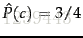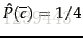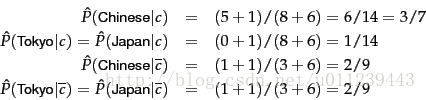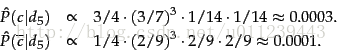深入理解Spark ML:多項式樸素貝葉斯原理與原始碼分析
貝葉斯估計
如果一個給定的類和特徵值在訓練集中沒有一起出現過,那麼基於頻率的估計下該概率將為0。這將是一個問題。因為與其他概率相乘時將會把其他概率的資訊統統去除。所以常常要求要對每個小類樣本的概率估計進行修正,以保證不會出現有為0的概率出現。常用到的平滑就是加1平滑(也稱拉普拉斯平滑):
lambda>=0,等價於在隨機變數各個取值的頻數上賦予一個正數lambda>0。
同樣的:
N為資料條數,K為label類別數。
多項式樸素貝葉斯
多項式樸素貝葉斯和上述貝葉斯模型不同的是,上述貝葉斯模型對於某特徵的不同取值代表著不同的類別,而多項式樸素貝葉斯對於某特徵的不同取值代表著該特徵決定該label類別的重要程度。
比如一個文字中,單詞Chinese出現的頻數,1次還是10次,並不代表著Chinese單詞這個特徵的類別,而代表著Chinese單詞這個特徵的決定該文字label類別的重要程度。
n為特徵維度數
我們來舉個例子:
我們設lambda為1,共有6個不同的單詞,則特徵維度數為6。
所以,我們將d5 分類到 yes
API 使用
下面是Spark 樸素貝葉斯的使用例子:
import org.apache.spark.ml.classification.NaiveBayes
// 載入資料
val data = spark.read.format("libsvm" 原始碼分析
接下來我們來分析下原始碼~
NaiveBayes
train
NaiveBayes().fit呼叫NaiveBayes的父類Predictor中的fit,將label和weight轉為Double,儲存label和weight原資訊,最後呼叫NaiveBayes的train:
override protected def train(dataset: Dataset[_]): NaiveBayesModel = {
trainWithLabelCheck(dataset, positiveLabel = true)
}trainWithLabelCheck:
ml假設輸入labels範圍在[0, numClasses). 但是這個實現也被mllib NaiveBayes呼叫,它允許其他型別的輸入labels如{-1, +1}. positiveLabel 用於確定label是否需要被檢查。
private[spark] def trainWithLabelCheck(
dataset: Dataset[_],
positiveLabel: Boolean): NaiveBayesModel = {
//檢測label
if (positiveLabel && isDefined(thresholds)) {
val numClasses = getNumClasses(dataset)
require($(thresholds).length == numClasses, this.getClass.getSimpleName +
".train() called with non-matching numClasses and thresholds.length." +
s" numClasses=$numClasses, but thresholds has length ${$(thresholds).length}")
}
//模型型別 多項式樸素貝葉斯是 Multinomial
val modelTypeValue = $(modelType)
val requireValues: Vector => Unit = {
modelTypeValue match {
case Multinomial =>
// 確認所有的值非負
// values.forall(_ >= 0.0)
requireNonnegativeValues
......
}
}
// Instrumentation 是 一個小封裝,用來定義為一個estimator定義一個training session和該session中有學用的資訊的log方法
val instr = Instrumentation.create(this, dataset)
instr.logParams(labelCol, featuresCol, weightCol, predictionCol, rawPredictionCol,
probabilityCol, modelType, smoothing, thresholds)
// 得到特徵維度數,即公式中的 n
val numFeatures = dataset.select(col($(featuresCol))).head().getAs[Vector](0).size
instr.logNumFeatures(numFeatures)
// 得到記錄的權重 為設定 預設為 1.0
val w = if (!isDefined(weightCol) || $(weightCol).isEmpty) lit(1.0) else col($(weightCol))
// 聚合
val aggregated = dataset.select(col($(labelCol)), w, col($(featuresCol))).rdd
.map { row => (row.getDouble(0), (row.getDouble(1), row.getAs[Vector](2)))
// 根據key labelCol 進行聚合
// value 的初始值為 0.0,Vectors.zeros(numFeatures).toDense
}.aggregateByKey[(Double, DenseVector)]((0.0, Vectors.zeros(numFeatures).toDense))(
// 合併在同一