與spring結合的策略模式
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-02-06
策略模式是23種設計模式之一,客戶端通過制定多個演算法並且封裝,使得不同場景可以使用不同的策略演算法。使得程式降低了耦合提高程式碼的複用性。接下來通過一個簡單的例項來說明在實戰中如何使用(即使是業務邏輯也是可以用設計模式的)。
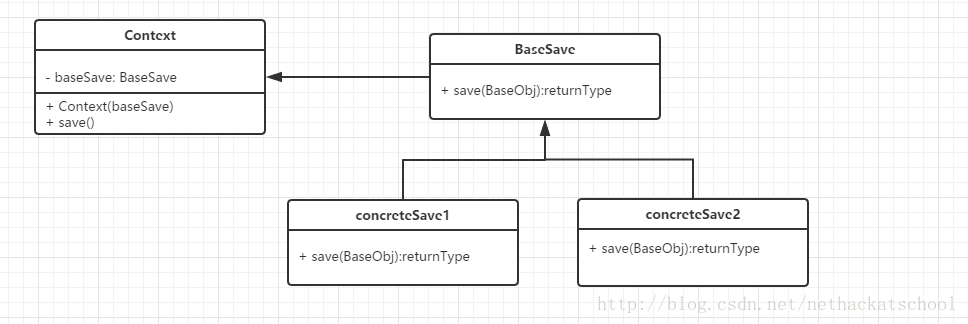
例子很簡單,就是通過同一個儲存的service來做不同型別產品的儲存。如下圖:
接下來看具體實現:
BaseObj:
public abstract class BaseObj implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String goodsName;
//省略getter,setter方法 DiscountGoods:
public class DiscountGoods extends BaseObj implements Serializable{
private double discountRate;
//省略getter,setter方法
public Byte getType() {
return 2;
}
}StrandardGoods:
public class StrandardGoods extends BaseObj BaseSaveService:
public interface BaseService<T> {
Boolean save(T obj);
}StrandardGoodsService:
@Service
public StrandardGoodsService implements BaseSaveService<StrandardGoods>{
public Boolean save DiscountGoodsService:
@Service
public DiscountGoodsService implements BaseSaveService<DiscountGoods>{
public Boolean save(DiscountGoodsgoods){
return this.saveDiscountGoods(goods);
}
}StrategyContext:
public StrategyContext {
prviate final Map<BaseObj,BaseSaveService> list=new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
//使用spring注入所有實現了BaseSaveService介面的bean
@Autowired
public StrategyContext (List<BaseSaveService> beansOfType) {
beansOfType.forEach(v -> list.put((BaseObj) v.getEntryInstance(), v));
}
public boolean save(BaseObj baseObj) {
boolean flag = true;
for (Map.Entry<BaseObj, BaseSaveService> entry : list.entrySet()) {
//判斷是否對應要儲存的具體物件
if (entry.getKey().getClass().isAssignableFrom(baseObj.getClass())) {
flag = entry.getValue().save(baseObj);
}
}
return flag;
}
}通過與spring結合,以後還會新增不同型別的goods儲存只需要新增儲存策略,也就是儲存的service並不需要改變其他地方的程式碼就可完成儲存。