Spring資源載入
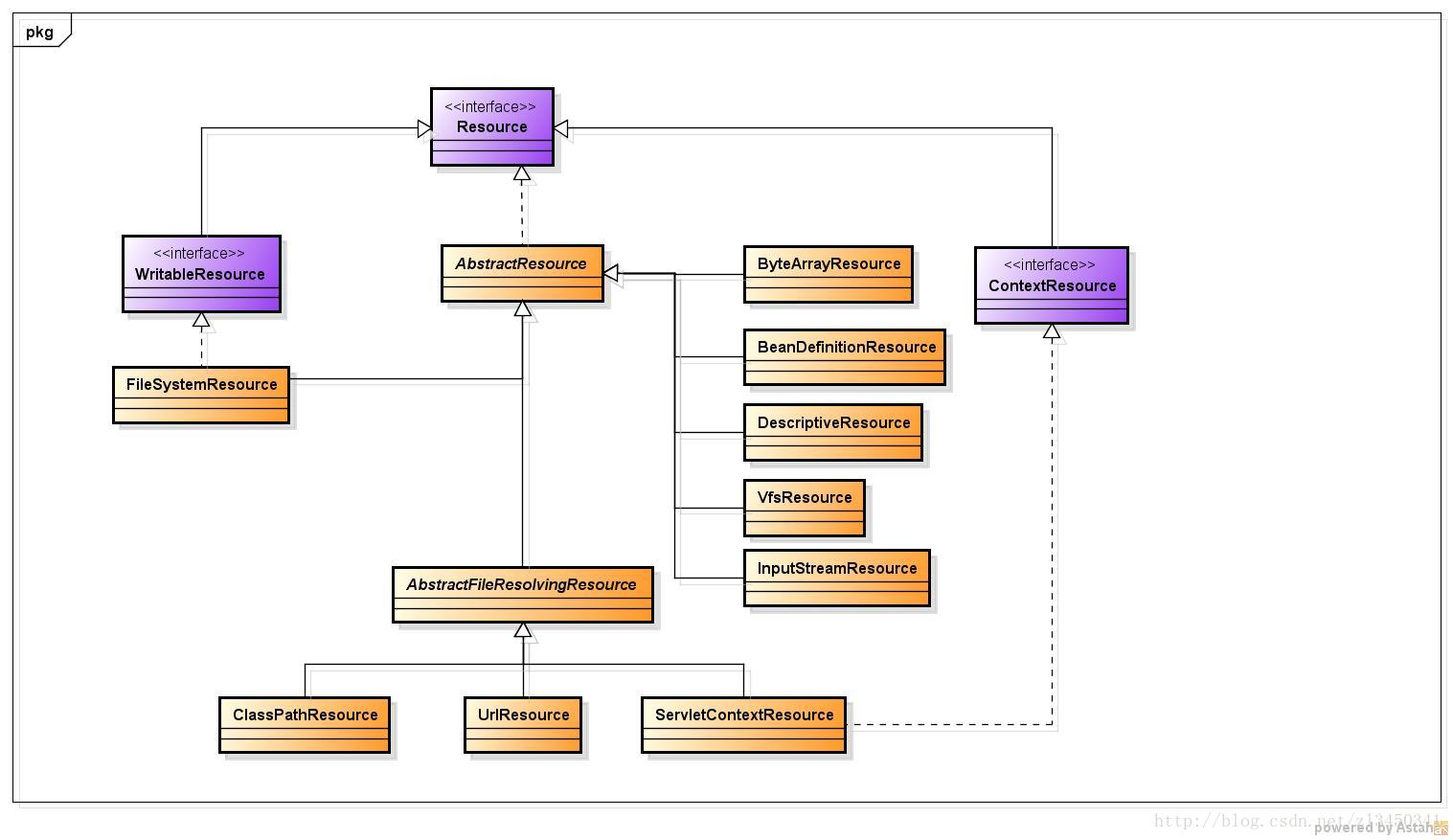
1 資源介面,繼承關係,類簡介
1.1 資源介面
Resource介面為應用提供了底層資源訪問的能力。該介面的主要作用是描述實際的資源。
public interface Resource extends InputStreamSource { //資源是否存在 boolean exists(); //資源是否可讀 default boolean isReadable() {return true;} //資源是否被開啟 default boolean isOpen() {return false;} //確定此資源是否代表檔案系統中的檔案 default boolean isFile() {return false;} //返回資源的URL控制代碼 URL getURL() throws IOException; //返回資源的URI控制代碼 URI getURI() throws IOException; //返回資源的檔案物件 File getFile() throws IOException; //根據相對路徑建立資源 Resource createRelative(String relativePath) throws IOException; //資源名稱 String getFilename(); //資源描述 String getDescription(); }
繼承父類介面方法InputStream getInputStream() throw IOError:返回資源對應的輸入流
1.2 繼承關係
1.3 類簡介
ByteArrayResource:用於從任何給定的位元組陣列中載入內容,特別適用於從本地內容建立位元組陣列。因為isOpen()返回false。所有ByuteArrayResource可以多次使用。當然該資源也可以通過程式碼直接建立。
InputStreamResource:java.io.InputStream位元組流,對於“getInputStream ”操作將直接返回該位元組流,因此只能讀取一次該位元組流,即“isOpen”永遠返回true
FileSystemResource:java.io.File資源,對於“getInputStream ”操作將返回底層檔案的位元組流,“isOpen”將永遠返回false,從而表示可多次讀取底層檔案的位元組流
ClassPathResource:類路徑下的資源,資源以相對類路徑的方式表示。該資源可以存放在如下的位置:1.類路徑下的檔案系統2.類路徑下的jar中。
isOpen返回false,表示可以多次讀取。ClassPathResource替代了Class類和ClassLoader類的getReesource(String name)和getResourceAsStream(String name)載入類路徑資源的方式。提供一致的訪問方式。建構函式如下:
public ClassPathResource(String path):使用預設的ClassLoader載入資源
ublic ClassPathResource(String path,ClassLoader classLoader):採用自定義的ClassLoader載入資源
ublic ClassPathResource(String path,Class<?> class):使用指定類載入器載入資源,載入的是相對於當前類的路徑的資源
如果載入的是jar包中的資源可以採用getURL()獲得資源路徑,因為資源不在檔案系統中所以無法使用getFile
WritableResource:可寫資源介面,獲取資源後,可以對該資源進行寫操作。可以通過程式設計的方式動態的改變資源
FileSystemResource:檔案系統資源
ServletContextResource:為web容器上下文中的資源服務。負責從相對於web根目錄的路徑下載入資源。支援以流和URL的方式訪問。在war解壓的情況下可以通過File的方式訪問,該類也可以從jar中載入資源
UrlResource:是對java.net.URL的封裝,可以訪問任何以URL表示的資源。eg檔案系統資源,FTP資源,HTTP資源。
PathResource:該類封裝了java.net.URL,java.nio.file.path,檔案系統資源,也就說凡是可以採用UrlResource和FileSystemResource表示的資源,也可以採用該類表示
2 資源地址標識
| 字首 | 示例 | 說明 | 備註 |
| classpath: | classpath:aa/bb/cc/bean.xml | 類路徑下的資源,資源可以在檔案系統,也可以在jar/zip檔案中 | classpath: 和classpath:/是等價的 |
| file: | file:aa/bb/cc/bean.xml | 表示檔案系統中資源,使用UrlResource表示 | |
| http:// | http://http://mp.blog.csdn.net/bean.xml | 使用UrlResource從網路上的資源 | |
| ftp:// | ftp://http://mp.blog.csdn.net/bean.xml | 使用UrlResource從FTP上的資源 | |
| 沒有 | a/bb/cc/bean.xml | 根據ApplicationContext的具體實現類採用對應型別的Resource | 如果是web應用,採用ServletContextResource,否則採用calsspath:a/bb/cc/bean.xml |
3 地址萬用字元
| 萬用字元 | 示例 | 說明 | 備註 |
| ? | a/bb/c?/bean?.xml | 匹配單個字元 | |
| * | a/bb/*/bean*.xml | 匹配一個或者多個字元 | |
** | a/bb/**/bean**.xml | 匹配一個或者多個路徑 | bean**.xml中**按照*處理 |
?和*是針對於字元匹配而**是針對於路徑匹配
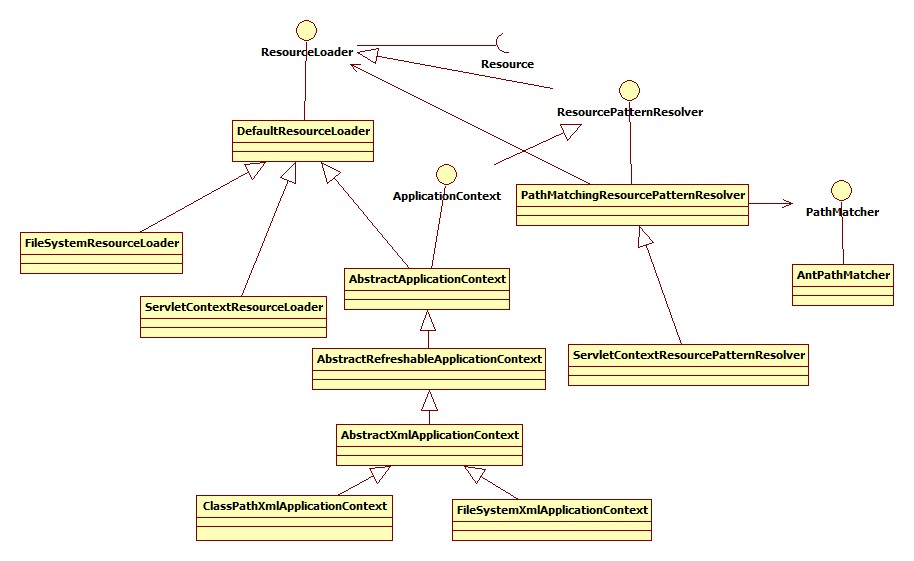
4 資源載入介面,繼承關係以及類說明
4.1 資源載入介面
ResourceLoader介面用於實現不同的Resource載入策略,即將不同Resource例項的建立交給ResourceLoader,該介面只支援以classpath:不支援classpath*:如果想要支援後者的介面是ResourcePatternResolver
public interface ResourceLoader {
/** Pseudo URL prefix for loading from the class path: "classpath:" */
String CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX = ResourceUtils.CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX;
/**
* 按照給定的路徑建立資源,支援如下幾種模式
* 1.以file字首描述的資源 eg:file:/work/bean.xml
* 2.以classpath字首描述的資源 eg:classpath:/aa/bb/bean.xml
* 3.相對路徑描述的資源 /WEB-INF/bean.xml<p>
* 返回的資源並不一定存在需要呼叫Resource#exists判斷
Resource getResource(String location);
/**
* 獲得ResourceLoader的類載入器,在建立ClassPathResource時被傳入
* 在某些需要使用載入器的應用中可以直接通過該方法獲得而不是採用thread context ClassLoader
* 在某些情況下兩個ClassLoader並不一樣
*/
@Nullable
ClassLoader getClassLoader();
}public interface ResourcePatternResolver extends ResourceLoader {
String CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX = "classpath*:";
/**
* 根據給定路徑,獲取該路徑下的所有的Resource
*/
Resource[] getResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException;
}4.2 繼承關係
4.2 類說明
4.2.1 DefaultResourceLoader
是ResourceLoader提供的預設實現,具體流程如下
1.判斷liocation是否定義了協議:file,zip,jar,war...如果定義了直接返回該資源
2.是否以/開始,如果是就在類路徑的上下文中載入該資源
3.判斷是否以classpath:開始,如果是建立ClassPathResource
4.嘗試建立URLResource
5.建立UrlResource失敗後,就在類路徑的上下文中載入該資源
@Override
public Resource getResource(String location) {
Assert.notNull(location, "Location must not be null");
for (ProtocolResolver protocolResolver : this.protocolResolvers) {
//資源是否定義了協議eg:file,zip,http
Resource resource = protocolResolver.resolve(location, this);
if (resource != null) {
return resource;
}
}
//判斷是否為相對路徑
if (location.startsWith("/")) {
return getResourceByPath(location);
}
//是否以classpath:
else if (location.startsWith(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX)) {
return new ClassPathResource(location.substring(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX.length()), getClassLoader());
}
else {
try {
// 建立URLResource
URL url = new URL(location);
return new UrlResource(url);
}
catch (MalformedURLException ex) {
//在檔案系統中載入資源,getResourceByPath會在FileSystemResourceLoader中重寫
return getResourceByPath(location);
}
}
}
protected Resource getResourceByPath(String path) {
return new ClassPathContextResource(path, getClassLoader());
}4.2.2 FileSystemResourceLoader
載入檔案系統中的資源
protected Resource getResourceByPath(String path) {
if (path.startsWith("/")) {
path = path.substring(1);
}
return new FileSystemContextResource(path);
}4.2.3 ServletContextResourceLoader
從Servlet上下文路徑中載入資源它實現了自己的getResourceByPath方法,這裡的path即使以”/”開頭,也是相對ServletContext的路徑,而不是絕對路徑,要使用絕對路徑,需要新增”file:”字首
protected Resource getResourceByPath(String path) {
return new ServletContextResource(this.servletContext, path);
}4.2.4 PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver
匹配模式下的資源載入,持有ResourceLoader介面,不含有地址萬用字元的情況下要麼採用預設的方式,要麼採用具體的實現方式載入對應的資源
private final ResourceLoader resourceLoader;
public ResourceLoader getResourceLoader() {
return this.resourceLoader;
}
public Resource getResource(String location) {
return getResourceLoader().getResource(location);
}含有地址萬用字元查詢主要分如下幾種情況
case 1:以classpath*開始且路徑中含有萬用字元
case 2:以classpath*開始且路徑中不含有萬用字元
case 3:不以classpath*開始且路徑中含有萬用字元
case 4:不以classpath*開始且路徑中不含有萬用字元
其中case 1和case 3執行的邏輯一致,case 4直接採用ClassLoader載入資源比較簡單
public Resource[] getResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException {
Assert.notNull(locationPattern, "Location pattern must not be null”);
//是否以classpath*:開始
if (locationPattern.startsWith(CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX)) {
// a class path resource (multiple resources for same name possible)
if (getPathMatcher().isPattern(locationPattern.substring(CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX.length()))) {
// a class path resource pattern
// case 1:以classpath*開始且路徑中含有萬用字元
return findPathMatchingResources(locationPattern);
}
else {
// all class path resources with the given name
//case 2: 以classpath*開始且路徑中不含萬用字元
return findAllClassPathResources(locationPattern.substring(CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX.length()));
}
}
else {
// Generally only look for a pattern after a prefix here,
// and on Tomcat only after the "*/" separator for its "war:" protocol.
int prefixEnd = (locationPattern.startsWith("war:") ? locationPattern.indexOf("*/") + 1 :
locationPattern.indexOf(":") + 1);
if (getPathMatcher().isPattern(locationPattern.substring(prefixEnd))) {
// a file pattern
//case 3: 不以classpath*開始且路徑中含有萬用字元和case 1處理的邏輯一致
return findPathMatchingResources(locationPattern);
}
else {
// a single resource with the given name
//case 4: 不以classpath*開始且路徑中不含萬用字元
return new Resource[] {getResourceLoader().getResource(locationPattern)};
}
}
}case 1:以classpath*開始且路徑中含有萬用字元
protected Resource[] findPathMatchingResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException {
//確定根路徑,該路徑中不含有任何的萬用字元的最長路徑
String rootDirPath = determineRootDir(locationPattern);
//rootDirPath之後的包含模式匹配字元的路徑信pattern
String subPattern = locationPattern.substring(rootDirPath.length());
//遞迴查詢該根路徑下匹配的資源
Resource[] rootDirResources = getResources(rootDirPath);
Set<Resource> result = new LinkedHashSet<>(16);
for (Resource rootDirResource : rootDirResources) {
rootDirResource = resolveRootDirResource(rootDirResource);
URL rootDirUrl = rootDirResource.getURL();
if (equinoxResolveMethod != null) {
if (rootDirUrl.getProtocol().startsWith("bundle")) {
URL resolvedUrl = (URL) ReflectionUtils.invokeMethod(equinoxResolveMethod, null, rootDirUrl);
if (resolvedUrl != null) {
rootDirUrl = resolvedUrl;
}
//建立UrlResource
rootDirResource = new UrlResource(rootDirUrl);
}
}
if (rootDirUrl.getProtocol().startsWith(ResourceUtils.URL_PROTOCOL_VFS)) {
result.addAll(VfsResourceMatchingDelegate.findMatchingResources(rootDirUrl, subPattern, getPathMatcher()));
}
//jar中資源
else if (ResourceUtils.isJarURL(rootDirUrl) || isJarResource(rootDirResource)) {
result.addAll(doFindPathMatchingJarResources(rootDirResource, rootDirUrl, subPattern));
}
else {
//非jar中的資源
result.addAll(doFindPathMatchingFileResources(rootDirResource, subPattern));
}
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Resolved location pattern [" + locationPattern + "] to resources " + result);
}
return result.toArray(new Resource[result.size()]);
}從程式碼分析case 1分為3種case
1.查詢並建立VfsResource
2.在jar中查詢Resource,步驟如下
1.計算當前Resource在Jar檔案中的根路徑
2.判斷路徑
3.建立資源並新增到結果集中
protected Set<Resource> doFindPathMatchingJarResources(Resource rootDirResource, URL rootDirURL, String subPattern)
throws IOException {
……
//計算當前Resource在Jar檔案中的根路徑
if (!"".equals(rootEntryPath) && !rootEntryPath.endsWith("/")) {
// Root entry path must end with slash to allow for proper matching.
// The Sun JRE does not return a slash here, but BEA JRockit does.
rootEntryPath = rootEntryPath + "/";
}
Set<Resource> result = new LinkedHashSet<>(8);
for (Enumeration<JarEntry> entries = jarFile.entries(); entries.hasMoreElements();) {
JarEntry entry = entries.nextElement();
String entryPath = entry.getName();
//以rootEntryPath開頭
if (entryPath.startsWith(rootEntryPath)) {
String relativePath = entryPath.substring(rootEntryPath.length());
//相對路徑和subPattern匹配
if (getPathMatcher().match(subPattern, relativePath)) {
//建立一個Resource。將新建立的Resource新增入結果集中
result.add(rootDirResource.createRelative(relativePath));
}
}
}
return result;
}
}2.在非jar中查詢Resource,步驟如下
1.獲取資源根路徑的絕對路徑
2.獲得該路徑下的所有檔案
3.路徑匹配
protected Set<Resource> doFindPathMatchingFileResources(Resource rootDirResource, String subPattern)
throws IOException {
File rootDir;
try {
//獲得資源絕根路徑的對路徑
rootDir = rootDirResource.getFile().getAbsoluteFile();
}
return doFindMatchingFileSystemResources(rootDir, subPattern);
}protected Set<Resource> doFindMatchingFileSystemResources(File rootDir, String subPattern) throws IOException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Looking for matching resources in directory tree [" + rootDir.getPath() + "]");
}
Set<File> matchingFiles = retrieveMatchingFiles(rootDir, subPattern);
Set<Resource> result = new LinkedHashSet<>(matchingFiles.size());
for (File file : matchingFiles) {
//建立資源並新增到結果集
result.add(new FileSystemResource(file));
}
return result;
}
protected Set<File> retrieveMatchingFiles(File rootDir, String pattern) throws IOException {
….
String fullPattern = StringUtils.replace(rootDir.getAbsolutePath(), File.separator, "/");
if (!pattern.startsWith("/")) {
fullPattern += "/";
}
fullPattern = fullPattern + StringUtils.replace(pattern, File.separator, "/");
Set<File> result = new LinkedHashSet<>(8);
doRetrieveMatchingFiles(fullPattern, rootDir, result);
return result;
}protected void doRetrieveMatchingFiles(String fullPattern, File dir, Set<File> result) throws IOException {
File[] dirContents = dir.listFiles();
Arrays.sort(dirContents);
for (File content : dirContents) {
String currPath = StringUtils.replace(content.getAbsolutePath(), File.separator, "/");
//路徑匹配
if (content.isDirectory() && getPathMatcher().matchStart(fullPattern, currPath + "/")) {
if (!content.canRead()) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Skipping subdirectory [" + dir.getAbsolutePath() +
"] because the application is not allowed to read the directory");
}
}
else {
//遞迴呼叫
doRetrieveMatchingFiles(fullPattern, content, result);
}
}
if (getPathMatcher().match(fullPattern, currPath)) {
result.add(content);
}
}
}case 2: 以classpath*開始且路徑中不含萬用字元,步驟如下
1.採用ClassLoader#getResources(String)獲取資源URL
2.遍歷URL建立資源
3.如果擷取後的path=“”,根據ClassLoaer的型別建立資源,
4.如果ClassLoader型別不匹配,就採用父載入器查詢並建立資源
protected Resource[] findAllClassPathResources(String location) throws IOException {
……
Set<Resource> result = doFindAllClassPathResources(path);
……
return result.toArray(new Resource[result.size()]);
}protected Set<Resource> doFindAllClassPathResources(String path) throws IOException {
ClassLoader cl = getClassLoader();
//採用ClassLoaer獲取資源
Enumeration<URL> resourceUrls = (cl != null ? cl.getResources(path) : ClassLoader.getSystemResources(path));
while (resourceUrls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = resourceUrls.nextElement();
//建立Resource
result.add(convertClassLoaderURL(url));
}
if ("".equals(path)) {
// The above result is likely to be incomplete, i.e. only containing file system references.
// We need to have pointers to each of the jar files on the classpath as well...
// 從jar中載入資源
addAllClassLoaderJarRoots(cl, result);
}
return result;
}protected Resource convertClassLoaderURL(URL url) {
return new UrlResource(url);
}protected void addAllClassLoaderJarRoots(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader, Set<Resource> result) {
if (classLoader instanceof URLClassLoader) {
try {
for (URL url : ((URLClassLoader) classLoader).getURLs()) {
try {
//建立Resource
UrlResource jarResource = new UrlResource(
ResourceUtils.JAR_URL_PREFIX + url.toString() + ResourceUtils.JAR_URL_SEPARATOR);
if (jarResource.exists()) {
result.add(jarResource);
}
}
……
}
}
……
}
if (classLoader == ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader()) {
// "java.class.path" manifest evaluation...
//從java.class.path載入資源
addClassPathManifestEntries(result);
}
if (classLoader != null) {
try {
// Hierarchy traversal...
//從父載入器中查詢資源
addAllClassLoaderJarRoots(classLoader.getParent(), result);
}
……
}
}protected void addClassPathManifestEntries(Set<Resource> result) {
try {
String javaClassPathProperty = System.getProperty("java.class.path");
for (String path : StringUtils.delimitedListToStringArray(
javaClassPathProperty, System.getProperty("path.separator"))) {
try {
File file = new File(path);
UrlResource jarResource = new UrlResource(ResourceUtils.JAR_URL_PREFIX +
ResourceUtils.FILE_URL_PREFIX + file.getAbsolutePath() +
ResourceUtils.JAR_URL_SEPARATOR);
if (jarResource.exists()) {
result.add(jarResource);
}
}
……
}
}
……
}case 3: 不以classpath*開始且路徑中含有萬用字元
return findPathMatchingResources(locationPattern);case 4: 不以classpath*開始且路徑中不含萬用字元
直接採用ClassLoader載入資源
// a single resource with the given name
return new Resource[] {getResourceLoader().getResource(locationPattern)};對classpath下的資源,相同名字的資源可能存在多個,如果使用”classpath*:”作為字首,表明需要找到classpath下所有該名字資源,因而需要呼叫findClassPathResources方法查詢classpath下所有該名稱的Resource,對非classpath下的資源,對於不存在模式字元的location,一般認為一個location對應一個資源,因而直接呼叫ResourceLoader.getResource()方法即可(對classpath下沒有以”classpath*:”開頭的location也適用)
無論是classpath還是classpath*都可以載入整個classpath下(包括jar包裡面)的資原始檔。classpath只會返回第一個匹配的資源,查詢路徑是優先在專案中查詢資原始檔,再查詢jar包。檔名字包含萬用字元資源,如果根目錄為"", classpath載入不到任何資源, 而classpath*則可以載入到classpath中可以匹配的目錄中的資源,但是不能載入到jar包中的資源4.2.5 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
預設將通過classpath進行載入返回ClassPathResource4.2.6 FileSystemXmlApplicationContext
將載入“configLocation”位置的資源,可以是相對路徑也可以是絕對路徑4.2.7 ServletContextResourcePatternResolver
重寫了父類的查詢邏輯,它使用ServletContext.getResourcePaths()方式來查詢引數目錄下的檔案,而不是File.listFiles()方法
protected Set<Resource> doFindPathMatchingFileResources(Resource rootDirResource, String subPattern)
throws IOException {
if (rootDirResource instanceof ServletContextResource) {
ServletContextResource scResource = (ServletContextResource) rootDirResource;
ServletContext sc = scResource.getServletContext();
String fullPattern = scResource.getPath() + subPattern;
Set<Resource> result = new LinkedHashSet<>(8);
doRetrieveMatchingServletContextResources(sc, fullPattern, scResource.getPath(), result);
return result;
}
else {
return super.doFindPathMatchingFileResources(rootDirResource, subPattern);
}
}protected void doRetrieveMatchingServletContextResources(
ServletContext servletContext, String fullPattern, String dir, Set<Resource> result)
throws IOException {
Set<String> candidates = servletContext.getResourcePaths(dir);
}5 Note
war/jar/zip中的資源如果使用resource.getFile()會丟擲FileNotFoundError.此時需要使用Resource.getInputStream()讀取資源。
6 參考
1. Spring原始碼
2.https://www.cnblogs.com/doit8791/p/5774743.html
3.https://yq.aliyun.com/articles/46894