7.787 * xval + 16.0 / 116.0;
if (zVal > 0.008856)
fZ = pow(zVal, 1.0 / 3.0);
else
fZ = 7.787 * zVal + 16.0 / 116.0;
aval = 500.0 * (fX - fY) + 128.0;
bval = 200.0 * (fY - fZ) + 128.0;
lvec[j] = lval;
avec[j] = aval;
bvec[j] = bval;
}
}
//==============================================================================
/// GaussianSmooth
///
/// Blur an image with a separable binomial kernel passed in.
//==============================================================================
void Saliency::GaussianSmooth(
const vector<double>& inputImg,
const int& width,
const int& height,
const vector<double>& kernel,
vector<double>& smoothImg)
{
int center = int(kernel.size()) / 2;
int sz = width*height;
smoothImg.clear();
smoothImg.resize(sz);
vector<double> tempim(sz);
int rows = height;
int cols = width;
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Blur in the x direction.
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
{int index(0);
for (int r = 0; r < rows; r++)
{
for (int c = 0; c < cols; c++)
{
double kernelsum(0);
double sum(0);
for (int cc = (-center); cc <= center; cc++)
{
if (((c + cc) >= 0) && ((c + cc) < cols))
{
sum += inputImg[r*cols + (c + cc)] * kernel[center + cc];
kernelsum += kernel[center + cc];
}
}
tempim[index] = sum / kernelsum;
index++;
}
}}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Blur in the y direction.
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
{int index = 0;
for (int r = 0; r < rows; r++)
{
for (int c = 0; c < cols; c++)
{
double kernelsum(0);
double sum(0);
for (int rr = (-center); rr <= center; rr++)
{
if (((r + rr) >= 0) && ((r + rr) < rows))
{
sum += tempim[(r + rr)*cols + c] * kernel[center + rr];
kernelsum += kernel[center + rr];
}
}
smoothImg[index] = sum / kernelsum;
index++;
}
}}
}
//===========================================================================
/// GetSaliencyMap
///
/// Outputs a saliency map with a value assigned per pixel. The values are
/// normalized in the interval [0,255] if normflag is set true (default value).
//===========================================================================
void Saliency::GetSaliencyMap(
const vector<unsigned int>& inputimg,
const int& width,
const int& height,
vector<double>& salmap,
const bool& normflag)
{
int sz = width*height;
salmap.clear();
salmap.resize(sz);
vector<double> lvec(0), avec(0), bvec(0);
RGB2LAB(inputimg, lvec, avec, bvec);
//--------------------------
// Obtain Lab average values
//--------------------------
double avgl(0), avga(0), avgb(0);
{for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++)
{
avgl += lvec[i];
avga += avec[i];
avgb += bvec[i];
}}
avgl /= sz;
avga /= sz;
avgb /= sz;
vector<double> slvec(0), savec(0), sbvec(0);
//----------------------------------------------------
// The kernel can be [1 2 1] or [1 4 6 4 1] as needed.
// The code below show usage of [1 2 1] kernel.
//----------------------------------------------------
vector<double> kernel(0);
kernel.push_back(1.0);
kernel.push_back(2.0);
kernel.push_back(1.0);
GaussianSmooth(lvec, width, height, kernel, slvec);
GaussianSmooth(avec, width, height, kernel, savec);
GaussianSmooth(bvec, width, height, kernel, sbvec);
{for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++)
{
salmap[i] = (slvec[i] - avgl)*(slvec[i] - avgl) +
(savec[i] - avga)*(savec[i] - avga) +
(sbvec[i] - avgb)*(sbvec[i] - avgb);
}}
if (true == normflag)
{
vector<double> normalized(0);
Normalize(salmap, width, height, normalized);
swap(salmap, normalized);
}
}以上兩個程式碼不需要改動,直接加入工程檔案即可。
Main_cpp
// Main.cpp : 定義控制檯應用程式的入口點。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "Saliency.h"
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
Saliency sal;
Mat src = imread("./xr.jpg");
if (src.empty()) return -1;
vector<unsigned int >imgInput;
vector<double> imgSal;
//Mat to vector
int nr = src.rows; // number of rows
int nc = src.cols; // total number of elements per line
if (src.isContinuous()) {
// then no padded pixels
nc = nc*nr;
nr = 1; // it is now a 1D array
}
for (int j = 0; j<nr; j++) {
uchar* data = src.ptr<uchar>(j);
for (int i = 0; i<nc; i++) {
unsigned int t = 0;
t += *data++;
t <<= 8;
t += *data++;
t <<= 8;
t += *data++;
imgInput.push_back(t);
}
}
sal.GetSaliencyMap(imgInput, src.cols, src.rows, imgSal);
//vector to Mat
int index0 = 0;
Mat imgout(src.size(), CV_64FC1);
for (int h = 0; h < src.rows; h++) {
double* p = imgout.ptr<double>(h);
for (int w = 0; w < src.cols; w++) {
*p++ = imgSal[index0++];
}
}
normalize(imgout, imgout, 0, 1, NORM_MINMAX);
imshow("原影象", src);
imshow("顯著性影象", imgout);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
說明
- 其中最重要的函式就是
GetSaliencyMap,其輸入和輸出都為vector,所以重點是要將Mat轉為vector。 - 在原程式中有一段說明:
// Assume we already have an unsigned integer buffer inputImg of
// inputWidth and inputHeight (in row-major order).
// Each unsigned integer has 32 bits and contains pixel data in ARGB
// format. I.e. From left to right, the first 8 bits contain alpha
// channel value and are not used in our case. The next 8 bits
// contain R channel value; the next 8 bits contain G channel value;
// the last 8 bits contain the B channel value.
按照這段話,把Mat中的資料轉成vector<unsigned int>。 - 但是我有一點不理解的地方:在使用了
isContinuous()函式之後,註釋說就變成了一維的資料??