Spring IoC容器構建過程分析(二)(草稿,持續整理中)
接上一篇的內容:http://blog.csdn.net/caihaijiang/article/details/35795781
5、invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors
該方法的主要功能就是從spring配置檔案中,獲取實現 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 介面的bean,然後按不同的優先順序順序,依次執行BeanFactoryPostProcessor的 postProcessBeanFactory 方法。該方法的具體實現如下:
/** * Instantiate and invoke all registered BeanFactoryPostProcessor beans, * respecting explicit order if given. * <p>Must be called before singleton instantiation. */ protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { // Invoke factory processors registered with the context instance. for (Iterator it = getBeanFactoryPostProcessors().iterator(); it.hasNext();) { BeanFactoryPostProcessor factoryProcessor = (BeanFactoryPostProcessor) it.next(); factoryProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); } // Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans // uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them! String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false); // Separate between BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered, // Ordered, and the rest. List priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList(); List orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList(); List nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList(); for (int i = 0; i < postProcessorNames.length; i++) { if (isTypeMatch(postProcessorNames[i], PriorityOrdered.class)) { priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorNames[i])); } else if (isTypeMatch(postProcessorNames[i], Ordered.class)) { orderedPostProcessorNames.add(postProcessorNames[i]); } else { nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(postProcessorNames[i]); } } // First, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered. Collections.sort(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, new OrderComparator()); invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors); // Next, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement Ordered. List orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList(); for (Iterator it = orderedPostProcessorNames.iterator(); it.hasNext();) { String postProcessorName = (String) it.next(); orderedPostProcessors.add(getBean(postProcessorName)); } Collections.sort(orderedPostProcessors, new OrderComparator()); invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors); // Finally, invoke all other BeanFactoryPostProcessors. List nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList(); for (Iterator it = nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.iterator(); it.hasNext();) { String postProcessorName = (String) it.next(); nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(getBean(postProcessorName)); } invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, nonOrderedPostProcessors); } /** * Invoke the given BeanFactoryPostProcessor beans. */ private void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List postProcessors) { for (Iterator it = postProcessors.iterator(); it.hasNext();) { BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor = (BeanFactoryPostProcessor) it.next(); postProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); } }
在第二步中,通過beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false),獲取所有實現BeanFactoryPostProcessor介面的bean。
接下來,根據bean實現的不同排序介面,進行分組、排序。實現PriorityOrdered介面的bean,優先執行postProcessBeanFactory方法;實現Ordered介面的bean,第二優先順序執行對應的方法;而對於沒有實現排序介面的類,則在最後執行對應的方法。在執行postProcessBeanFactory之前,先通過BeanFactory.getBean獲取到對應的bean,然後再執行對應的方法。getBean是spring的核心之一,這裡先不深入,後面再分析。
6、registerBeanPostProcessors
該方法的主要功能是:例項化並註冊所有實現BeanPostProcessor介面的bean。方法的實現如下:
protected void registerBeanPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanPostProcessor.class, true, false); // Register BeanPostProcessorChecker that logs an info message when // a bean is created during BeanPostProcessor instantiation, i.e. when // a bean is not eligible for getting processed by all BeanPostProcessors. int beanProcessorTargetCount = beanFactory.getBeanPostProcessorCount() + 1 + postProcessorNames.length; beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new BeanPostProcessorChecker(beanFactory, beanProcessorTargetCount)); // Separate between BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered, // Ordered, and the rest. List priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList(); List orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList(); List nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList(); for (int i = 0; i < postProcessorNames.length; i++) { if (isTypeMatch(postProcessorNames[i], PriorityOrdered.class)) { priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorNames[i])); } else if (isTypeMatch(postProcessorNames[i], Ordered.class)) { orderedPostProcessorNames.add(postProcessorNames[i]); } else { nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(postProcessorNames[i]); } } // First, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered. Collections.sort(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, new OrderComparator()); registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors); // Next, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement Ordered. List orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList(); for (Iterator it = orderedPostProcessorNames.iterator(); it.hasNext();) { String postProcessorName = (String) it.next(); orderedPostProcessors.add(getBean(postProcessorName)); } Collections.sort(orderedPostProcessors, new OrderComparator()); registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors); // Finally, register all other BeanPostProcessors. List nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList(); for (Iterator it = nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.iterator(); it.hasNext();) { String postProcessorName = (String) it.next(); nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(getBean(postProcessorName)); } registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, nonOrderedPostProcessors); } /** * Register the given BeanPostProcessor beans. */ private void registerBeanPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List postProcessors) { for (Iterator it = postProcessors.iterator(); it.hasNext();) { BeanPostProcessor postProcessor = (BeanPostProcessor) it.next(); beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(postProcessor); } }
第一步,通過beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanPostProcessor.class, true, false),獲取spring配置檔案中所有實現BeanPostProcessor介面的bean。
第二步,註冊內建的BeanPostProcessor:BeanPostProcessorChecker。這裡說的註冊,其實就是將bean放入AbstractBeanFactory類的beanPostProcessors列表中,為後續的使用做準備。BeanPostProcessorChecker只是列印日誌,沒有做什麼實際性的工作。
第三步,根據bean實現的不同排序介面,進行分組、排序,然後逐一註冊。實現PriorityOrdered介面的bean,優先註冊;實現Ordered介面的bean,第二優先順序註冊;而對於沒有實現排序介面的類,則在最後註冊。同樣,在註冊之前,先通過BeanFactory.getBean獲取到對應的bean。
7、initMessageSource
這個方法主要功能就是為spring容器初始化MessageSource,功能相對簡單,如果spring配置檔案沒有定義messageSource,則使用預設的。預設的MessageSource實現類為:DelegatingMessageSource。方法的實現如下:
protected void initMessageSource() {
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean(MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME)) {
this.messageSource = (MessageSource) beanFactory.getBean(MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME, MessageSource.class);
// Make MessageSource aware of parent MessageSource.
if (this.parent != null && this.messageSource instanceof HierarchicalMessageSource) {
HierarchicalMessageSource hms = (HierarchicalMessageSource) this.messageSource;
if (hms.getParentMessageSource() == null) {
// Only set parent context as parent MessageSource if no parent MessageSource
// registered already.
hms.setParentMessageSource(getInternalParentMessageSource());
}
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Using MessageSource [" + this.messageSource + "]");
}
}
else {
// Use empty MessageSource to be able to accept getMessage calls.
DelegatingMessageSource dms = new DelegatingMessageSource();
dms.setParentMessageSource(getInternalParentMessageSource());
this.messageSource = dms;
beanFactory.registerSingleton(MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME, this.messageSource);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Unable to locate MessageSource with name '" + MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME +
"': using default [" + this.messageSource + "]");
}
}
}在建立MessageSource之後,呼叫beanFactory.registerSingleton(MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME, this.messageSource)進行註冊。該方法對應的實現類是DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry,具體實現如下(只摘錄了該類的一部分程式碼):
<span style="font-size:12px;">public class DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry extends SimpleAliasRegistry implements SingletonBeanRegistry {
/** Cache of singleton objects: bean name --> bean instance */
private final Map singletonObjects = CollectionFactory.createConcurrentMapIfPossible(16);
/** Cache of singleton factories: bean name --> ObjectFactory */
private final Map singletonFactories = new HashMap();
/** Cache of early singleton objects: bean name --> bean instance */
private final Map earlySingletonObjects = new HashMap();
/** Set of registered singletons, containing the bean names in registration order */
private final Set registeredSingletons = new LinkedHashSet(16);
public void registerSingleton(String beanName, Object singletonObject) throws IllegalStateException {
Assert.notNull(beanName, "'beanName' must not be null");
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
Object oldObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (oldObject != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Could not register object [" + singletonObject +
"] under bean name '" + beanName + "': there is already object [" + oldObject + "] bound");
}
addSingleton(beanName, singletonObject);
}
}
/**
* Add the given singleton object to the singleton cache of this factory.
* <p>To be called for eager registration of singletons.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param singletonObject the singleton object
*/
protected void addSingleton(String beanName, Object singletonObject) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
this.singletonObjects.put(beanName, (singletonObject != null ? singletonObject : NULL_OBJECT));
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
this.earlySingletonObjects.remove(beanName);
this.registeredSingletons.add(beanName);
}
}
}</span>從上面的程式碼可以看出,DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry繼承了SimpleAliasRegistry並實現SingletonBeanRegistry,使得它既有管理SingletonBean的功能,又提供了別名的功能,它是一個通用的儲存共享bean例項的地方。在註冊一個SingletonBean的時候,用到了四個儲存器:
- singletonObjects:用來存放註冊的SingletonBean,具體的實現類是ConcurrentHashMap。
- singletonFactories:儲存製造 singleton 的工廠。
- earlySingletonObjects:是singletonFactory 製造出來的 singleton 的快取。
- registeredSingletons:按順序存放已經註冊的SingletonBean的名稱。
在 getSingleton的時候,spring的預設實現是,先從singletonObjects尋找,如果找不到,再從earlySingletonObjects尋找,仍然找不到,那就從singletonFactories尋找對應的製造singleton的工廠,然後呼叫工廠的getObject方法,造出對應的SingletonBean,並放入earlySingletonObjects中。具體見DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.getSingleton,如下:
public Object getSingleton(String beanName) {
return getSingleton(beanName, true);
}
protected Object getSingleton(String beanName, boolean allowEarlyReference) {
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && allowEarlyReference) {
ObjectFactory singletonFactory = (ObjectFactory) this.singletonFactories.get(beanName);
if (singletonFactory != null) {
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
this.earlySingletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
}
}
}
}
return (singletonObject != NULL_OBJECT ? singletonObject : null);
}8、initApplicationEventMulticaster
這個方法的主要功能是為spring容器初始化ApplicationEventMulticaster,功能也相對簡單,如果spring配置檔案沒有定義applicationEventMulticaster,則使用預設的。預設的ApplicationEventMulticaster實現類是SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster。方法的實現如下:
protected void initApplicationEventMulticaster() {
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME)) {
this.applicationEventMulticaster = (ApplicationEventMulticaster)
beanFactory.getBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, ApplicationEventMulticaster.class);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Using ApplicationEventMulticaster [" + this.applicationEventMulticaster + "]");
}
}
else {
this.applicationEventMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster();
beanFactory.registerSingleton(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, this.applicationEventMulticaster);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Unable to locate ApplicationEventMulticaster with name '" +
APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME +
"': using default [" + this.applicationEventMulticaster + "]");
}
}
}9、onRefresh
該方法,預設是一個空的實現,留給子類去重寫。
10、registerListeners
該方法的主要功能是註冊實現ApplicationListener介面的bean。方法的具體實現如下:
protected void registerListeners() {
// Register statically specified listeners first.
for (Iterator it = getApplicationListeners().iterator(); it.hasNext();) {
addListener((ApplicationListener) it.next());
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let post-processors apply to them!
Collection listenerBeans = getBeansOfType(ApplicationListener.class, true, false).values();
for (Iterator it = listenerBeans.iterator(); it.hasNext();) {
addListener((ApplicationListener) it.next());
}
}
/**
* Subclasses can invoke this method to register a listener.
* Any beans in the context that are listeners are automatically added.
* @param listener the listener to register
*/
protected void addListener(ApplicationListener listener) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListener(listener);
}第二步,呼叫beanFactory.getBeansOfType(ApplicationListener.class, true, false),獲取所有實現ApplicationListener介面的bean。該方法底層先呼叫getBeanNamesForType方法獲取所有實現ApplicationListener介面的beanName,然後針對每個beanName,呼叫getBean方法獲取對應的bean例項。
第三步,呼叫getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListener(listener),註冊每個bean。
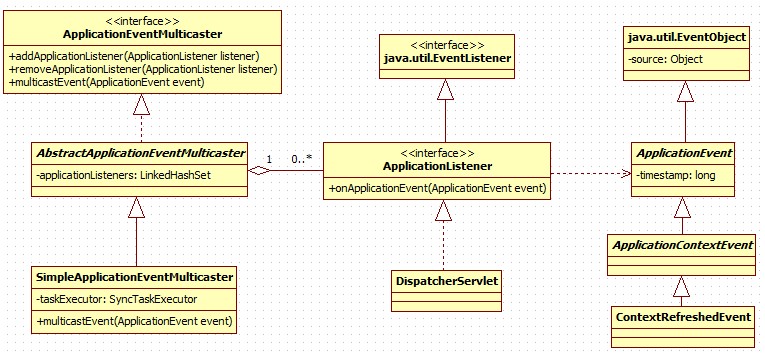
spring的ApplicationListener是一個典型的觀察者模式,類圖結構如下:
ApplicationEventMulticaster在接收到ApplicationEvent事件之後,通過multicastEvent方法,通知所有的觀察者ApplicationListener。SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster類的multicastEvent方法實現如下:
public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event) {
for (Iterator it = getApplicationListeners().iterator(); it.hasNext();) {
final ApplicationListener listener = (ApplicationListener) it.next();
getTaskExecutor().execute(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
listener.onApplicationEvent(event);
}
});
}
}11、finishBeanFactoryInitialization
這個方法的主要功能是建立Bean 的例項物件以及構建 Bean 例項物件之間的關聯關係,該方法所做的事情,是spring的一個核心關鍵所在。方法的實現如下:
protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Stop using the temporary ClassLoader for type matching.
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(null);
// Allow for caching all bean definition metadata, not expecting further changes.
beanFactory.freezeConfiguration();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons();
} public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
this.logger.info("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this);
}
synchronized (this.beanDefinitionMap) {
for (Iterator it = this.beanDefinitionNames.iterator(); it.hasNext();) {
String beanName = (String) it.next();
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {
FactoryBean factory = (FactoryBean) getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
if (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean && ((SmartFactoryBean) factory).isEagerInit()) {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
else {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
}
}1)根據beanName,獲取bean的定義資訊,得到RootBeanDefinition物件例項;
2)對於非抽象的、單例的、非延遲載入的bean,先判斷是否為FactoryBean,如果是,則通過在前面加“&”,呼叫getBean獲取對應的FactoryBean。如果是普通的bean,則直接呼叫getBean方法獲取bean。
getBean方法,是spring的核心所在,具體實現如下:
public Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException {
return getBean(name, null, null);
}
public Object getBean(String name, Class requiredType, Object[] args) throws BeansException {
return doGetBean(name, requiredType, args, false);
}
protected Object doGetBean(
final String name, final Class requiredType, final Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly) throws BeansException {
final String beanName = transformedBeanName(name);
Object bean = null;
// Eagerly check singleton cache for manually registered singletons.
Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (sharedInstance != null && args == null) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
logger.debug("Returning eagerly cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName +
"' that is not fully initialized yet - a consequence of a circular reference");
}
else {
logger.debug("Returning cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
}
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, null);
}
else {
// Fail if we're already creating this bean instance:
// We're assumably within a circular reference.
if (isPrototypeCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName);
}
// Check if bean definition exists in this factory.
BeanFactory parentBeanFactory = getParentBeanFactory();
if (parentBeanFactory != null && !containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) {
// Not found -> check parent.
String nameToLookup = originalBeanName(name);
if (args != null) {
// Delegation to parent with explicit args.
return parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, args);
}
else {
// No args -> delegate to standard getBean method.
return parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, requiredType);
}
}
if (!typeCheckOnly) {
markBeanAsCreated(beanName);
}
final RootBeanDefinition mbd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
checkMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanName, args);
// Guarantee initialization of beans that the current bean depends on.
String[] dependsOn = mbd.getDependsOn();
if (dependsOn != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < dependsOn.length; i++) {
String dependsOnBean = dependsOn[i];
getBean(dependsOnBean);
registerDependentBean(dependsOnBean, beanName);
}
}
// Create bean instance.
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, new ObjectFactory() {
public Object getObject() throws BeansException {
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there
// eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution.
// Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean.
destroySingleton(beanName);
throw ex;
}
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
else if (mbd.isPrototype()) {
// It's a prototype -> create a new instance.
Object prototypeInstance = null;
try {
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
prototypeInstance = createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(prototypeInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
else {
String scopeName = mbd.getScope();
final Scope scope = (Scope) this.scopes.get(scopeName);
if (scope == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope '" + scopeName + "'");
}
try {
Object scopedInstance = scope.get(beanName, new ObjectFactory() {
public Object getObject() throws BeansException {
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(scopedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName,
"Scope '" + scopeName + "' is not active for the current thread; " +
"consider defining a scoped proxy for this bean if you intend to refer to it from a singleton",
ex);
}
}
}
// Check if required type matches the type of the actual bean instance.
if (requiredType != null && bean != null && !requiredType.isAssignableFrom(bean.getClass())) {
throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass());
}
return bean;
} 12、finishRefresh
該方法的作用是,傳送一個ContextRefreshedEvent事件,通知相關的觀察者。方法的實現如下:
protected void finishRefresh() {
publishEvent(new ContextRefreshedEvent(this));
}
public void publishEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
Assert.notNull(event, "Event must not be null");
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Publishing event in context [" + getId() + "]: " + event);
}
getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(event);
if (this.parent != null) {
this.parent.publishEvent(event);
}
}
至此,完成了spring IoC容器的構建過程分析。
補充說明:
對於web應用,spring容器的初始化,是在org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener的contextInitialized方法完成的,方法的實現如下:
/**
* Initialize the root web application context.
*/
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
this.contextLoader = createContextLoader();
this.contextLoader.initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}第二步,呼叫ContextLoader的initWebApplicationContext方法,該方法的實現如下:
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext)
throws IllegalStateException, BeansException {
if (servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - " +
"check whether you have multiple ContextLoader* definitions in your web.xml!");
}
servletContext.log("Initializing Spring root WebApplicationContext");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization started");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
// Determine parent for root web application context, if any.
ApplicationContext parent = loadParentContext(servletContext);
// Store context in local instance variable, to guarantee that
// it is available on ServletContext shutdown.
this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext, parent);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);
currentContextPerThread.put(Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(), this.context);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Published root WebApplicationContext as ServletContext attribute with name [" +
WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE + "]");
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization completed in " + elapsedTime + " ms");
}
return this.context;
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, ex);
throw ex;
}
catch (Error err) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", err);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, err);
throw err;
}
}
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(
ServletContext servletContext, ApplicationContext parent) throws BeansException {
Class contextClass = determineContextClass(servletContext);
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Custom context class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type [" + ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.getName() + "]");
}
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac =
(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
wac.setParent(parent);
wac.setServletContext(servletContext);
wac.setConfigLocation(servletContext.getInitParameter(CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM));
customizeContext(servletContext, wac);
wac.refresh();
return wac;
}