SpringMVC攔截器原始碼解析
前言:提到攔截器,我們一定會想到Spring Aop。在看SpringMVC原始碼以前,一直以為SpringMVC的攔截器是用Spring Aop的動態代理來實現,並且也很困惑,如果用動態代理如何實現攔截器?這裡就不介紹Spring Aop實現攔截器的方式,剖析SpringMVC 攔截器實現的細節。
SpringMVC攔截器也是Aop(面向切面)思想構建,但不是SpringAop動態代理實現的,主要採用責任鏈和介面卡的設計模式來實現,直接嵌入到SpringMVC入口程式碼裡面。
涉及到設計模式,有利於對程式碼的理解
一、攔截器的介面類結構
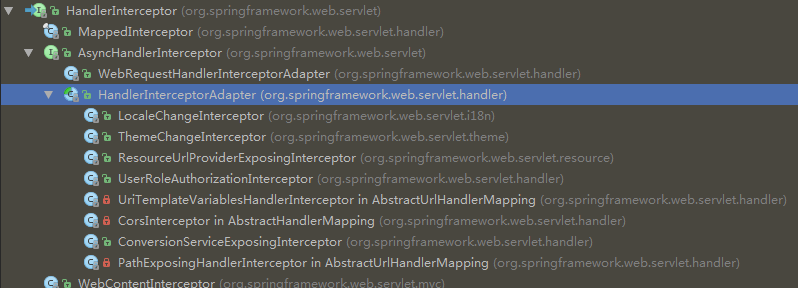
攔截器的頂級介面為HandleInterceptor,提供三個介面,分別是preHandle(請求前)、postHandle(請求提交)、afterCompletion(請求完成後攔截)
package org.springframework.web.servlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.web.method.HandlerMethod;
/**
* 攔截器頂級介面
*/
public interface HandlerInterceptor {
//請求前攔截
boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) 而我們通常使用的是HandlerInterceptorAdapter(攔截器介面卡),運用介面介面卡模式。在實際運用中,介面中可以定義了很多方法,子類可能實現幾個方法,介面介面卡模式就起到了作用。
package org.springframework.web.servlet.handler;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.AsyncHandlerInterceptor;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
public abstract class HandlerInterceptorAdapter implements AsyncHandlerInterceptor {
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
return true;
}
@Override
public void postHandle(
HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView)
throws Exception {
}
@Override
public void afterCompletion(
HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex)
throws Exception {
}
/**
* This implementation is empty.
* 來自實現AsyncHandlerInterceptor 的方法
*/
@Override
public void afterConcurrentHandlingStarted(
HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
}
}二、攔截器原始碼執行的呼叫流程
1. HandlerMapping初始化
瞭解到SpringMVC攔截器介面HandlerInterceptorAdapter,我們再進入SpringMVC請求入口org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet,攔截器運作工作流程由此展開。DispatcherServlet作為控制中心,攔截器就嵌入在入口方法中doDispatch中。SpringMVC又是如何將定義的攔截器加入進去呢?
/**
* 完成Servlet一系列初始化工作,包括檢視解析器、處理器對映器、處理器介面卡、主題解析器...
*/
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
initMultipartResolver(context);
initLocaleResolver(context);
initThemeResolver(context);
// 初始化RequestMapping,攔截器是作用在RequestMapping
initHandlerMappings(context);
initHandlerAdapters(context);
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
initViewResolvers(context);
initFlashMapManager(context);
}初始化RequestMapping的時候,獲取到RequestMapping的集合,因為攔截器作用在單個RequestMapping,來實現攔截器鏈。這裡就不詳細介紹RequestMapping的獲取。
2. DispatcherServlet執行呼叫,doService作為Servlet主要執行者,通過呼叫doDispatch來真正執行請求處理
在initStrategies(ApplicationContext context)完成初始化準備工作後,來正式進入DispatcherServlet請求進入的處理過程。DispatcherServlet基於Servlet開發,它的執行方式是 doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
/**
* doService做了一部分請求準備預處理的工作, 而實際處理的工作呼叫doDispatch(request, response)
*/
@Override
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
String resumed = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).hasConcurrentResult() ? " resumed" : "";
logger.debug("DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'" + resumed +
" processing " + request.getMethod() + " request for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "]");
}
// 對請求屬性快照的保持和儲存後的使用,
Map<String, Object> attributesSnapshot = null;
if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) {
attributesSnapshot = new HashMap<String, Object>();
Enumeration<?> attrNames = request.getAttributeNames();
while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement();
if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PREFIX)) {
attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName));
}
}
}
//對SpringMVC框架中處理器Handle和檢視渲染,提前做準備工作
request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext());
request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource());
// FlashMap是對重定向的引數傳遞的處理
FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response);
if (inputFlashMap != null) {
request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap));
}
request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap());
request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager);
try {
//***請求的實際處理邏輯***-----進入方法
doDispatch(request, response);
}
finally {
if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include.
if (attributesSnapshot != null) {
restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot);
}
}
}
}3. doDispatch中完成攔截器的新增和攔截器攔截處理
doService做了一部分請求準備預處理的工作,包括請求中設定處理器和檢視的屬性,作用於後續處理器的運作和檢視渲染, 而實際請求邏輯處理的工作呼叫doDispatch(request, response),也是我們需要重點跟進的程式碼。或許大家初次看doDispatch方法中的程式碼,還不知道攔截器在哪裡運作。
處理流程是:
- 通過getHandler(HttpServletRequest request)獲取到HandlerExecutionChain處理器執行鏈,將攔截器注入到HandlerExecutionChain屬性
- 分別呼叫HandlerExecutionChain的三個方法,applyPreHandle、applyPostHandle、triggerAfterCompletion,實現前置攔截/請求提交攔截和請求完成後攔截。使用責任鏈的設計模式,實際呼叫的是HandleInterceptor的三個介面,分別對應preHandle、postHandle、afterCompletion
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
//***獲取到請求執行鏈,攔截器的新增在裡面完成***---進入方法
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null || mappedHandler.getHandler() == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// 獲取到相應處理器介面卡
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "] is: " + lastModified);
}
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
//1.請求前攔截處理---進入方法細看(責任鏈模式,呼叫攔截器鏈的執行)
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// Actually invoke the handler.
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
//2.請求提交的攔截處理---進入方法細看(責任鏈模式,呼叫攔截器鏈的執行)
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
// 3.請求結果檢視渲染完成後,呼叫mappedHandler.triggerAfterCompletion(),實現請求完成後攔截
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}三、結合責任鏈設計在攔截器中的運用
責任鏈模式的定義:使多個物件都有機會處理請求,從而避免請求的傳送者和接受者之間的耦合關係, 將這個物件連成一條鏈,並沿著這條鏈傳遞該請求,直到有一個物件處理他為止。
分析 1、如何將攔截器新增到HandlerExecutionChain中
首先遍歷HandlerMappings集合,HandlerMappings是在initHandlerMappings(context)初始化得到。根據request查詢到相應 HandlerMapping的HandlerExecutionChain。
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
//遍歷處理器對映器集合,找到相應請求的處理器對映器
for (HandlerMapping hm : this.handlerMappings) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(
"Testing handler map [" + hm + "] in DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
//***請求匹配到對映器,並返回HandlerExecutionChain***---進入方法細看
//----攔截器的新增在方法裡面完成
HandlerExecutionChain handler = hm.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
return null;
}@Override
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);
if (handler == null) {
handler = getDefaultHandler();
}
if (handler == null) {
return null;
}
// Bean name or resolved handler?
if (handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
handler = getApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
//***獲取HandlerExecutionChain,攔截器的新增 ***---進一步跟進程式碼
HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
if (CorsUtils.isCorsRequest(request)) {
CorsConfiguration globalConfig = this.globalCorsConfigSource.getCorsConfiguration(request);
CorsConfiguration handlerConfig = getCorsConfiguration(handler, request);
CorsConfiguration config = (globalConfig != null ? globalConfig.combine(handlerConfig) : handlerConfig);
executionChain = getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(request, executionChain, config);
}
return executionChain;
}/**
* 走到這裡,才真正看到了HandlerExecutionChain的建立和攔截器的新增
*/
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandlerExecutionChain(Object handler, HttpServletRequest request) {
//獲取到HandlerExecutionChain
HandlerExecutionChain chain = (handler instanceof HandlerExecutionChain ?
(HandlerExecutionChain) handler : new HandlerExecutionChain(handler));
String lookupPath = this.urlPathHelper.getLookupPathForRequest(request);
//遍歷攔截器,adaptedInterceptors也是在initHandlerMapping初始化得到
for (HandlerInterceptor interceptor : this.adaptedInterceptors) {
if (interceptor instanceof MappedInterceptor) {
MappedInterceptor mappedInterceptor = (MappedInterceptor) interceptor;
if (mappedInterceptor.matches(lookupPath, this.pathMatcher)) {
//將攔截器新增
chain.addInterceptor(mappedInterceptor.getInterceptor());
}
}
else {
chain.addInterceptor(interceptor);
}
}
return chain;
}分析2、如何執行多個攔截器,通過責任鏈模式
boolean applyPreHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors = getInterceptors();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(interceptors)) {
for (int i = 0; i < interceptors.length; i++) {
HandlerInterceptor interceptor = interceptors[i];
if (!interceptor.preHandle(request, response, this.handler)) {
triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null);
return false;
}
this.interceptorIndex = i;
}
}
return true;
}
/**
* Apply postHandle methods of registered interceptors.
*/
void applyPostHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, ModelAndView mv) throws Exception {
HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors = getInterceptors();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(interceptors)) {
for (int i = interceptors.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
HandlerInterceptor interceptor = interceptors[i];
interceptor.postHandle(request, response, this.handler, mv);
}
}
}/**
* Trigger afterCompletion callbacks on the mapped HandlerInterceptors.
* Will just invoke afterCompletion for all interceptors whose preHandle invocation
* has successfully completed and returned true.
*/
void triggerAfterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Exception ex)
throws Exception {
HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors = getInterceptors();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(interceptors)) {
for (int i = this.interceptorIndex; i >= 0; i--) {
HandlerInterceptor interceptor = interceptors[i];
try {
interceptor.afterCompletion(request, response, this.handler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable ex2) {
logger.error("HandlerInterceptor.afterCompletion threw exception", ex2);
}
}
}
}