java jdbc連線資料庫(使用mysql進行連線)
一、JDBC簡介
Java 資料庫連線,(Java Database Connectivity,簡稱JDBC)是Java語言中用來規範客戶端程式如何來訪問資料庫的應用程式介面,提供了諸如查詢和更新資料庫中資料的方法。JDBC也是Sun Microsystems的商標。它JDBC是面向關係型資料庫的。
1、JDBC架構:
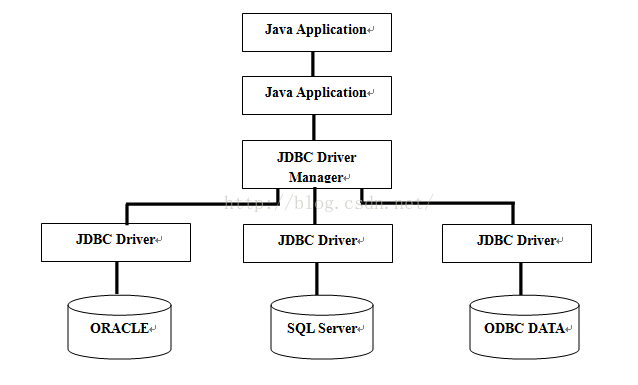
JDBC API支援兩層和三層處理模型進行資料庫訪問,但在一般的JDBC體系結構由兩層組成:
JDBC API: 提供了應用程式對JDBC的管理連線;
JDBC Driver API: 支援JDBC管理到驅動器連線;
JDBC API的使用驅動程式管理器和資料庫特定的驅動程式提供透明的連線到異構資料庫;
JDBC驅動程式管理器可確保正確的驅動程式來訪問每個資料來源,該驅動程式管理器能夠支援連線到多個異構資料庫的多個併發的驅動程式;
以下是結構圖,它顯示了驅動程式管理器方面的JDBC驅動程式和Java應用程式的位置:
2、常見的JDBC元件:
JDBC API提供了以下介面和類:
DriverManager: 這個類管理資料庫驅動程式的列表,內容是否符合從Java應用程式使用的通訊子協議正確的資料庫驅動程式的連線請求,識別JDBC在一定子協議的第一個驅動器將被用來建立資料庫連線;
Driver: 此介面處理與資料庫伺服器通訊,很少直接與驅動程式物件,相反,使用DriverManager中的物件,它管理此型別的物件,它也抽象與驅動程式物件工作相關的詳細資訊;
Connection : 此介面與接觸資料庫的所有方法,連線物件表示通訊上下文,即,與資料庫中的所有的通訊是通過唯一的連線物件;
Statement : 可以使用這個介面建立的物件的SQL語句提交到資料庫,一些派生的介面接受除執行儲存過程的引數;
ResultSet: 這些物件儲存從資料庫後,執行使用Statement物件的SQL查詢中檢索資料,它作為一個迭代器,讓您可以通過移動它的資料;
SQLException: 這個類處理髮生在一個數據庫應用程式的任何錯誤.
二、連線JDBC需要掌握的基本知識
1、資料庫的基本操作,
eg:Mysql的安裝和基本操作(insert,delete,update,query)
2、java開發工具的使用,
eg:Eclipse/MyEclipse (包括mysql-connector-java-5.0.3-bin.jar的匯入)
三、JDBC的連線及程式碼演示
1、JDBC連線工具類
1)、Configuration.java:可以從.xml檔案中連線資料庫的配置資訊,需要引入dom4j-1.6.1.jar包
package cn.java.jdbc; import java.io.InputStream; import org.dom4j.Document; import org.dom4j.DocumentException; import org.dom4j.Element; import org.dom4j.io.SAXReader; public class Configuration { private String url; private String driver; private String username; private String password; public Configuration() { } public Configuration(String url, String driver, String username, String password) { super(); this.url = url; this.driver = driver; this.username = username; this.password = password; } public static Configuration getConfigure() { try { InputStream in = Configuration.class.getResourceAsStream("/db.xml"); if (null!=in) { return load(in); } return null; } catch (DocumentException e) { e.printStackTrace(); return null; } } private static Configuration load(InputStream in) throws DocumentException { SAXReader reader = new SAXReader(); Document doc = reader.read(in); Element jdbc = doc.getRootElement(); String url = jdbc.element("url").getText(); String driver = jdbc.element("driver").getText(); String username = jdbc.element("username").getText(); String password = jdbc.element("password").getText(); Configuration cfg = new Configuration(url, driver, username, password); return cfg; } public String getUrl() { return url; } public void setUrl(String url) { this.url = url; } public String getDriver() { return driver; } public void setDriver(String driver) { this.driver = driver; } public String getUsername() { return username; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } }
2)、db.xml:儲存資料庫的配置資訊
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<jdbc>
<url>jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test</url>
<driver>com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</driver>
<username>root</username>
<password></password>
</jdbc>package cn.java.jdbc;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class ConnectionFactory {
private static ConnectionFactory connectionFactory=null;
private static Configuration config=Configuration.getConfigure();
private ConnectionFactory()
{
try {
Class.forName(config.getDriver());
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
}
}
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException
{
Connection con=null;
try {
con=DriverManager.getConnection(config.getUrl(), config.getUsername(), config.getPassword());
return con;
}finally{
// if (null != con) {
// con.close();
// }
}
}
public static ConnectionFactory getInstance()
{
if (null==connectionFactory) {
connectionFactory=new ConnectionFactory();
}
return connectionFactory;
}
}
4)、ConnectionFactory2.java:JDBC連線工廠方法之二
package cn.java.jdbc;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import com.mysql.jdbc.jdbc2.optional.MysqlDataSource;
public class ConnectionFactory2 {
private DataSource ds ;
private static ConnectionFactory2 connectionFactory2 = null;
private ConnectionFactory2() {
MysqlDataSource myDS = new MysqlDataSource() ;
myDS.setServerName("localhost");
myDS.setDatabaseName("test");
myDS.setPort(3306) ;
myDS.setUser("root");
myDS.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
myDS.setPassword("");
this.ds = myDS ;
}
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
Connection conn = null;
try {
conn = ds.getConnection() ;
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
return conn;
} catch (SQLException e) {
if (null != conn) {
conn.close();
}
throw e;
}
}
public static ConnectionFactory2 getInstance() {
if (null == connectionFactory2) {
connectionFactory2 = new ConnectionFactory2();
}
return connectionFactory2;
}
}
5)、User.java:定義資料庫表user中的id和name的bean類,其中id是自動增長的
package cn.java.jdbc;
public class User {
private int id;
private String name;
public User() {
}
public User(int id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
6)、UserDao.java:user表的操作類,實現了insert、delete、update、query等方法
package cn.java.jdbc;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class UserDao {
private PreparedStatement st = null;
private ResultSet rs = null;
public UserDao() {
}
public void insert( Connection con,String name) throws SQLException,IOException {
String sql="insert into user(name) values(?) ";
try{
st=con.prepareStatement(sql);
st.setString(1, name);
st.executeUpdate();
}finally{
if (null!=st) {
st.close();
}
}
}
public void delete(Connection con,int id) throws SQLException,IOException {
String sql="delete from user where id=?";
try{
st=con.prepareStatement(sql);
st.setInt(1, id);
st.executeUpdate();
}finally{
if (null!=st) {
st.close();
}
}
}
public void update( Connection con,int id,String name) throws SQLException,IOException {
String sql="update user set name=? where id=?";
try{
st=con.prepareStatement(sql);
st.setString(1, name);
st.setInt(2, id);
st.executeUpdate();
}finally{
if (null!=st) {
st.close();
}
}
}
public User query(Connection con,int index) throws SQLException,IOException{
User user=new User();
String sql="select * from user where id=?";
try{
st=con.prepareStatement(sql);
st.setInt(1, index);
rs=st.executeQuery();
while (rs.next()) {
user.setId(rs.getInt(1));
user.setName(rs.getString(2));
break;
}
}finally{
if (null!=rs) {
rs.close();
}
if (null!=st) {
st.close();
}
}
return user;
}
public List<User> queryAll(Connection con) throws SQLException,IOException {
List<User> list=new ArrayList<>();
String sql="select * from user";
try {
st=con.prepareStatement(sql);
rs=st.executeQuery();
while (rs.next()) {
User user=new User();
user.setId(rs.getInt(1));
user.setName(rs.getString(2));
list.add(user);
}
}finally{
if (null!=rs) {
rs.close();
}
if (null!=st) {
st.close();
}
}
return list;
}
}
2、JDBC連線的測試類
1)、TestJdbc.java:資料庫測試類
package cn.java.jdbc;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.List;
public class TestJdbc {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection con=null;
try {
con=(Connection) ConnectionFactory.getInstance().getConnection();
UserDao userDao=new UserDao();
//con=(Connection) ConnectionFactory2.getInstance().getConnection();
if (null!=con) {
System.out.println("Link JDBC SUCESS");
//userDao.insert(con, "zhangsir");
//userDao.delete(con, 4);
//userDao.update(con, 1, "david");
List<User> list=userDao.queryAll(con);
for (User user : list) {
System.out.println("id="+user.getId()+" name="+user.getName());
}
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if (null!=con) {
try {
con.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
}
}
}
}
}
三、JDBC連線總結
JDBC操作的基本步驟是:
1、建立Connection物件,傳入SQL查詢命令字串;
2、獲取PreparedStatement物件:通過Connection物件傳入SQL查詢命令獲取;
3、獲取ResultSet:對PreparedStatement執行executeUpdate()或者executeQurey()獲取;
4、依次關閉開啟的物件:先後關閉ResultSet、PreparedStatement和Connection物件.