Linux下清除快取 drop_caches,sysctl(備忘)
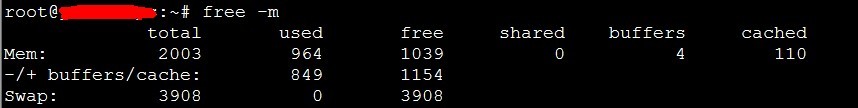
1. 用命令 free -m 檢視一下記憶體的使用情況:
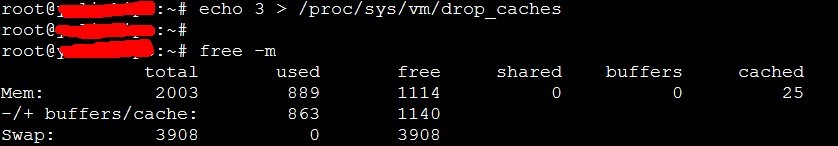
然後清除快取後再來檢視一下記憶體的使用情況:
前後對比可發現,快取由之前的110M縮小到了25M,效果比較明顯。
2. 下面說一下 drop_caches:
清空 pagecache:
sync
echo 1 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches
或者:
sync
sysctl -w vm.drop_caches=1
清空 dentries 和 inodes:
sync
echo 2 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches
或者:
sync
sysctl -w vm.drop_caches=2
清空所有快取(pagecache、dentries 和 inodes):
sync
echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches
或者:
sync
sysctl -w vm.drop_caches=3
3. 如果嘗試向 drop_caches 中寫入 0,會報下面錯誤:
-bash: echo: write error: Invalid argument
我的核心是3.4.39,64 位。至於什麼原因,我沒找到。但是從下面關於 drop_caches 的說明來看,drop_caches 的值並沒有說可以設定成 0 的,但是 drop_caches 的預設值是 0。但是 2.6.x 的核心將 drop_caches 的值設定為 0 是沒有問題的。
關於 drop_caches:
Kernels 2.6.16 and newer provide a mechanism to have the kernel drop the page cache and/or inode and dentry caches on command, which can help free up a lot of memory. Now you can throw away that script that allocated a ton of memory just to get rid of the cache...
To use /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches, just echo a number to it.
To free pagecache:
# echo 1 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches
To free dentries and inodes:
# echo 2 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches
To free pagecache, dentries and inodes:
echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches
This is a non-destructive operation and will only free things that are completely unused. Dirty objects will continue to be in use until written out to disk and are not freeable. If you run "sync" first to flush them out to disk, these drop operations will tend to free more memory.
參考:
博主所有文章已轉自私人部落格 Joe 的個人部落格,謝謝關注!