SpringBoot整合Mybatis完整詳細版
記得剛接觸SpringBoot時,大吃一驚,世界上居然還有這麼省事的框架,立馬感嘆:SpringBoot是世界上最好的框架。哈哈!
後來進了新公司,用不到而且忙於任務,今天重溫一遍居然有些忘了,看來真是好記性不如爛筆頭。於是寫下本篇SpringBoot整合Mybatis的文章,做個筆記。
天也不早了,言歸正傳,開始
IDE:idea、DB:mysql
-
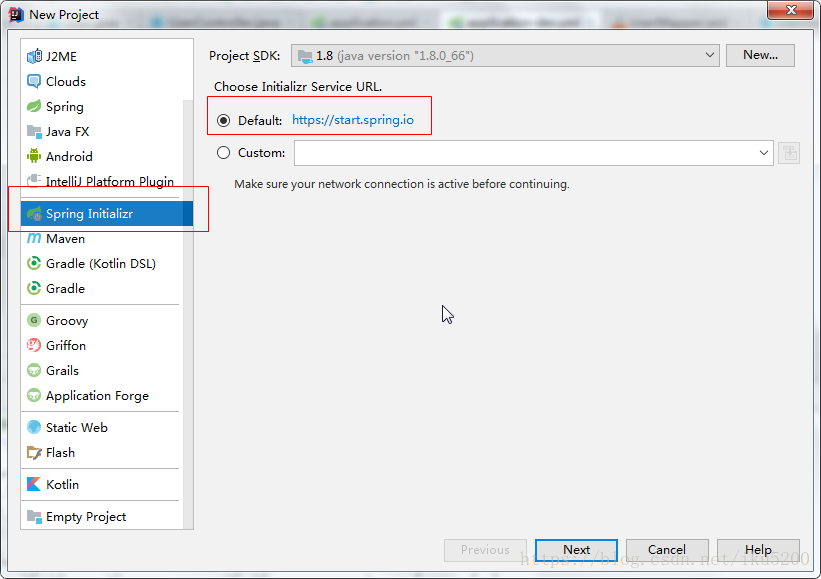
新建一個Spring Initializr專案
- 建立專案的檔案結構以及jdk的版本
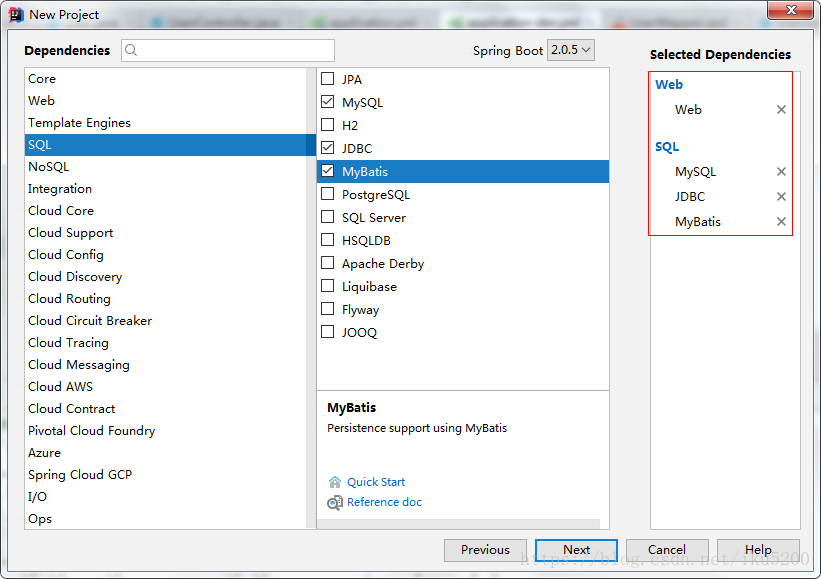
- 選擇專案所需要的依賴
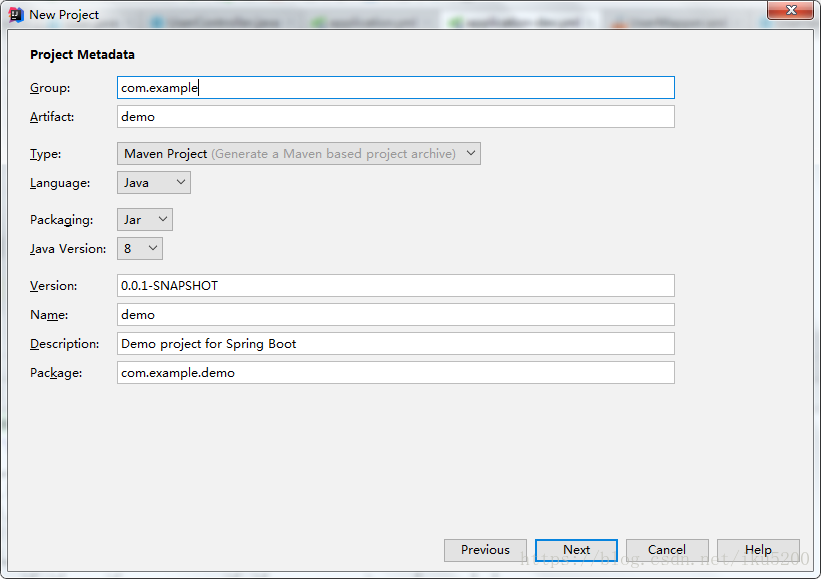
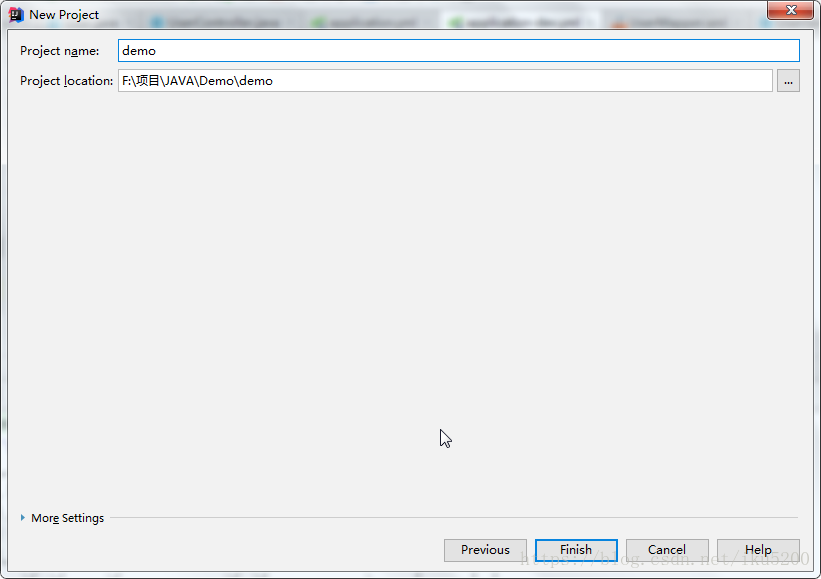
- 修改專案名,finish完成
- 來看下建好後的pom
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.example</groupId> <artifactId>demo</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <packaging>jar</packaging> <name>demo</name> <description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.0.5.RELEASE</version> <relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository --> </parent> <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding> <java.version>1.8</java.version> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>1.3.2</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <scope>runtime</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>
- 修改配置檔案
本文不使用application.properties檔案 而使用更加簡潔的application.yml檔案。將resource資料夾下原有的application.properties檔案刪除,建立application.yml配置檔案(備註:其實SpringBoot底層會把application.yml檔案解析為application.properties),本文建立了兩個yml檔案(application.yml和application-dev.yml),分別來看一下內容
application.yml
spring: profiles: active: dev
application-dev.yml
server: port: 8080 spring: datasource: username: root password: 1234 url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=true&serverTimezone=UTC driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver mybatis: mapper-locations: classpath:mapping/*Mapper.xml type-aliases-package: com.example.entity #showSql logging: level: com: example: mapper : debug
兩個檔案的意思是:
在專案中配置多套環境的配置方法。
因為現在一個專案有好多環境,開發環境,測試環境,準生產環境,生產環境,每個環境的引數不同,所以我們就可以把每個環境的引數配置到yml檔案中,這樣在想用哪個環境的時候只需要在主配置檔案中將用的配置檔案寫上就行如application.yml筆記:在Spring Boot中多環境配置檔名需要滿足application-{profile}.yml的格式,其中{profile}對應你的環境標識,比如:
application-dev.yml:開發環境
application-test.yml:測試環境
application-prod.yml:生產環境
至於哪個具體的配置檔案會被載入,需要在application.yml檔案中通過spring.profiles.active屬性來設定,其值對應{profile}值。
還有配置檔案中最好不要有中文註釋,會報錯。
接下來把啟動檔案移到com.example下,而且springboot的啟動類不能放在java目錄下!!!必須要個包將它包進去
否則會報錯誤:
Your ApplicationContext is unlikely to start due to a @ComponentScan of the default package.這個原因值得注意就是因為有時候很難在IDEA中的專案目錄認出來這個錯誤並且還容易掃描不到一些類,傳送門:SpringBoot掃描不到controller
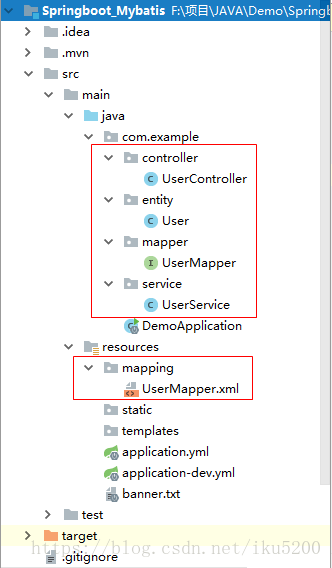
- 然後開始建立實體類實現業務流程
建立包controller、entity、mapper、service。resources下建立mapping資料夾,用於寫sql語句,也可以用註解的方式直接寫在mapper檔案裡。下面直接貼程式碼
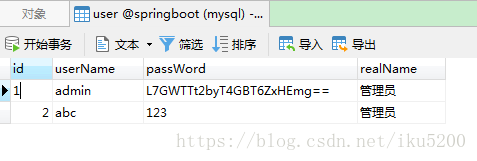
資料庫表結構(之前小專案的表,直接拿來用)
CREATE TABLE `user` (
`id` int(32) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`userName` varchar(32) NOT NULL,
`passWord` varchar(50) NOT NULL,
`realName` varchar(32) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=3 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;entity.java
package com.example.entity;
/**
* @Author:wjup
* @Date: 2018/9/26 0026
* @Time: 14:39
*/
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String userName;
private String passWord;
private String realName;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public String getPassWord() {
return passWord;
}
public void setPassWord(String passWord) {
this.passWord = passWord;
}
public String getRealName() {
return realName;
}
public void setRealName(String realName) {
this.realName = realName;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", userName='" + userName + '\'' +
", passWord='" + passWord + '\'' +
", realName='" + realName + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
UserController.java
package com.example.controller;
import com.example.entity.User;
import com.example.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @Author:wjup
* @Date: 2018/9/26 0026
* @Time: 14:42
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/testBoot")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
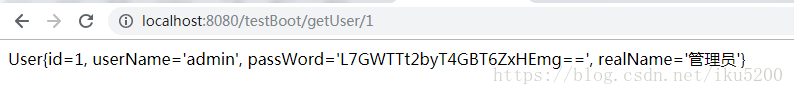
@RequestMapping("getUser/{id}")
public String GetUser(@PathVariable int id){
return userService.Sel(id).toString();
}
}
UserService.java
package com.example.service;
import com.example.entity.User;
import com.example.mapper.UserMapper;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @Author:wjup
* @Date: 2018/9/26 0026
* @Time: 15:23
*/
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
UserMapper userMapper;
public User Sel(int id){
return userMapper.Sel(id);
}
}
UserMapper.java
package com.example.mapper;
import com.example.entity.User;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
/**
* @Author:wjup
* @Date: 2018/9/26 0026
* @Time: 15:20
*/
@Repository
public interface UserMapper {
User Sel(int id);
}
UserMapping.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.example.mapper.UserMapper">
<resultMap id="BaseResultMap" type="com.example.entity.User">
<result column="id" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="id" />
<result column="userName" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="userName" />
<result column="passWord" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="passWord" />
<result column="realName" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="realName" />
</resultMap>
<select id="Sel" resultType="com.example.entity.User">
select * from user where id = #{id}
</select>
</mapper>
- 最終框架結構
- 完成以上,下面在啟動類里加上註解用於給出需要掃描的mapper檔案路徑@MapperScan("com.example.mapper")
package com.example;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@MapperScan("com.example.mapper") //掃描的mapper
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
測試成功,就這樣基本框架就搭建成功了
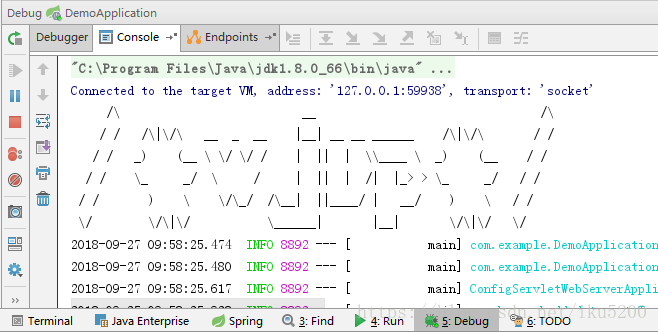
- 最後給個番外篇如何更改啟動時顯示的字元拼成的字母,就是更改下圖示紅框的地方
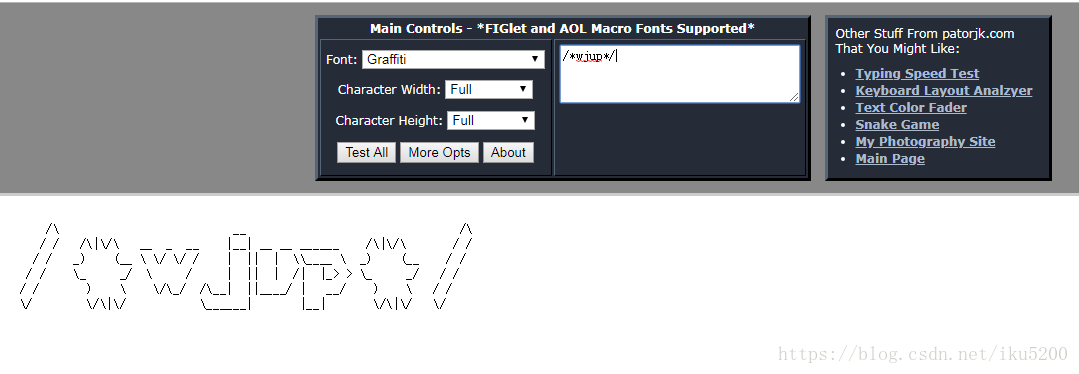
其實很好改,只需要在resources下新建一個txt檔案就可以,命名為banner.txt,那這種字元該怎麼拼出來呢,下面推薦一個網址,有這種工具,連結傳送門:字母轉字元。如下:
直接輸入要生成的字母,系統會自動轉換,然後複製下面轉換好的字元到新建的banner.txt檔案中,重新啟動專案就可以了。
---路漫漫其修遠兮,吾將上下而求索