sklearn之樣本生成(2)
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-02-04
上一篇《sklearn之樣本生成(1)》主要講make_blobs的使用方法。本文重點講make_classification,make_gaussian_quantiles、make_hastie_10_2、make_circles和make_moons
1)make_classification
通常用於分類演算法。sklearn.datasets.make_classification(n_samples=100, n_features=20, n_informative=2, n_redundant=2, n_repeated=0, n_classes=2, n_clusters_per_class=2, weights=None, flip_y=0.01, class_sep=1.0, hypercube=True,shift=0.0, scale=1.0, shuffle=True, random_state=None)
n_features :特徵個數= n_informative() + n_redundant + n_repeated
n_informative:多資訊特徵的個數
n_redundant:冗餘資訊,informative特徵的隨機線性組合
n_repeated :重複資訊,隨機提取n_informative和n_redundant 特徵
n_classes:分類類別
n_clusters_per_class :某一個類別是由幾個cluster構成的
2)make_gaussian_quantiles 和make_hastie_10_2
利用高斯分位點區分不同資料sklearn.datasets.make_gaussian_quantiles(mean=None, cov=1.0, n_samples=100, n_features=2, n_classes=3, shuffle=True, random_state=None)
sklearn.datasets.make_hastie_10_2(n_samples=12000, random_state=None)程式碼
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn.datasets import make_classification from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs from sklearn.datasets import make_gaussian_quantiles from sklearn.datasets import make_hastie_10_2 plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8)) plt.subplots_adjust(bottom=.05, top=.9, left=.05, right=.95) plt.subplot(421) plt.title("One informative feature, one cluster per class", fontsize='small') X1, Y1 = make_classification(n_samples=1000,n_features=2, n_redundant=0, n_informative=1, n_clusters_per_class=1) plt.scatter(X1[:, 0], X1[:, 1], marker='o', c=Y1) plt.subplot(422) plt.title("Two informative features, one cluster per class", fontsize='small') X1, Y1 = make_classification(n_samples=1000,n_features=2, n_redundant=0, n_informative=2, n_clusters_per_class=1) plt.scatter(X1[:, 0], X1[:, 1], marker='o', c=Y1) plt.subplot(423) plt.title("Two informative features, two clusters per class", fontsize='small') X2, Y2 = make_classification(n_samples=1000,n_features=2, n_redundant=0, n_informative=2) plt.scatter(X2[:, 0], X2[:, 1], marker='o', c=Y2) plt.subplot(424) plt.title("Multi-class, two informative features, one cluster", fontsize='small') X1, Y1 = make_classification(n_samples=1000,n_features=2, n_redundant=0, n_informative=2, n_clusters_per_class=1, n_classes=3) plt.scatter(X1[:, 0], X1[:, 1], marker='o', c=Y1) plt.subplot(425) plt.title("Three blobs", fontsize='small') X1, Y1 = make_blobs(n_samples=1000,n_features=2, centers=3) plt.scatter(X1[:, 0], X1[:, 1], marker='o', c=Y1) plt.subplot(426) plt.title("Gaussian divided into four quantiles", fontsize='small') X1, Y1 = make_gaussian_quantiles(n_samples=1000,n_features=2, n_classes=4) plt.scatter(X1[:, 0], X1[:, 1], marker='o', c=Y1) plt.subplot(427) plt.title("hastie data ", fontsize='small') X1, Y1 = make_hastie_10_2(n_samples=1000) plt.scatter(X1[:, 0], X1[:, 1], marker='o', c=Y1) plt.show()

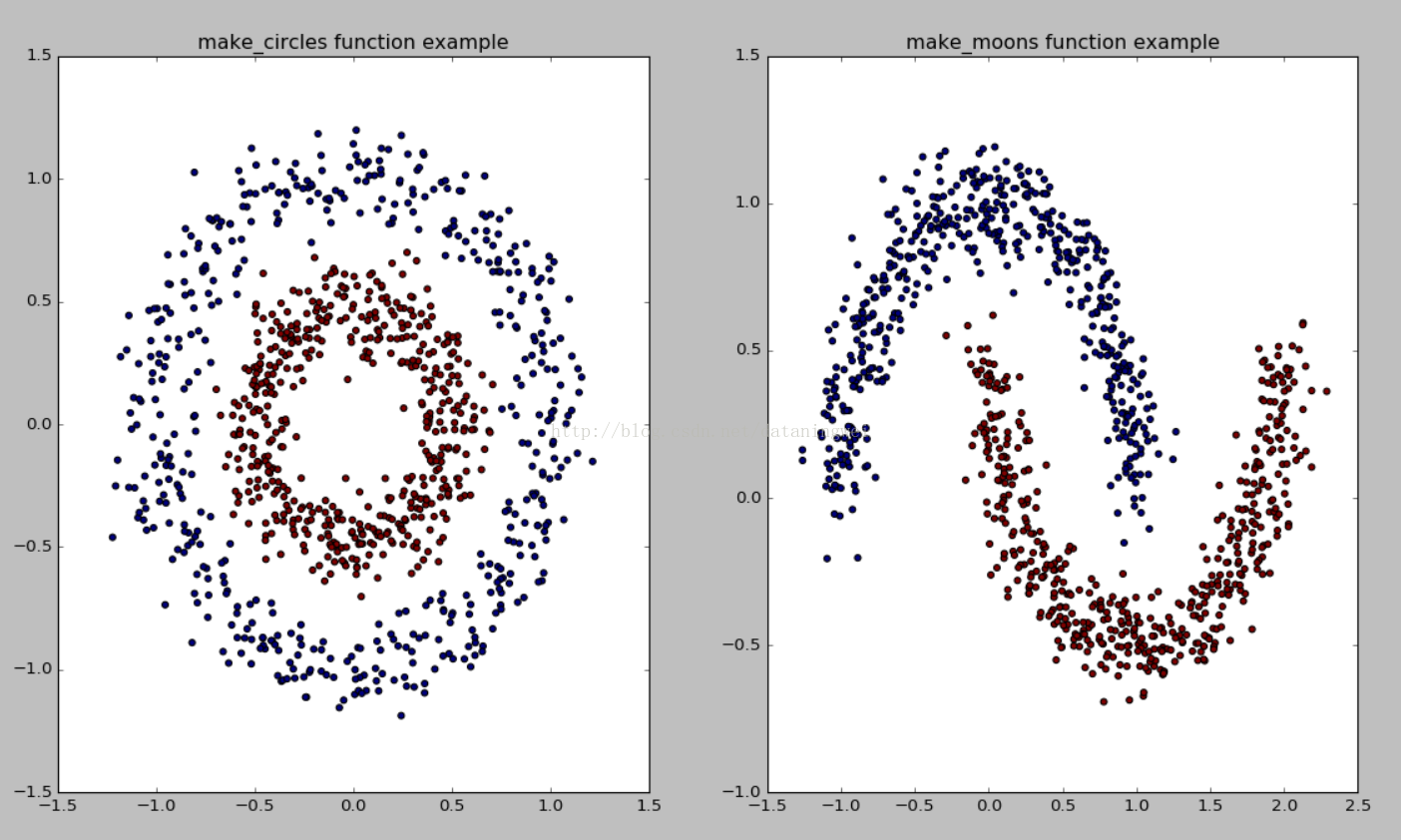
3)make_circles and make_moons
sklearn.datasets.make_circles(n_samples=100, shuffle=True, noise=None, random_state=None, factor=0.8)factor :外圈與內圈的尺度因子<1
sklearn.datasets.make_moons(n_samples=100, shuffle=True, noise=None, random_state=None)from sklearn.datasets import make_circles
from sklearn.datasets import make_moons
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
fig=plt.figure(1)
x1,y1=make_circles(n_samples=1000,factor=0.5,noise=0.1)
plt.subplot(121)
plt.title('make_circles function example')
plt.scatter(x1[:,0],x1[:,1],marker='o',c=y1)
plt.subplot(122)
x1,y1=make_moons(n_samples=1000,noise=0.1)
plt.title('make_moons function example')
plt.scatter(x1[:,0],x1[:,1],marker='o',c=y1)
plt.show()