結構體模擬實現棧
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-02-08
棧是很基本也很重要的資料結構,這裡通過結構體模擬實現順序棧,使用上節的順序表實現,還有鏈棧(使用連結串列),本篇僅包含順序棧的實現。我們知道C++的STL中有對棧的實現,直接提供了棧操作的所有函式,使用起來更簡潔,但是作為一個好的Programmer,應該是個多面手,只是會用還是不行的。
棧的基本思想:先進後出
行為:初始化、判空、元素入棧、出棧、銷燬棧、棧頂元素
入棧思想:top指標先加一再賦值
出棧思想:先取值再使top指標減一
程式碼如下:
#include<cstdio> #include<cstdlib> #define MaxSize 100 #define Elemtype int using namespace std; typedef struct{ Elemtype data[MaxSize]; int top; }SqStack; //建立棧 SqStack createStack(){ SqStack *stack = (SqStack*)malloc(sizeof(SqStack)); return *stack; } //初始化棧 bool InitStack(SqStack &S){ S.top = -1; printf("成功初始化\n"); } //判空 bool StackEmpty(SqStack &S){ if(S.top == -1){ printf("棧為空\n"); return true; } printf("棧不為空\n"); return false; } //進棧 bool Push(SqStack &S){ int num; printf("請輸入要入棧的元素,按0退出:\n"); while(scanf("%d\n",&num),num){ if(S.top == MaxSize-1){ printf("棧空間已滿\n"); return false; } S.data[++S.top] = num; printf("%d成功入棧\n",num); } return true; } //出棧 bool Pop(SqStack &S,Elemtype &val){ if(S.top==-1){ printf("棧為空,不能出棧操作\n"); return false; } val = S.data[S.top--]; printf("%d已成功出棧\n",val); return true; } //讀取棧頂元素 bool GetTop(SqStack &S,Elemtype &val){ if(S.top == -1){ printf("棧為空,沒有棧頂元素\n"); return false; } val = S.data[S.top]; printf("棧頂元素為%d\n",val); return true; } bool ClearStack(SqStack &S){ S.top = -1; printf("很遺憾,不良棧已被和諧\n"); return true; } int main(){ //建立棧 SqStack stack = createStack(); int x; while(scanf("%d",&x),x){//x為0時推出迴圈 switch(x){ case 1: InitStack(stack);//初始化 break; case 2: StackEmpty(stack);//判空 break; case 3: Push(stack);//入棧 break; case 4: Pop(stack,x);//出棧 break; case 5: GetTop(stack,x);//棧頂元素 break; default : ClearStack(stack);//偽銷燬 } } printf("程式執行完畢\n"); return 0; }
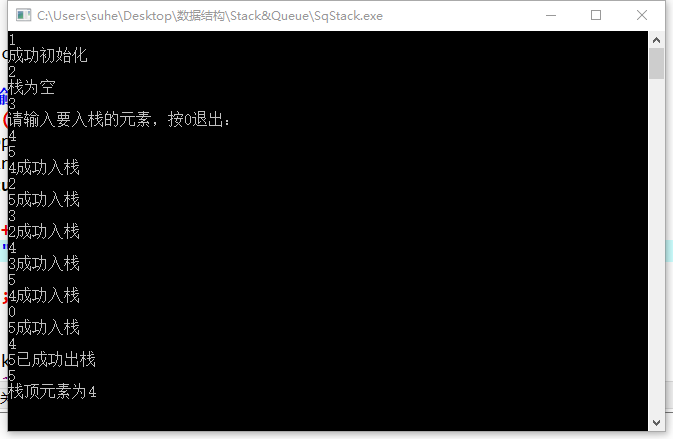
程式截圖:
貌似有點bug,入棧後不能及時顯示成功入棧,不清楚是哪的問題,這就要向大家求助了QAQ~