【Java】——自定義註解對引數進行校驗、spring掃描自定義註解
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-02-04
前提
上篇部落格中詳細介紹自定義註解的使用,本文主要是對自定義註解的進一步深入。會使用CGLIb進行動態代理來完成對方法引數是否為空的判斷,以及再spring中如何掃描自定義註解
自定義註解對方法引數為空校驗
為什麼要用動態代理?
因為Java的反射拿不到引數的相關資訊,對方法引數進行校驗,肯定是要在方法執行前進行校驗,所以就需要動態代理來完成。對真實的物件進行代理,讓代理物件執行引數校驗這一部分的操作。
1、自定義註解
@Target({ElementType.FIELD,ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.PARAMETER}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface MyAnnotation { String msg() default "引數不能為空"; }
2、代理類以及校驗方法
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.Enhancer; import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor; import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.lang.reflect.Parameter; public class HelloServiceCgLib implements MethodInterceptor { private Class target; public Object getInstance(Class target) { this.target = target; Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer(); enhancer.setSuperclass(this.target); enhancer.setCallback(this); return enhancer.create(); } @Override public Object intercept(Object object, Method method, Object[] objects, MethodProxy proxy) throws Throwable { System.out.println("我是CGLIB的動態代理"); System.out.println("我準備執行了"); if (!check(method,objects)) { System.out.println("我沒能成功執行"); return false; } Object returnObj = proxy.invokeSuper(object, objects); System.out.println("我已經正確執行過了"); return returnObj; } /** * 對引數校驗的方法 * @param method 目標方法 * @param objects 相關引數值 * @return */ public boolean check(Method method,Object[] objects) { Parameter[] parameters = method.getParameters(); for (int i = 0; i <parameters.length; i++) { Parameter parameter = parameters[i]; if (parameter.isAnnotationPresent(MyAnnotation.class)) { MyAnnotation annotation = parameter.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class); if (objects==null ||objects[i]==null) { System.out.println(parameter.getName()+annotation.msg()); return false; } } } return true; } }
3、真實類
public class Hello {
public void sayHello(@MyAnnotation String name,@MyAnnotation String start) {
System.out.println("hello "+name);
System.out.println(start);
}
}4、呼叫過程
public class AnnotationTest { public static void main(String[] args) { HelloServiceCgLib helloServiceCgLib = new HelloServiceCgLib(); Hello proxy = (Hello) helloServiceCgLib.getInstance(Hello.class); proxy.sayHello("world",null); }
5、執行結果
對第二個引數進行攔截,判斷為空,阻止方法的非正常執行。
spring掃描自定義註解
在使用Spring的時候需要自定義annotation來滿足專案需求。
在Bean初始化的過程都會呼叫BeanPostProcessor介面即Spring中的後置處理器,這個介面是Spring IOC容器給我們提供擴充套件介面,方便在Spring容器中完成bean例項化,配置以及其他初始化方法前後新增一些自己處理的邏輯。
在bean建立好之後都會呼叫後置處理器的postProcessAfterInitialization方法,所以可以利用自定義這個方法,達到讓spring掃描自定義註解的目的。
1、自定義註解
@Target({ElementType.FIELD,ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.PARAMETER})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyListener {
String value() default "spring";
}2、配置spring掃描
@Component
public class MyListenerProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
Method[] methods = ReflectionUtils.getAllDeclaredMethods(bean.getClass());
if (methods != null) {
for (Method method : methods) {
MyListener myListener = AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(method, MyListener.class);
// process
if (myListener != null) {
System.out.println(method.getName());
System.out.println(myListener.value());
}
}
}
return bean;
}
}
3、配置要掃描的方法
@Service
public class MyService {
@MyListener
public void onMessage() {
System.out.println("我被呼叫了");
}
}
4、初始化,判斷spring是否正確掃描註解
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Config.class);
MyService bean = ac.getBean(MyService.class);}
}
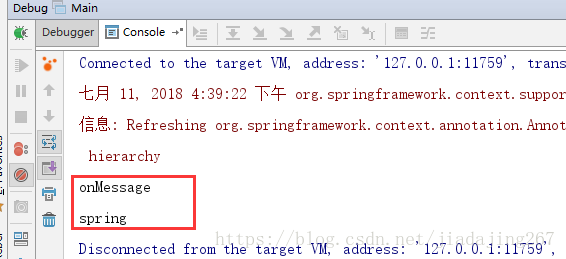
5、註解被spring掃描到了
總結
通過對自定義註解的使用可以很好加深對動態代理這些概念的認識,對spring框架的理解同樣可以更進一步。