python的元組、集合和字典
#################元組##################
# 元組: 帶了緊箍咒的列表;
不可變資料型別,沒有增刪改查;
可以儲存任意資料型別;
# 定義元組#
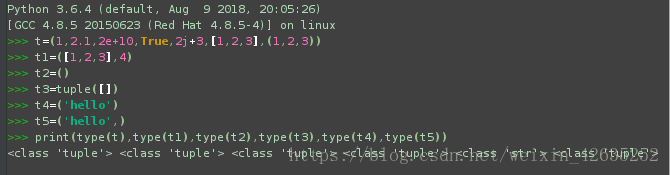
t = (1, 2.1, 2e+10, True, 2j+3, [1,2,3],(1,2,3) )
print(t, type(t))# 如果元組裡麵包含可變資料型別, 可以間接修改元組內容;
t1 = ([1,2,3], 4)
t1[0].append(4)
print(t1)
t2 = ()
t3 = tuple([]) #定義一個空元組
# 元組如果只有一個元素, 後面一定要加逗號, 否則資料型別不確定;
t4 = ('hello')
t5 = ('hello',)
print(type(t2), type(t3), type(t4), type(t5))
#元組的特性#
# 索引, 切片, 重複, 連線, 成員操作符
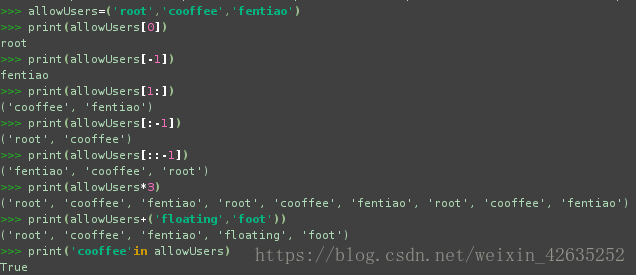
allowUsers=('root','cooffee','fentiao')
print(allowUsers[0])
print(allowUsers[-1])
print(allowUsers[1:])
print(allowUsers[:-1])
print(allowUsers[::-1])
print(allowUsers*3)
print(allowUsers+('floating','foot'))
print('cooffee'in allowUsers)
#for迴圈#
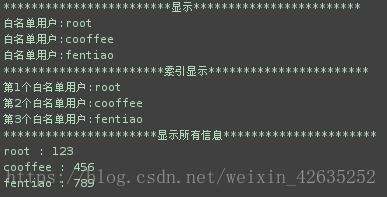
allowUsers = ('root', 'cooffee', 'fentiao') allowPasswd = ('123', '456', '789') print("顯示".center(50,'*')) for user in allowUsers: #for迴圈依次遍歷 print("白名單使用者:%s" %(user)) print("索引顯示".center(50,'*')) for index,user in enumerate(allowUsers): #for迴圈並且求索引(列舉) print("第%d個白名單使用者:%s" %(index+1,user)) print("顯示所有資訊".center(50,'*')) for user,passwd in zip(allowUsers,allowPasswd): #zip: 集和使用者名稱和密碼兩個元組, 元素之間一一對應 print(user,':',passwd)
#元組的常用方法#
• t.count(value)-->int
返回value在元組中出現的次數;
• t.index(value)
返回value在元組中的偏移量(即索引值)
#元組的應用場景#
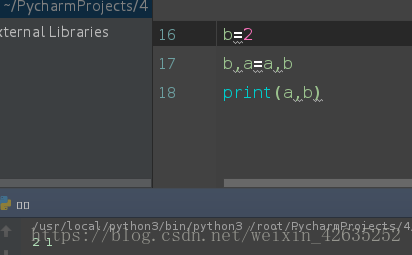
1. 變數交換數值:
a = 1
b = 2b,a = a,b
#先把(a,b)封裝成一個元組, (1,2)
#b,a = a,b ======> b,a =(1,2)
# b = (1,2)[0], a=(1,2)[1]
print(a,b)
2.列印變數值
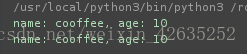
name = 'cooffee'
age = 10
t = (name, age)
print("name: %s, age: %d" %(name, age))
print("name: %s, age: %d" %t)
3.元組的賦值: 有多少個元素, 就用多少個變數接收
t = ('cooffee', 10, 100)
name, age,score = t
print(name, age, score)
4.先對元組進行排序
scores = (100, 89, 45, 78, 65)
# scoresLi = list(scores)
# scoresLi.sort()
# print(scoresLi)
scores = sorted(scores) #注意這是一個列表
5.python3中可以用*middleScore接收中間的元素
#去掉一個最高分和最低分求平均分
scores = (100, 89, 45, 78, 65)
scores = sorted(scores)
minScore, *middleScore, maxScore = scores
print(minScore, middleScore, maxScore)
print("最終成績為: %.2f" %(sum(middleScore)/len(middleScore)))
#################集合###################
# 集合裡面的元素是不可重複的;
# 集合應用1: 列表去重
s = {1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3}
print(s, type(s))
li = [1,2,3,1,2,3]
print(list(set(li)))
#集合的定義
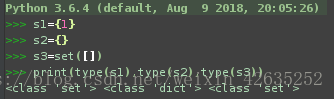
s1={1}
s2={} #是字典
s3=set([])
print(type(s1),type(s2),type(s3))
#集合的特性#
# 索引, 切片, 重複, 連線, 成員操作符
# 集合支援的特性只有 成員操作符, 索引, 切片, 重複, 連線,均不支援;
# for迴圈#
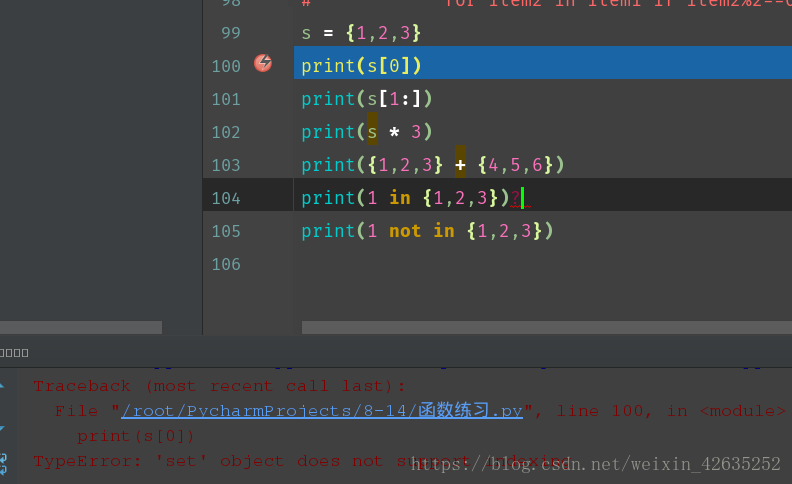
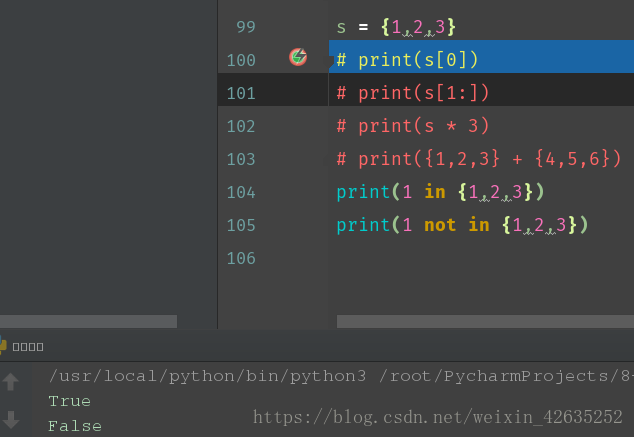
s={1,2,3}
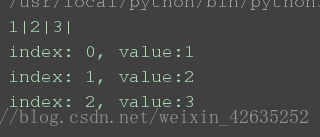
for i in s:
print(i, end='|')print()
for i, v in enumerate(s): #for迴圈並且求索引(列舉)
print("index: %s, value:%s" %(i, v))
#集合常用方法#
# 增加:
可變, 無序資料型別
新增的順序, 和在集合中儲存的順序不同;
s={3,2,4}
s.add(1)
print(s)
s.update({7,8,9}) # # 增加多個元素
print(s)
# # 刪除
s.remove(2) # # 刪除指定的元素
print(s)s.pop()
print(s)
# 交集, 並集, 差集
s1 = {1, 2, 3}
s2 = {2, 3, 4}# 並集
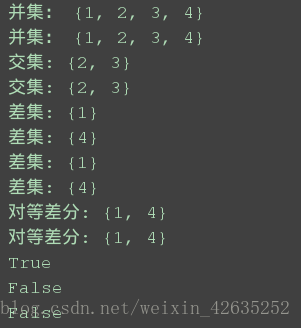
print("並集:", s1.union(s2))
print("並集:", s1 | s2)# 交集
print("交集:", s1.intersection(s2))
print("交集:", s1 & s2)# 差集
print("差集:", s1.difference(s2)) # s1- (s1&s2)
print("差集:", s2.difference(s1)) # s2- (s1&s2)
print("差集:",s1-s2)
print("差集:",s2-s1)
# 對等差分: 並集-交集
print("對等差分:", s1.symmetric_difference((s2)))
print("對等差分:", s1^s2)#子集和父集關係
s3 = {1,2}
s4 = {1,2,3}
print(s3.issubset(s4)) #s3是s4子集
print(s3.issuperset(s4)) #父集
print(s3.isdisjoint(s4)) #s3和s4沒有交集
###########字典############
#字典: key-value值, 鍵值對;
value值可以是任意資料型別: int,float,long, complex, list, tuple,set, dict
#定義字典:
- 定義空字典, {}, dict()
- 賦值: d = {'key':'value', 'key1':'value1'}
- 初始化所有value值: fromkeys()
- 根據已有的資料建立字典:
s={} #定義空字典
print(type(s))
s1=dict() #定義空字典
print(type(s1))
s2={'cooffee':[18,'happy'],'floating':[18,'sad']}
print(s2,type(s2))
s3=[1,2,3,4,5]
print({}.fromkeys(s3)) #fromkeys第一個引數可以列表/tuple/str/set, 將列表的每一個元素作為字典的key值,
print({}.fromkeys(s3,'666')) 第二個引數是key的value值,若無定義為None
# 字典的巢狀;
students = {
'13021001': {
'name':'張龍',
'age':18,
'score':100
},
'13021003': {
'name': '張',
'age': 18,
'score': 90
}
}print(students['13021001']['name'])
#工廠函式
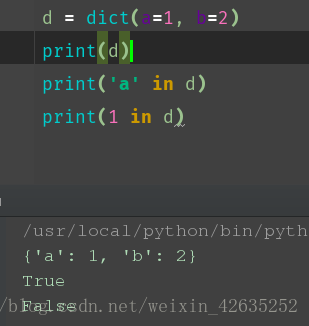
d5 = dict(a=1, b=2)
print(d5)
#字典的特性#
# 索引, 切片, 重複, 連線, 成員操作符
字典沒有索引,切片,重複,連線 , 成員操作符, 預設判斷key值是否存在.
d = dict(a=1, b=2)
print(d)
print('a' in d)
print(1 in d)
#for迴圈: 預設遍歷字典的key值;
d=dict(a=1,b=2)
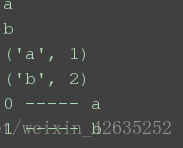
d = dict(a=1, b=2) for i in d: print(i) for i in d.items(): #可用次方法遍歷得到value print(i) for i,v in enumerate(d): print(i, '-----', v) #列舉可求value
#字典的增刪改查#
1.增加
d = dict(a=1, b=2,c=3,d=4)
# 新增或者更改key-value對
d['g'] = 10
d['a'] = 10
print(d)
# # update:
# 如果key值已經存在, 更新value值;
# 如果key值不存在, 新增key-value值;
d.update({'c':4, 'f':1})
print(d)
# # setdefault
# 如果key值已經存在, 不做修改;
# 如果key值不存在, 新增key-value值;預設情況下value值為None
d.setdefault('k', 10)
d.setdefault('d',12)
print(d)
2.刪除
d = dict(a=1, b=2, c=3,d=4)
# pop:彈出指定key-value值
d.pop('a')
print(d)
# popitem
d.popitem()
print(d)
del d['c']
print(d)
d.clear()
print(d)
3.修改與檢視
#檢視
services = {
'http':80,
'mysql':3306
}
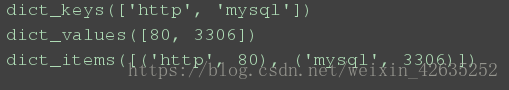
# 檢視字典裡面所有的key值
print(services.keys())# 檢視字典裡面所有的value值
print(services.values())# 檢視字典裡面所有的key-value值
print(services.items())
# 遍歷
services = {
'http':80,
'mysql':3306
}
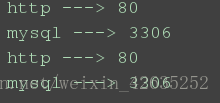
for k,v in services.items(): # k,v = ('http', 80)
print(k , '--->', v)
for k in services:
print(k, '--->', services[k])
# 檢視指定key對應的value值, 注意: key不存在, 就會報錯
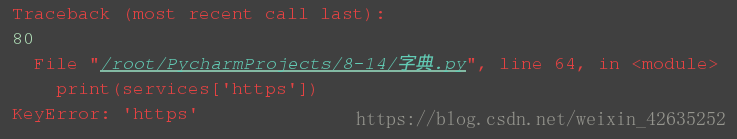
services = { 'http':80, 'mysql':3306 }
print(services['http'])
# print(services['https']) ##會報錯
# get方法獲取指定可以對應的value值
如果key值存在, 返回對應的value值;
如果key值不存在, 預設返回None, 如果需要指定返回的值, 傳值即可;
services = { 'http':80, 'mysql':3306 }
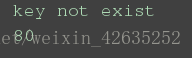
print(services.get('https', 'key not exist')) print(services.get('http'))
##########知識拓展############
#可變與不可變資料型別#
判別方法:該資料型別是否可以增刪改查
# 可變資料型別:list, set, dict
# 不可變: 數值型別, str, tuple,數值,bool
#有序與無序資料型別
有序:str,list,tuple
無序:數值,bool,set
python2:dict無序 python3:dict有序
#列表的去重#
# 1. 列表去重:轉換為集合
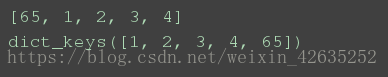
li = [1, 2, 3, 4, 65, 1, 2, 3]
print(list(set(li)))
# 2. 通過字典的方式去重
# ** 字典的key值是不能重複的.
li = [1, 2, 3, 4, 65, 1, 2, 3]
print({}.fromkeys(li).keys())
#python裡面實現switch語句#
python裡面是不支援switch語句的
C++:
char grade = 'B'
switch(grade)
{
case 'A':
print('')
break
case 'B':
print('')
break
default:
print('error')
}
"""
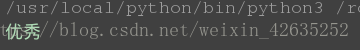
grade = 'A' d = { 'A': '優秀', 'B':'良好', 'C':"及格" } print(d.get(grade, "無效的成績"))