資料結構之堆的基本操作
在實現堆的操作之前,先來明白什麼是堆?
- 堆中某個節點的值總是不大於或不小於其父節點的值
- 堆總是一棵完全二叉樹。
要說到完全二叉樹,直觀的判斷就是,層序遍歷一棵樹,如果樹的某個節點沒有右子樹或者是沒有子樹,那麼從這個節點後面的所有節點都不能夠有任何子樹。
接下來我們說說堆。堆分為大堆跟小堆。大堆的意思就是每一個節點都是它這個節點樹的最大值。小堆同理是最小值。
基本操作與實現
基本操作
//heap.h
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stddef.h>
#define HEAPMAX 1000 實現
其實堆的操作都很簡單,但是最核心的兩個就是插入與刪除。這兩個我們單獨來說。
#include "heap.h"
#define HEAD printf("===================%s====================\n",__FUNCTION__); 插入
我們在實現堆的時,利用一個順序表來實現。由於是層序遍歷,且堆是完全二叉樹。所以順序表完全能夠處理好堆的基本操作。再者,定義一個函式指標,這個函式指標可以確定我們的堆是大堆還是小堆。接著就是插入了,由於要考慮到插入完畢後還是堆,那麼就要考慮到堆的性質,首先是完全二叉樹,接著每個節點都是它節點子樹的最大值或最小值。插入很簡單,我們只需要在順序表尾部插入即可。那如何保證堆的第二條性質呢?

所以在插入的時候,要對插入的元素與它的父節點進行比較。而如何確定它的父節點呢?這很簡單,由於是層序遍歷在順序表內。那麼一個節點的父節點的下標就是它自己的下標減一除二。即parent = (child - 1)/2
//實現
void Swap(HeapType* a, HeapType* b)
{
HeapType tmp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = tmp;
}
void HeapInsert(Heap* heap, HeapType to_insert)//在堆中插入
{
if(heap == NULL) {
return;
}
if(heap->size >= HEAPMAX) {
return;
}
heap->data[heap->size] = to_insert;
++heap->size;
size_t child = heap->size - 1;
size_t parent = (child - 1) / 2;//父節點
while(child >= 0 && child < heap->size &&
parent >= 0 && parent < heap->size) {
if(heap->data[child] > heap->data[parent]){//判斷是否需要交換
Swap(&heap->data[child], &heap->data[parent]);
child = parent;//交換完畢後,要上浮,此時子節點變成之前的父節點,以此類推
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
} else {
break;
}
}
return;
}
刪除
在實現完插入之後,接下來就是刪除。同樣,刪除也得滿足刪除後的樹仍舊是一個堆。且滿足堆的基本條件。這裡,我們的思路採用的是刪除堆頂。具體如下:
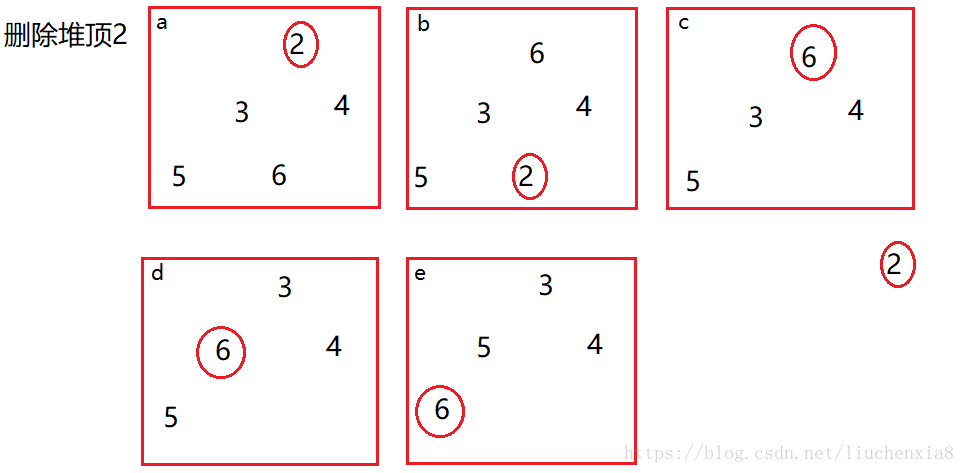
這裡,我們在刪除之前,先將堆頂元素與最後一個元素交換,然後刪除最後一個元素,也就是結構體內的size減一。刪除完畢後,開始調整。調整的過程就是下沉。此時堆頂是6,先將節點元素與其左右子樹分別比較。將左右子樹中較小的與節點交換。如果沒有右子樹,那麼直接與左子樹交換。一次交換完畢後,此時新節點等於交換的子樹。以此類推。這就是下沉。
//實現
void HeapErase(Heap* heap)//刪除堆頂元素
{
if(heap == NULL) {
return;
}
if(heap->size == 0) {
return;
}
Swap(&heap->data[heap->size - 1], &heap->data[0]);
--heap->size;
size_t parent = 0;
size_t child = 2*parent + 1;//交換並刪除
while(child >= 0 && child< heap->size &&
parent >= 0 && parent < heap->size) {
if((child + 1) < heap->size){//判斷是否有右子樹,並且取出其中較小的
if(!heap->cmp(heap->data[child], heap->data[child+1])) {
child = child + 1;
}
}
if(heap->data[child] > heap->data[parent]) {//判斷是否需要下沉
Swap(&heap->data[child], &heap->data[parent]);
parent = child;
child = 2*parent + 1;
} else {
break;
}
}
printf("\n");
return;
}
堆排
在實現完堆的基本操作以後,我們可以考慮一下堆排序的實現。我們其實可以發現,在刪除堆內元素的時候每次刪除的都是最大的一個。並且最大或最小的一個都沉底了。
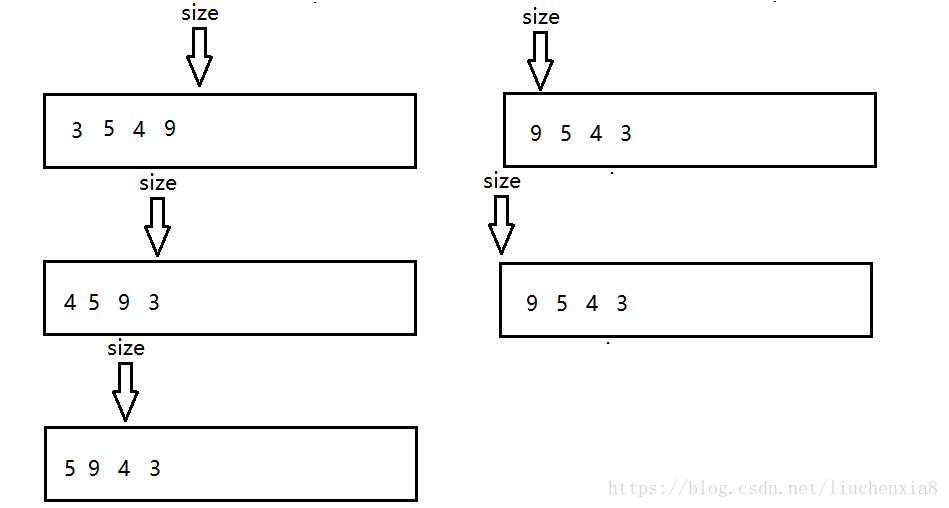
我們發現,每次刪除一次,後面的元素都是一個有序的。而刪除到最後,整個順序表就是一個有序的順序表。如果這時候將size放到最後,那麼此時恰好就是一個有序的陣列。
//實現
void HeapSort(HeapType array[], size_t size)//堆排
{
if(array == NULL || size == 0) {
return;
}
Heap heap;
HeapInit(&heap, Greater);
HeapCreat(&heap, array, size);//先將陣列插入堆中
size_t i = 0;
for(; i < size; ++i) {
HeapErase(&heap);//刪除堆內所有元素
}
heap.size = size;
i = 0;
for(; i < size; ++i) {
array[i] = heap.data[i];//把堆內元素複製到陣列中,完成排序
}
return;
}測試程式碼如下
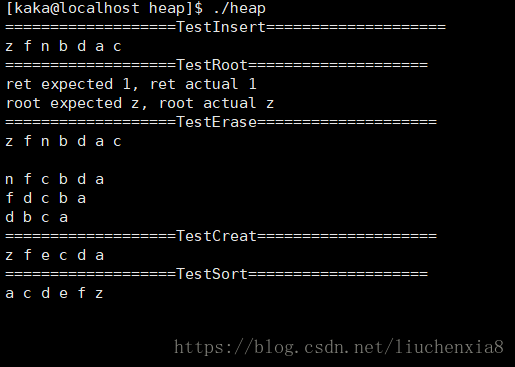
void TestInsert()
{
HEAD;
Heap heap;
HeapInit(&heap, Greater);
HeapInsert(&heap, 'b');
HeapInsert(&heap, 'z');
HeapInsert(&heap, 'a');
HeapInsert(&heap, 'f');
HeapInsert(&heap, 'd');
HeapInsert(&heap, 'c');
HeapInsert(&heap, 'n');
HeapPrintChar(&heap);
}
void TestRoot()
{
HEAD;
Heap heap;
HeapInit(&heap, Greater);
HeapInsert(&heap, 'b');
HeapInsert(&heap, 'z');
HeapInsert(&heap, 'a');
HeapInsert(&heap, 'f');
HeapInsert(&heap, 'd');
HeapInsert(&heap, 'c');
HeapInsert(&heap, 'n');
HeapType root;
int ret = HeapRoot(&heap, &root);
printf("ret expected 1, ret actual %d\n",ret);
printf("root expected z, root actual %c\n",root);
}
void TestErase()
{
HEAD;
Heap heap;
HeapInit(&heap, Greater);
HeapInsert(&heap, 'b');
HeapInsert(&heap, 'z');
HeapInsert(&heap, 'a');
HeapInsert(&heap, 'f');
HeapInsert(&heap, 'd');
HeapInsert(&heap, 'c');
HeapInsert(&heap, 'n');
HeapPrintChar(&heap);
printf("\n");
HeapErase(&heap);
HeapPrintChar(&heap);
HeapErase(&heap);
HeapPrintChar(&heap);
HeapErase(&heap);
HeapPrintChar(&heap);
}
void TestSort()
{
HEAD;
HeapType array[] = {'c', 'd', 'a', 'f', 'z', 'e'};
size_t size = sizeof(array)/sizeof(array[0]);
HeapSort(array, size);
size_t i = 0;
for(; i < size; ++i) {
printf("%c ", array[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
void TestCreat()
{
HEAD;
Heap heap;
HeapInit(&heap, Greater);
HeapType array[] = {'c', 'd', 'a', 'f', 'z', 'e'};
size_t size = sizeof(array)/sizeof(array[0]);
HeapCreat(&heap, array, size);
HeapPrintChar(&heap);
}
int main()
{
TestInsert();
TestRoot();
TestErase();
TestCreat();
TestSort();
printf("\n");
printf("\n");
printf("\n");
printf("\n");
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
歡迎大家共同討論,如有錯誤及時聯絡作者指出,並改正。謝謝大家!