java輸入輸出流(I/O)總結
io流的四個基本類
Java.io包中包含了流式I/O所需要的所有類。在java.io包中有四個基本類:InputStream、OutputStream及Reader、Writer類,它們分別處理位元組流和字元流:
基本資料流的I/O
|
輸入/輸出 |
位元組流 |
字元流 |
|
輸入流 |
Inputstream |
Reader |
|
輸出流 |
OutputStream |
Writer |
Java中其他多種多樣變化的流均是由它們派生出來的:
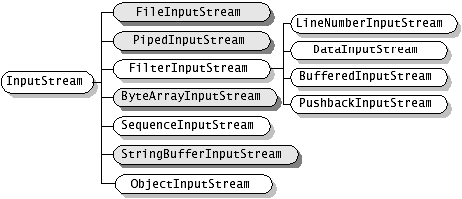
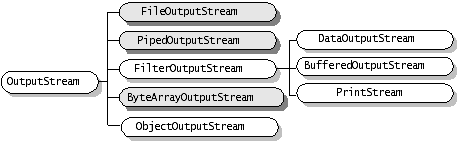
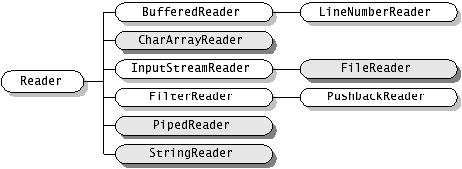
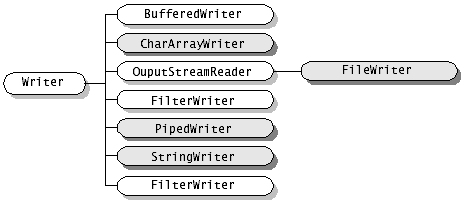
JDK1.4版本開始引入了新I/O類庫,它位於java.nio包中,新I/O類庫利用通道和緩衝區等來提高I/O操作的效率。
在java.io包中, java.io.InputStream 表示位元組輸入流, java.io.OutputStream表示位元組輸出流,處於java.io包最頂層。這兩個類均為抽象類,也就是說它們不能被例項化,必須生成子類之後才能實現一定的功能。
1. io流的具體分類
1.1.按I/O型別來總體分類:
1. Memory 1)從/向記憶體陣列讀寫資料: CharArrayReader、 CharArrayWriter、ByteArrayInputStream、ByteArrayOutputStream
2)從/向記憶體字串讀寫資料 StringReader、StringWriter、StringBufferInputStream
2.Pipe管道 實現管道的輸入和輸出(程序間通訊): PipedReader、PipedWriter、PipedInputStream、PipedOutputStream
3.File 檔案流。對檔案進行讀、寫操作 :FileReader、FileWriter、FileInputStream、FileOutputStream
4. ObjectSerialization 物件輸入、輸出 :ObjectInputStream、ObjectOutputStream
5.DataConversion資料流 按基本資料型別讀、寫(處理的資料是Java的基本型別(如布林型,位元組,整數和浮點數)):DataInputStream、DataOutputStream
6.Printing 包含方便的列印方法 :PrintWriter、PrintStream
7.Buffering緩衝 在讀入或寫出時,對資料進行快取,以減少I/O的次數:BufferedReader、BufferedWriter、BufferedInputStream、BufferedOutputStream
8.Filtering 濾流,在資料進行讀或寫時進行過濾:FilterReader、FilterWriter、FilterInputStream、FilterOutputStream過
9.Concatenation合併輸入 把多個輸入流連線成一個輸入流 :SequenceInputStream
10.Counting計數 在讀入資料時對行記數 :LineNumberReader、LineNumberInputStream
11.Peeking Ahead 通過快取機制,進行預讀 :PushbackReader、PushbackInputStream
12.Converting between Bytes and Characters 按照一定的編碼/解碼標準將位元組流轉換為字元流,或進行反向轉換(Stream到Reader,Writer的轉換類):InputStreamReader、OutputStreamWriter
1.2.按資料來源(去向)分類:
1、File(檔案): FileInputStream, FileOutputStream, FileReader, FileWriter2、byte[]:ByteArrayInputStream, ByteArrayOutputStream
3、Char[]: CharArrayReader, CharArrayWriter
4、String: StringBufferInputStream, StringReader, StringWriter
5、網路資料流:InputStream, OutputStream, Reader, Writer
2. 位元組流InputStream/OutputStream
2.1. InputStream抽象類
InputStream 為位元組輸入流,它本身為一個抽象類,必須依靠其子類實現各種功能,此抽象類是表示位元組輸入流的所有類的超類。 繼承自InputStream 的流都是向程式中輸入資料的,且資料單位為位元組(8bit);
InputStream是輸入位元組資料用的類,所以InputStream類提供了3種過載的read方法.Inputstream類中的常用方法:
(1) public abstract int read( ):讀取一個byte的資料,返回值是高位補0的int型別值。若返回值=-1說明沒有讀取到任何位元組讀取工作結束。
(2) public int read(byte b[ ]):讀取b.length個位元組的資料放到b陣列中。返回值是讀取的位元組數。該方法實際上是呼叫下一個方法實現的
(3) public int read(byte b[ ], int off, int len):從輸入流中最多讀取len個位元組的資料,存放到偏移量為off的b陣列中。
(4) public int available( ):返回輸入流中可以讀取的位元組數。注意:若輸入阻塞,當前執行緒將被掛起,如果InputStream物件呼叫這個方法的話,它只會返回0,這個方法必須由繼承InputStream類的子類物件呼叫才有用,
(5) public long skip(long n):忽略輸入流中的n個位元組,返回值是實際忽略的位元組數, 跳過一些位元組來讀取
(6) public int close( ) :我們在使用完後,必須對我們開啟的流進行關閉.
主要的子類:

1) FileInputStream把一個檔案作為InputStream,實現對檔案的讀取操作
2) ByteArrayInputStream:把記憶體中的一個緩衝區作為InputStream使用
3) StringBufferInputStream:把一個String物件作為InputStream
4) PipedInputStream:實現了pipe的概念,主要線上程中使用
5) SequenceInputStream:把多個InputStream合併為一個InputStream
2.2.OutputStream抽象類
OutputStream提供了3個write方法來做資料的輸出,這個是和InputStream是相對應的。1. public void write(byte b[ ]):將引數b中的位元組寫到輸出流。
2. public void write(byte b[ ], int off, int len) :將引數b的從偏移量off開始的len個位元組寫到輸出流。
3. public abstract void write(int b) :先將int轉換為byte型別,把低位元組寫入到輸出流中。
4. public void flush( ) : 將資料緩衝區中資料全部輸出,並清空緩衝區。
5. public void close( ) : 關閉輸出流並釋放與流相關的系統資源。
主要的子類:

1) ByteArrayOutputStream:把資訊存入記憶體中的一個緩衝區中
2) FileOutputStream:把資訊存入檔案中
3) PipedOutputStream:實現了pipe的概念,主要線上程中使用
4) SequenceOutputStream:把多個OutStream合併為一個OutStream
流結束的判斷:方法read()的返回值為-1時;readLine()的返回值為null時。
2.3. 檔案輸入流: FileInputStream類
FileInputStream可以使用read()方法一次讀入一個位元組,並以int型別返回,或者是使用read()方法時讀入至一個byte陣列,byte陣列的元素有多少個,就讀入多少個位元組。在將整個檔案讀取完成或寫入完畢的過程中,這麼一個byte陣列通常被當作緩衝區,因為這麼一個byte陣列通常扮演承接資料的中間角色。

作用:以檔案作為資料輸入源的資料流。或者說是開啟檔案,從檔案讀資料到記憶體的類。
使用方法(1)
File fin=new File("d:/abc.txt");
FileInputStream in=new FileInputStream( fin);
使用方法(2)
FileInputStream in=new FileInputStream(“d: /abc.txt”);
程式舉例:
將InputFromFile.java的程式的內容顯示在顯示器上

- import java.io.IOException;
- import java.io.FileInputStream;
- ;
- publicclass TestFile {
- publicstaticvoid main(String args[]) throws IOException {
- try{
- FileInputStream rf=new FileInputStream("InputFromFile.java");
- int n=512; byte buffer[]=newbyte[n];
- while((rf.read(buffer,0,n)!=-1)&&(n>0)){
- System.out.println(new String(buffer) );
- }
- System.out.println();
- rf.close();
- } catch(IOException IOe){
- System.out.println(IOe.toString());
- }
- }
- }
2.4.檔案輸出流:FileOutputStream類
作用:用來處理以檔案作為資料輸出目的資料流;或者說是從記憶體區讀資料入檔案 FileOutputStream類用來處理以檔案作為資料輸出目的資料流;一個表示檔名的字串,也可以是File或FileDescriptor物件。
建立一個檔案流物件有兩種方法:
方式1:
File f=new File (“d:/myjava/write.txt ");
FileOutputStream out= new FileOutputStream (f);
方式2:
FileOutputStream out=new FileOutputStream(“d:/myjava/write.txt ");
方式3:建構函式將 FileDescriptor()物件作為其引數。
FileDescriptor() fd=new FileDescriptor();
FileOutputStream f2=new FileOutputStream(fd);
方式4:建構函式將檔名作為其第一引數,將布林值作為第二引數。
FileOutputStream f=new FileOutputStream("d:/abc.txt",true);
注意: (1)檔案中寫資料時,若檔案已經存在,則覆蓋存在的檔案;(2)的讀/寫操作結束時,應呼叫close方法關閉流。

- import java.io.IOException;
- import java.io.FileOutputStream;
- publicclass TestFile {
- publicstaticvoid main(String args[]) throws IOException {
- try {
- System.out.println("please Input from Keyboard");
- int count, n = 512;
- byte buffer[] = newbyte[n];
- count = System.in.read(buffer);
- FileOutputStream wf = new FileOutputStream("d:/myjava/write.txt");
- wf.write(buffer, 0, count);
- wf.close(); // 當流寫操作結束時,呼叫close方法關閉流。
- System.out.println("Save to the write.txt");
- } catch (IOException IOe) {
- System.out.println("File Write Error!");
- }
- }
- }
2.5. FileInputStream流和FileOutputStream的應用
利用程式將檔案file1.txt 拷貝到file2.txt中。- import java.io.File;
- import java.io.IOException;
- import java.io.FileOutputStream;
- import java.io.FileInputStream;
- publicclass TestFile {
- publicstaticvoid main(String args[]) throws IOException {
- try {
- File inFile = new File("copy.java");
- File outFile = new File("copy2.java");
- FileInputStream finS = new FileInputStream(inFile);
- FileOutputStream foutS = new FileOutputStream(outFile);
- int c;
- while ((c = finS.read()) != -1) {
- foutS.write(c);
- }
- finS.close();
- foutS.close();
- } catch (IOException e) {
- System.err.println("FileStreamsTest: " + e);
- }
- }
- }
2.6. 緩衝輸入輸出流 BufferedInputStream/ BufferedOutputStream

計算機訪問外部裝置非常耗時。訪問外存的頻率越高,造成CPU閒置的概率就越大。為了減少訪問外存的次數,應該在一次對外設的訪問中,讀寫更多的資料。為此,除了程式和流節點間交換資料必需的讀寫機制外,還應該增加緩衝機制。緩衝流就是每一個數據流分配一個緩衝區,一個緩衝區就是一個臨時儲存資料的記憶體。這樣可以減少訪問硬碟的次數,提高傳輸效率。
BufferedInputStream:當向緩衝流寫入資料時候,資料先寫到緩衝區,待緩衝區寫滿後,系統一次性將資料傳送給輸出裝置。
BufferedOutputStream :當從向緩衝流讀取資料時候,系統先從緩衝區讀出資料,待緩衝區為空時,系統再從輸入裝置讀取資料到緩衝區。
1)將檔案讀入記憶體:將BufferedInputStream與FileInputStream相接
FileInputStream in=new FileInputStream( “file1.txt ” );
BufferedInputStream bin=new BufferedInputStream( in);
2)將記憶體寫入檔案:
將BufferedOutputStream與 FileOutputStream相接
FileOutputStreamout=new FileOutputStream(“file1.txt”);
BufferedOutputStream bin=new BufferedInputStream(out);
3)鍵盤輸入流讀到記憶體 將BufferedReader與標準的資料流相接 InputStreamReader sin=new InputStreamReader (System.in) ; BufferedReader bin=new BufferedReader(sin);
- import java.io.*;
- publicclass ReadWriteToFile {
- publicstaticvoid main(String args[]) throws IOException {
- InputStreamReader sin = new InputStreamReader(System.in);
- BufferedReader bin = new BufferedReader(sin);
- FileWriter out = new FileWriter("myfile.txt");
- BufferedWriter bout = new BufferedWriter(out);
- String s;
- while ((s = bin.readLine()).length() > 0) {
- bout.write(s, 0, s.length());
- }
- }
- }
從鍵盤讀入字元,並寫入到檔案中BufferedReader類的方法:String readLine()
作用:讀一行字串,以回車符為結束。
BufferedWriter類的方法:bout.write(String s,offset,len)
作用:從緩衝區將字串s從offset開始,len長度的字串寫到某處。
3. 字元流Writer/Reader
Java中字元是採用Unicode標準,一個字元是16位,即一個字元使用兩個位元組來表示。為此,JAVA中引入了處理字元的流。
3.1. Reader抽象類
用於讀取字元流的抽象類。子類必須實現的方法只有 read(char[], int, int) 和 close()。但是,多數子類將重寫此處定義的一些方法,以提供更高的效率和/或其他功能。

1) FileReader :與FileInputStream對應
主要用來讀取字元檔案,使用預設的字元編碼,有三種建構函式:
(1)將檔名作為字串 :FileReader f=new FileReader(“c:/temp.txt”);
(2)建構函式將File物件作為其引數。
File f=new file(“c:/temp.txt”);
FileReader f1=new FileReader(f);
(3) 建構函式將FileDescriptor物件作為引數
FileDescriptor() fd=new FileDescriptor()
FileReader f2=new FileReader(fd);
(1) 用指定字元陣列作為引數:CharArrayReader(char[])
(2) 將字元陣列作為輸入流:CharArrayReader(char[], int, int)
讀取字串,建構函式如下: public StringReader(String s);
2) CharArrayReader:與ByteArrayInputStream對應
3) StringReader : 與StringBufferInputStream對應
4) InputStreamReader
從輸入流讀取位元組,在將它們轉換成字元:Public inputstreamReader(inputstream is);
5) FilterReader: 允許過濾字元流
protected filterReader(Reader r);
6) BufferReader :接受Reader物件作為引數,並對其新增字元緩衝器,使用readline()方法可以讀取一行。
Public BufferReader(Reader r);
主要方法:
(1) public int read() throws IOException; //讀取一個字元,返回值為讀取的字元
(2) public int read(char cbuf[]) throws IOException; /*讀取一系列字元到陣列cbuf[]中,返回值為實際讀取的字元的數量*/
(3) public abstract int read(char cbuf[],int off,int len) throws IOException;
/*讀取len個字元,從陣列cbuf[]的下標off處開始存放,返回值為實際讀取的字元數量,該方法必須由子類實現*/
3.2. Writer抽象類
寫入字元流的抽象類。子類必須實現的方法僅有 write(char[], int, int)、flush() 和 close()。但是,多數子類將重寫此處定義的一些方法,以提供更高的效率和/或其他功能。 其子類如下:

1) FileWrite: 與FileOutputStream對應
將字元型別資料寫入檔案,使用預設字元編碼和緩衝器大小。
Public FileWrite(file f);
2) chararrayWrite:與ByteArrayOutputStream對應 ,將字元緩衝器用作輸出。
Public CharArrayWrite();
3) PrintWrite:生成格式化輸出
public PrintWriter(outputstream os);
4) filterWriter:用於寫入過濾字元流
protected FilterWriter(Writer w);
5) PipedWriter:與PipedOutputStream對應
6) StringWriter:無與之對應的以位元組為導向的stream
主要方法:
(1) public void write(int c) throws IOException; //將整型值c的低16位寫入輸出流
(2) public void write(char cbuf[]) throws IOException; //將字元陣列cbuf[]寫入輸出流
(3) public abstract void write(char cbuf[],int off,int len) throws IOException; //將字元陣列cbuf[]中的從索引為off的位置處開始的len個字元寫入輸出流
(4) public void write(String str) throws IOException; //將字串str中的字元寫入輸出流
(5) public void write(String str,int off,int len) throws IOException; //將字串str 中從索引off開始處的len個字元寫入輸出流
(6) flush( ) //刷空輸出流,並輸出所有被快取的位元組。
(7)close() 關閉流 public abstract void close() throws IOException
3.3 .InputStream與Reader差別 OutputStream與Writer差別
InputStream和OutputStream類處理的是位元組流,資料流中的最小單位是位元組(8個bit)
Reader與Writer處理的是字元流,在處理字元流時涉及了字元編碼的轉換問題
- import java.io.*;
- publicclass EncodeTest {
- privatestaticvoid readBuff(byte [] buff) throws IOException {
- ByteArrayInputStream in =new ByteArrayInputStream(buff);
- int data;
- while((data=in.read())!=-1) System.out.print(data+" ");
- System.out.println(); in.close(); }
- publicstaticvoid main(String args[]) throws IOException {
- System.out.println("記憶體中採用unicode字元編碼:" );
- char c='好';
- int lowBit=c&0xFF; int highBit=(c&0xFF00)>>8;
- System.out.println(""+lowBit+" "+highBit);
- String s="好";
- System.out.println("本地作業系統預設字元編碼:");
- readBuff(s.getBytes());
- System.out.println("採用GBK字元編碼:");
- readBuff(s.getBytes("GBK"));
- System.out.println("採用UTF-8字元編碼:");
- readBuff(s.getBytes("UTF-8")); }
- }

Reader類能夠將輸入流中採用其他編碼型別的字元轉換為Unicode字元,然後在記憶體中為其分配記憶體
Writer類能夠將記憶體中的Unicode字元轉換為其他編碼型別的字元,再寫到輸出流中。
