【原始碼學習】STL原始碼學習----lower_bound和upper_bound演算法
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-02-04
STL原始碼學習----lower_bound和upper_bound演算法
ForwardIter lower_bound(ForwardIterfirst, ForwardIterlast,const _Tp& val)返回一個非遞減序列[first, last)中的第一個大於等於值val的位置。
ForwardIter upper_bound(ForwardIter first, ForwardIterlast, const _Tp&val)返回一個非遞減序列[first, last)中第一個大於val的位置。
lower_bound和upper_bound如下圖所示:
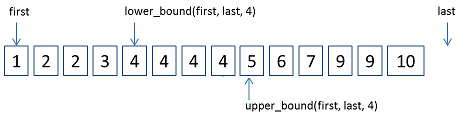
1, lower_bound
這個序列中可能會有很多重複的元素,也可能所有的元素都相同,為了充分考慮這種邊界條件,STL中的lower_bound演算法總體上是才用了二分查詢的方法,但是由於是查詢序列中的第一個出現的值大於等於val的位置,所以演算法要在二分查詢的基礎上做一些細微的改動。
首先是我修改資料結構課本上的二分查詢實現的lower_bound演算法:

int my_lower_bound(int *array, int size, int key)
{
int first = 0, last = size;
int middle, pos=0; //需要用pos記錄第一個大於等於key的元素位置 
STL中的實現比較精巧,下面貼出原始碼:

//這個演算法中,first是最終要返回的位置
int lower_bound(int *array, int size, int key)
{
int first = 0, middle;
int half, len;
len = size;
while(len > 0) {
half = len >> 1;
middle = first + half;
if(array[middle] < key) {
first = middle + 1;
len = len-half-1; //在右邊子序列中查詢
}
else
len = half; //在左邊子序列(包含middle)中查詢
}
return first;
}
2, upper_bound
upper_bound返回的是最後一個大於等於val的位置,也是有一個新元素val進來時的插入位置。
我依然將二分查詢略做修改:

int my_upper_bound(int *array, int size, int key)
{
int first = 0, last = size;
int middle, pos = 0;
while(first < last)
{
middle = (first+last)/2;
if(array[middle] > key){ //當中位數大於key時,last不動,讓first不斷逼近last
last = middle;
pos = last;
}
else{
first = middle + 1; //當中位數小於等於key時,將first遞增,並記錄新的位置
pos = first;
}
}
return pos;
}
下面的程式碼是STL中的upper_bound實現:

int upper_bound(int *array, int size, int key)
{
int first = 0, len = size-1;
int half, middle;
while(len > 0){
half = len >> 1;
middle = first + half;
if(array[middle] > key) //中位數大於key,在包含last的左半邊序列中查詢。
len = half;
else{
first = middle + 1; //中位數小於等於key,在右半邊序列中查詢。
len = len - half - 1;
}
}
return first;
}
lower_bound和upper_bound用法示例
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int a[15];
int main() {
int t;
cin>>t;
while (t--) {
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cin>>a[i];}
int kk = lower_bound(a, a + n + 1, 2)-a; //序列的長度是n+1,在[a,a+n+1)中找出大於等於2的位置,這個位置是從0開始的。
cout<<"未排序序列中 大於等於2的位置:"<<kk+1<<endl;
sort(a, a + n); //第一個
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cout<<a[i]<<" ";}
cout<<endl;
int kk2 = lower_bound(a, a + n + 1, 2)-a; //序列的長度是n+1,在[a,a+n+1)中找出大於等於2的位置,這個位置是從0開始的。
cout<<"排好序序列中 大於等於2的位置:"<<kk2+1<<endl;
return 0;
}
}
