【Linux】淺談Linux下的PCB—task_struct結構體
1.1 程序的概念
我之前在作業系統這門課中學過的有關程序的概念如下:
從作業系統層面上講:程序是程式的一次執行過程,是系統進行資源分配和處理機排程的一個獨立單位。程序的結構特性:程序=程式段+資料段+程序控制塊。程序的三種基本狀態:
對於一個程式來說,是不是隻要不在執行狀態,就一定不是程序呢?
不是。假如在單處理機的系統中,一次只能執行一個程序,即只有一個程序處於執行狀態,那麼其他的被載入到記憶體的程式(已經獲得了除處理機之外的所需的全部資源),
也是程序。
從核心的層面上講:程序擔當分配系統資源(包括記憶體等)的實體。 程序的兩個基本元素是程式程式碼(可能與其他程序共享)和與程式碼相關聯的資料集(這個是私有的)。這與程序的結構特性是一樣的:程序=程式段+資料段+程序控制塊。“。資料集就是指的是資料段和程序控制塊。其中程式碼段是共享的,資料段是私有的。
1.2 程序控制塊(PCB)
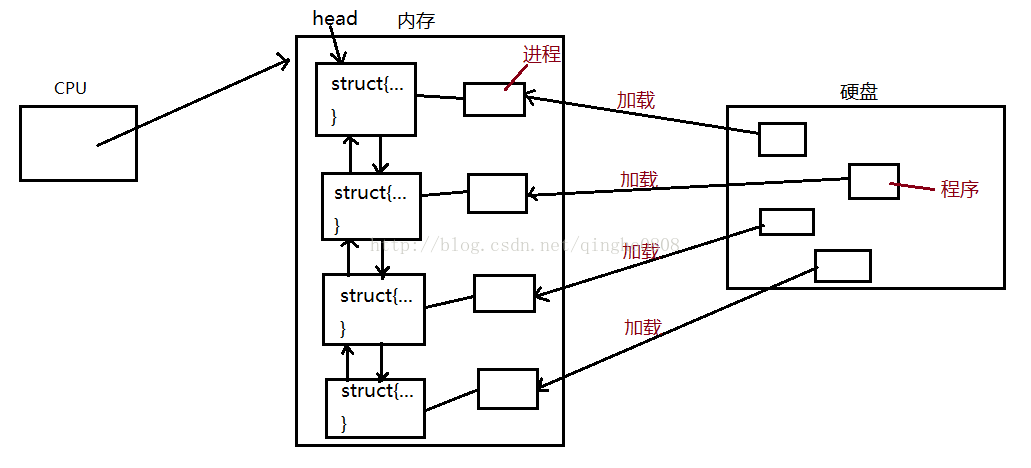
當一個程式載入到記憶體當中,計算機系統中就有了一個程序。每個程序在核心中都有一個程序控制塊(PCB)來維護自身程序的資訊,這個程序控制塊(PCB)是為了方便進行程序管理所設定的一個資料結構,裡面存放的是程序的相關資訊。也就是說,程序管理管理的是PCB。
程序控制塊(PCB)具體起什麼作用?在單處理機系統,我們每次只能執行一個程序,我們如何知道是哪個程序在執行?執行完這個程序之後,又需要去執行哪些程序?假如一個程序由於種種原因,需要被中斷,那麼之後再來執行此程序的時候,我們怎麼會知道之前執行到哪,等等情形,所以就需要程序控制塊。通過分析以上的種種情況,我們得出:程序控制塊至少應該包含程序標識(是程序的唯一標識,PID),還有程序的優先順序,記錄程序的上下文資訊,記錄程序下一次下一條指令的地址,程序中的程式的地址,等等。當作業系統要排程某程序去執行時,要從該程序的PCB中查詢程序的優先順序和現行狀態;當系統排程到某個程序時,要根據PCB中儲存的現行資訊先去恢復現場,然後再去修改程序的狀態,根據程式的地址,找到程式的位置,並開始執行;當程序由於某個原因需要暫停時,就必須將現行狀態儲存在PCB中,並記錄下一條指令的地址。可見,在程序的整個執行過程中,程序控制塊都起著非常重要的作用。
Linux核心的程序控制塊是task_struct結構體,task_struct是Linux核心的一種資料結構,它會被裝載到RAM裡並且包含著程序的資訊。每個程序都把它的資訊放在task_struct這個資料結構裡,task_struct裡包含了這些程序資訊:
識別符號、狀態、優先順序、程式計數器、記憶體指標、上下文資料、I/O狀態資訊、記賬資訊。
在Linux系統中,所有執行在系統裡的程序都是task_struct連結串列的形式存在核心裡。見下圖:
下面,我們開始剖析task_struct結構體。
1.3 task_struct結構體
centos6.5 Linux核心下,開啟/usr/src/kernels/2.6.32-431.el6.i686/include/linux/sched.h 可以找到task_struct的定義。
1>程序狀態(state)
volatile long state;
int exit_state;
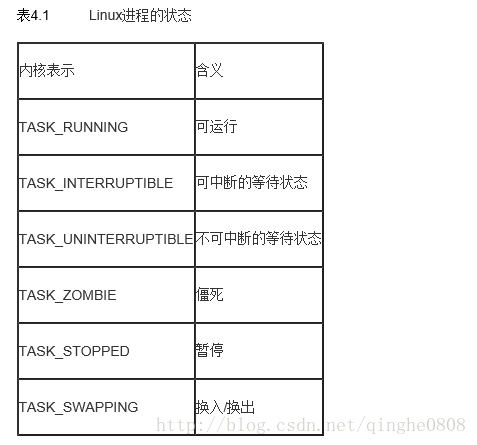
程序可能出現的狀態如下:
#define TASK_RUNNING 0
#define TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE 1
#define TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE 2
#define __TASK_STOPPED 4
#define __TASK_TRACED 8
/* in tsk->exit_state */
#define EXIT_ZOMBIE 16
#define EXIT_DEAD 32
/* in tsk->state again */
#define TASK_DEAD 64
#define TASK_WAKEKILL 128
#define TASK_WAKING 256
2>程序識別符號(PID)
pid_t pid;//程序的唯一標識
pid_t tgid;// 執行緒組的領頭執行緒的pid成員的值
PID的取值範圍是0到32767,即系統中的程序數最大為32768個。
在Linux系統中,一個執行緒組中的所有執行緒使用和該執行緒組的領頭執行緒(該組中的第一個輕量級程序)相同的PID,並被存放在tgid成員中。(執行緒是程式執行的最小單位,程序是程式執行的基本單位。)
3>程序核心棧
void *stack
stack用來維護分配給程序的核心棧,核心棧的意義在於,程序task_struct所佔的記憶體是由核心動態分配的,確切的說就是核心根本不給task_struct分配記憶體,只給核心棧分配8KB記憶體,並且一部分會提供給task_struct使用。
task_struct結構體大約佔用的大小為1K左右,根據核心版本的不同,大小也會有差異。
所以,也就可以知道核心棧最大也就是7KB,否則,核心棧會覆蓋task_struct結構。
Linux核心通過thread_union聯合體來表示程序的核心棧.
union thread_union {
struct thread_info thread_info;
unsigned long stack[THREAD_SIZE/sizeof(long)];
};4>標記
unsigned int flags; /* per process flags, defined below */
用來反映一個程序的狀態資訊,但不是執行狀態,用於核心識別程序當前的狀態,flags成員的可能取值如下:
/*
* Per process flags
*/
#define PF_ALIGNWARN 0x00000001 /* Print alignment warning msgs */
/* Not implemented yet, only for 486*/
#define PF_STARTING 0x00000002 /* being created */
#define PF_EXITING 0x00000004 /* getting shut down */
#define PF_EXITPIDONE 0x00000008 /* pi exit done on shut down */
#define PF_VCPU 0x00000010 /* I'm a virtual CPU */
#define PF_FORKNOEXEC 0x00000040 /* forked but didn't exec */
#define PF_MCE_PROCESS 0x00000080 /* process policy on mce errors */
#define PF_SUPERPRIV 0x00000100 /* used super-user privileges */
#define PF_DUMPCORE 0x00000200 /* dumped core */
#define PF_SIGNALED 0x00000400 /* killed by a signal */
#define PF_MEMALLOC 0x00000800 /* Allocating memory */
#define PF_FLUSHER 0x00001000 /* responsible for disk writeback */
#define PF_USED_MATH 0x00002000 /* if unset the fpu must be initialized before use */
#define PF_FREEZING 0x00004000 /* freeze in progress. do not account to load */
#define PF_NOFREEZE 0x00008000 /* this thread should not be frozen */
#define PF_FROZEN 0x00010000 /* frozen for system suspend */
#define PF_FSTRANS 0x00020000 /* inside a filesystem transaction */
#define PF_KSWAPD 0x00040000 /* I am kswapd */
#define PF_LESS_THROTTLE 0x00100000 /* Throttle me less: I clean memory */
#define PF_KTHREAD 0x00200000 /* I am a kernel thread */
#define PF_RANDOMIZE 0x00400000 /* randomize virtual address space */
#define PF_SWAPWRITE 0x00800000 /* Allowed to write to swap */
#define PF_SPREAD_PAGE 0x01000000 /* Spread page cache over cpuset */
#define PF_SPREAD_SLAB 0x02000000 /* Spread some slab caches over cpuset */
#define PF_THREAD_BOUND 0x04000000 /* Thread bound to specific cpu */
#define PF_MCE_EARLY 0x08000000 /* Early kill for mce process policy */
#define PF_MEMPOLICY 0x10000000 /* Non-default NUMA mempolicy */
#define PF_MUTEX_TESTER 0x20000000 /* Thread belongs to the rt mutex tester */
#define PF_FREEZER_SKIP 0x40000000 /* Freezer should not count it as freezeable */
#define PF_FREEZER_NOSIG 0x80000000 /* Freezer won't send signals to it */
5>表示程序親屬關係的成員
struct task_struct *real_arent; /* real parent process */
struct task_struct *parent; /* recipient of SIGCHLD, wait4() reports */
struct list_head children; /* list of my children */
struct list_head sibling; /* linkage in my parent's children list */
struct task_struct *group_leader; /* threadgroup leader */
在Linux系統中,所有程序之間都有著直接或間接地聯絡,每個程序都有其父程序,也可能有零個或多個子程序。擁有同一父程序的所有程序具有兄弟關係。
real_parent指向其父程序,如果建立它的父程序不再存在,則指向PID為1的init程序。
parent指向其父程序,當它終止時,必須向它的父程序傳送訊號。它的值通常與real_parent相同。
children表示連結串列的頭部,連結串列中的所有元素都是它的子程序。
sibling用於把當前程序插入到兄弟連結串列中。
group_leader指向其所在程序組的領頭程序。
6>程序排程
int prio, static_prio, normal_prio;
unsigned int rt_priority;
const struct sched_class *sched_class;
struct sched_entity se;
struct sched_rt_entity rt;
unsigned int policy;
cpumask_t cpus_allowed;
prio用於儲存動態優先順序。
static_prio用於儲存靜態優先順序,可以通過nice系統呼叫來進行修改。 normal_prio的值取決於靜態優先順序和排程策略。rt_priority用於儲存實時優先順序。 policy表示程序的排程策略。 這裡重點說明一下程序排程策略,我們來看下關於排程策略的成員:
unsigned int policy;
const struct sched_class *sched_class;
struct sched_entity se;
struct sched_rt_entity rt;
 policy表示程序的排程策略,主要有以下五種:
policy表示程序的排程策略,主要有以下五種:
#define SCHED_NORMAL 0//按照優先順序進行排程(有些地方也說是CFS排程器)
#define SCHED_FIFO 1//先進先出的排程演算法
#define SCHED_RR 2//時間片輪轉的排程演算法
#define SCHED_BATCH 3//用於非互動的處理機消耗型的程序
#define SCHED_IDLE 5//系統負載很低時的排程演算法
#define SCHED_RESET_ON_FORK 0x40000000
7> ptrace系統呼叫
unsigned int ptrace;
struct list_head ptraced;
struct list_head ptrace_entry;
8>效能診斷工具——Performance Event
#ifdef CONFIG_PERF_EVENTS
#ifndef __GENKSYMS__
void * __reserved_perf__;
#else
struct perf_event_context *perf_event_ctxp;
#endif
struct mutex perf_event_mutex;
struct list_head perf_event_list;
#endif
PerformanceEvent是一款隨 Linux 核心程式碼一同釋出和維護的效能診斷工具。這些成員用於幫PerformanceEvent分析程序的效能問題。
9>程序的地址空間
struct mm_struct *mm, *active_mm;
mm 程序所擁有的使用者空間的記憶體描述符
| active_mm 指向程序執行時使用的記憶體描述符,對於普通的程序來說,mm和active_mm是一樣的,但是核心執行緒是沒有程序地址空間的,所以核心執行緒的mm是空的,所以需要初始化核心執行緒的active_mm |
10>時間與定時器
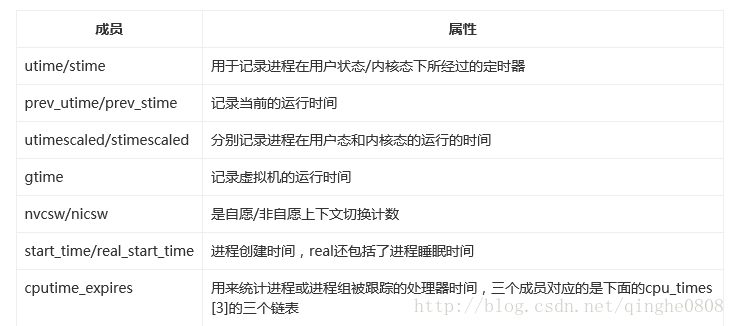
一個程序從建立到終止叫做該程序的生存期。程序在其生存期內使用CPU的時間,核心都要進行記錄,以便進行統計、計費等有關操作。程序耗費CPU的時間由兩部分組成:一是在使用者模式(或稱為使用者態)下耗費的時間、一是在系統模式(或稱為系統態)下耗費的時間。每個時鐘滴答,也就是每個時鐘中斷,核心都要更新當前程序耗費CPU的時間資訊。描述CPU時間的內容如下:
cputime_t utime, stime, utimescaled, stimescaled;
cputime_t gtime;
cputime_t prev_utime, prev_stime;
unsigned long nvcsw, nivcsw;
struct timespec start_time;
struct timespec real_start_time;
unsigned long min_flt, maj_flt;
struct task_cputime cputime_expires;
struct list_head cpu_timers[3];
struct list_head run_list;
unsigned long timeout;//當前已使用的時間(與開始時間的差值)
unsigned int time_slice;//程序的時間片的大小
int nr_cpus_allowed;
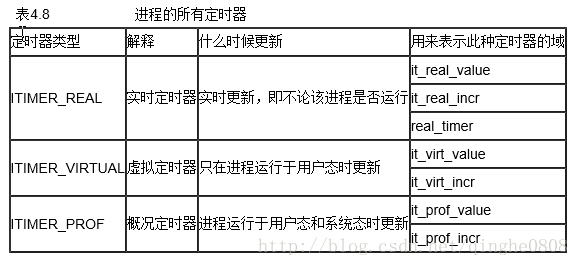
程序有三種類型的定時器:實時定時器、虛擬定時器和概況定時器。這三種定時器的特徵共有三個:到期時間、定時間隔、要觸發的事件。
11>判斷標誌
//用於程序判斷標誌
int exit_state;
int exit_code, exit_signal;
int pdeath_signal;
unsigned int personality;
unsigned did_exec:1;
unsigned in_execve:1;
unsigned in_iowait:1;
unsigned sched_reset_on_fork:1;
exit_state 程序終止的狀態
exit_code 設定程序的終止代號
exit_signal 設定為-1的時候表示是某個執行緒組當中的一員,只有當執行緒組的最後一個成員終止時,才會產生型號給父程序
pdeath_signal 用來判斷父程序終止時的訊號
12>訊號處理資訊
struct signal_struct *signal; //指向程序訊號描述符
struct sighand_struct *sighand; //指向程序訊號處理程式描述符
sigset_t blocked, real_blocked; //阻塞訊號的掩碼
sigset_t saved_sigmask;
struct sigpending pending; //程序上還需要處理的訊號
unsigned long sas_ss_sp; //訊號處理程式備用堆疊的地址
size_t sas_ss_size; //訊號處理程式的堆疊的地址
13>檔案系統資訊
程序可以開啟或關閉檔案,檔案屬於系統資源,Linux核心要對程序使用檔案的情況進行記錄。task_struct結構中有兩個資料結構用於描述程序與檔案相關的資訊。其中,fs_struct中描述了兩個VFS索引節點,這兩個索引節點叫做root和pwd。file_struct結構用來記錄了程序開啟的檔案的描述符。
//檔案系統資訊結構體
struct fs_struct *fs;
//開啟檔案相關資訊結構體
struct files_struct *files;struct fs_struct *fs 程序可執行映象所在的檔案系統
struct files_struct *files 程序當前開啟的檔案
14>task_struct的完整定義及註釋
struct task_struct {
//程序狀態(-1就緒態,0執行態,>0停止態)
volatile long state; /* -1 unrunnable, 0 runnable, >0 stopped */
//程序核心棧
void *stack;
//有幾個程序只在使用此結構
atomic_t usage;
//標記
unsigned int flags; /* per process flags, defined below */
//ptrace系統呼叫,關於實現斷點除錯,跟蹤程序執行。
unsigned int ptrace;
//鎖的深度
int lock_depth; /* BKL lock depth */
//SMP實現無加鎖的程序切換
#ifdef CONFIG_SMP
#ifdef __ARCH_WANT_UNLOCKED_CTXSW
int oncpu;
#endif
#endif
//關於程序排程
int prio, static_prio, normal_prio;
//優先順序
unsigned int rt_priority;
//關於程序
const struct sched_class *sched_class;
struct sched_entity se;
struct sched_rt_entity rt;
//preempt_notifier結構體連結串列
#ifdef CONFIG_PREEMPT_NOTIFIERS
/* list of struct preempt_notifier: */
struct hlist_head preempt_notifiers;
#endif
/*
* fpu_counter contains the number of consecutive context switches
* that the FPU is used. If this is over a threshold, the lazy fpu
* saving becomes unlazy to save the trap. This is an unsigned char
* so that after 256 times the counter wraps and the behavior turns
* lazy again; this to deal with bursty apps that only use FPU for
* a short time
*/
//FPU使用計數
unsigned char fpu_counter;
//塊裝置I/O層的跟蹤工具
#ifdef CONFIG_BLK_DEV_IO_TRACE
unsigned int btrace_seq;
#endif
//程序排程策略相關的欄位
unsigned int policy;
cpumask_t cpus_allowed;
//RCU同步原語
#ifdef CONFIG_TREE_PREEMPT_RCU
int rcu_read_lock_nesting;
char rcu_read_unlock_special;
struct rcu_node *rcu_blocked_node;
struct list_head rcu_node_entry;
#endif /* #ifdef CONFIG_TREE_PREEMPT_RCU */
//用於排程器統計程序執行資訊
#if defined(CONFIG_SCHEDSTATS) || defined(CONFIG_TASK_DELAY_ACCT)
struct sched_info sched_info;
#endif
//用於構架程序連結串列
struct list_head tasks;
struct plist_node pushable_tasks;
//關於程序的地址空間,指向程序的地址空間。(連結串列和紅黑樹)
struct mm_struct *mm, *active_mm;
/* task state */
//程序狀態引數
int exit_state;
//退出訊號處理
int exit_code, exit_signal;
//接收父程序終止的時候會發送訊號
int pdeath_signal; /* The signal sent when the parent dies */
/* ??? */
unsigned int personality;
unsigned did_exec:1;
unsigned in_execve:1; /* Tell the LSMs that the process is doing an
* execve */
unsigned in_iowait:1;
/* Revert to default priority/policy when forking */
unsigned sched_reset_on_fork:1;
//程序pid,父程序ppid。
pid_t pid;
pid_t tgid;
//防止核心堆疊溢位
#ifdef CONFIG_CC_STACKPROTECTOR
/* Canary value for the -fstack-protector gcc feature */
unsigned long stack_canary;
#endif
/*
* pointers to (original) parent process, youngest child, younger sibling,
* older sibling, respectively. (p->father can be replaced with
* p->real_parent->pid)
*/
//這部分是用來進行維護程序之間的親屬關係的。
//初始化父程序
struct task_struct *real_parent; /* real parent process */
//接納終止的程序
struct task_struct *parent; /* recipient of SIGCHLD, wait4() reports */
/*
* children/sibling forms the list of my natural children
*/
//維護子程序連結串列
struct list_head children; /* list of my children */
//兄弟程序連結串列
struct list_head sibling; /* linkage in my parent's children list */
//執行緒組組長
struct task_struct *group_leader; /* threadgroup leader */
/*
* ptraced is the list of tasks this task is using ptrace on.
* This includes both natural children and PTRACE_ATTACH targets.
* p->ptrace_entry is p's link on the p->parent->ptraced list.
*/
//ptrace,系統呼叫,關於斷點除錯。
struct list_head ptraced;
struct list_head ptrace_entry;
//PID與PID散列表的聯絡
/* PID/PID hash table linkage. */
struct pid_link pids[PIDTYPE_MAX];
//維護一個連結串列,裡面有該程序所有的執行緒
struct list_head thread_group;
//do_fork()函式
struct completion *vfork_done; /* for vfork() */
int __user *set_child_tid; /* CLONE_CHILD_SETTID */
int __user *clear_child_tid; /* CLONE_CHILD_CLEARTID */
//描述CPU時間的內容
//utime是使用者態下的執行時間
//stime是核心態下的執行時間
cputime_t utime, stime, utimescaled, stimescaled;
cputime_t gtime;
cputime_t prev_utime, prev_stime;
//上下文切換計數
unsigned long nvcsw, nivcsw; /* context switch counts */
struct timespec start_time; /* monotonic time */
struct timespec real_start_time; /* boot based time */
/* mm fault and swap info: this can arguably be seen as either mm-specific or thread-specific */
//缺頁統計
unsigned long min_flt, maj_flt;
struct task_cputime cputime_expires;
struct list_head cpu_timers[3];
/* process credentials */
//程序身份憑據
const struct cred *real_cred; /* objective and real subjective task
* credentials (COW) */
const struct cred *cred; /* effective (overridable) subjective task
* credentials (COW) */
struct mutex cred_guard_mutex; /* guard against foreign influences on
* credential calculations
* (notably. ptrace) */
struct cred *replacement_session_keyring; /* for KEYCTL_SESSION_TO_PARENT */
//去除路徑以後的可執行檔名稱,程序名
char comm[TASK_COMM_LEN]; /* executable name excluding path
- access with [gs]et_task_comm (which lock
it with task_lock())
- initialized normally by setup_new_exec */
/* file system info */
//檔案系統資訊
int link_count, total_link_count;
#ifdef CONFIG_SYSVIPC
/* ipc stuff */
//程序通訊
struct sysv_sem sysvsem;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_DETECT_HUNG_TASK
/* hung task detection */
unsigned long last_switch_count;
#endif
//該程序在特點CPU下的狀態
/* CPU-specific state of this task */
struct thread_struct thread;
//檔案系統資訊結構體
/* filesystem information */
struct fs_struct *fs;
//開啟檔案相關資訊結構體
/* open file information */
struct files_struct *files;
/* namespaces */
//名稱空間:
struct nsproxy *nsproxy;
/* signal handlers */
//關於進行訊號處理
struct signal_struct *signal;
struct sighand_struct *sighand;
sigset_t blocked, real_blocked;
sigset_t saved_sigmask; /* restored if set_restore_sigmask() was used */
struct sigpending pending;
unsigned long sas_ss_sp;
size_t sas_ss_size;
int (*notifier)(void *priv);
void *notifier_data;
sigset_t *notifier_mask;
//程序審計
struct audit_context *audit_context;
#ifdef CONFIG_AUDITSYSCALL
uid_t loginuid;
unsigned int sessionid;
#endif
seccomp_t seccomp;
#ifdef CONFIG_UTRACE
struct utrace *utrace;
unsigned long utrace_flags;
#endif
//執行緒跟蹤組
/* Thread group tracking */
u32 parent_exec_id;
u32 self_exec_id;
/* Protection of (de-)allocation: mm, files, fs, tty, keyrings, mems_allowed,
* mempolicy */
spinlock_t alloc_lock;
//中斷
#ifdef CONFIG_GENERIC_HARDIRQS
/* IRQ handler threads */
struct irqaction *irqaction;
#endif
//task_rq_lock函式所使用的鎖
/* Protection of the PI data structures: */
spinlock_t pi_lock;
//基於PI協議的等待互斥鎖
#ifdef CONFIG_RT_MUTEXES
/* PI waiters blocked on a rt_mutex held by this task */
struct plist_head pi_waiters;
/* Deadlock detection and priority inheritance handling */
struct rt_mutex_waiter *pi_blocked_on;
#endif
//死鎖檢測
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_MUTEXES
/* mutex deadlock detection */
struct mutex_waiter *blocked_on;
#endif
//中斷
#ifdef CONFIG_TRACE_IRQFLAGS
unsigned int irq_events;
int hardirqs_enabled;
unsigned long hardirq_enable_ip;
unsigned int hardirq_enable_event;
unsigned long hardirq_disable_ip;
unsigned int hardirq_disable_event;
int softirqs_enabled;
unsigned long softirq_disable_ip;
unsigned int softirq_disable_event;
unsigned long softirq_enable_ip;
unsigned int softirq_enable_event;
int hardirq_context;
int softirq_context;
#endif
//lockdep
#ifdef CONFIG_LOCKDEP
# define MAX_LOCK_DEPTH 48UL
u64 curr_chain_key;
int lockdep_depth;
unsigned int lockdep_recursion;
struct held_lock held_locks[MAX_LOCK_DEPTH];
gfp_t lockdep_reclaim_gfp;
#endif
//日誌檔案
/* journalling filesystem info */
void *journal_info;
/* stacked block device info */
//塊裝置連結串列
struct bio *bio_list, **bio_tail;
/* VM state */
//虛擬記憶體狀態,記憶體回收
struct reclaim_state *reclaim_state;
//存放塊裝置I/O流量資訊
struct backing_dev_info *backing_dev_info;
//I/O排程器所用資訊
struct io_context *io_context;
unsigned long ptrace_message;
siginfo_t *last_siginfo; /* For ptrace use. */
//記錄程序I/O計數
struct task_io_accounting ioac;
#if defined(CONFIG_TASK_XACCT)
u64 acct_rss_mem1; /* accumulated rss usage */
u64 acct_vm_mem1; /* accumulated virtual memory usage */
cputime_t acct_timexpd; /* stime + utime since last update */
#endif
//CPUSET功能
#ifdef CONFIG_CPUSETS
nodemask_t mems_allowed; /* Protected by alloc_lock */
#ifndef __GENKSYMS__
/*
* This does not change the size of the struct_task(2+2+4=4+4)
* so the offsets of the remaining fields are unchanged and
* therefore the kABI is preserved. Only the kernel uses
* cpuset_mem_spread_rotor and cpuset_slab_spread_rotor so
* it is safe to change it to use shorts instead of ints.
*/
unsigned short cpuset_mem_spread_rotor;
unsigned short cpuset_slab_spread_rotor;
int mems_allowed_change_disable;
#else
int cpuset_mem_spread_rotor;
int cpuset_slab_spread_rotor;
#endif
#endif
//Control Groups
#ifdef CONFIG_CGROUPS
/* Control Group info protected by css_set_lock */
struct css_set *cgroups;
/* cg_list protected by css_set_lock and tsk->alloc_lock */
struct list_head cg_list;
#endif
//futex同步機制
#ifdef CONFIG_FUTEX
struct robust_list_head __user *robust_list;
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
struct compat_robust_list_head __user *compat_robust_list;
#endif
struct list_head pi_state_list;
struct futex_pi_state *pi_state_cache;
#endif
//關於記憶體檢測工具Performance Event
#ifdef CONFIG_PERF_EVENTS
#ifndef __GENKSYMS__
void * __reserved_perf__;
#else
struct perf_event_context *perf_event_ctxp;
#endif
struct mutex perf_event_mutex;
struct list_head perf_event_list;
#endif
//非一致記憶體訪問
#ifdef CONFIG_NUMA
struct mempolicy *mempolicy; /* Protected by alloc_lock */
short il_next;
#endif
//檔案系統互斥資源
atomic_t fs_excl; /* holding fs exclusive resources */
//RCU連結串列
struct rcu_head rcu;
/*
* cache last used pipe for splice
*/
//管道
struct pipe_inode_info *splice_pipe;
//延遲計數
#ifdef CONFIG_TASK_DELAY_ACCT
struct task_delay_info *delays;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_FAULT_INJECTION
int make_it_fail;
#endif
struct prop_local_single dirties;
#ifdef CONFIG_LATENCYTOP
int latency_record_count;
struct latency_record latency_record[LT_SAVECOUNT];
#endif
/*
* time slack values; these are used to round up poll() and
* select() etc timeout values. These are in nanoseconds.
*/
//time slack values,常用於poll和select函式
unsigned long timer_slack_ns;
unsigned long default_timer_slack_ns;
//socket控制訊息
struct list_head *scm_work_list;
#ifdef CONFIG_FUNCTION_GRAPH_TRACER
//ftrace跟蹤器
/* Index of current stored adress in ret_stack */
int curr_ret_stack;
/* Stack of return addresses for return function tracing */
struct ftrace_ret_stack *ret_stack;
/* time stamp for last schedule */
unsigned long long ftrace_timestamp;
/*
* Number of functions that haven't been traced
* because of depth overrun.
*/
atomic_t trace_overrun;
/* Pause for the tracing */
atomic_t tracing_graph_pause;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_TRACING
/* state flags for use by tracers */
unsigned long trace;
/* bitmask of trace recursion */
unsigned long trace_recursion;
#endif /* CONFIG_TRACING */
/* reserved for Red Hat */
unsigned long rh_reserved[2];
#ifndef __GENKSYMS__
struct perf_event_context *perf_event_ctxp[perf_nr_task_contexts];
#ifdef CONFIG_CGROUP_MEM_RES_CTLR /* memcg uses this to do batch job */
struct memcg_batch_info {
int do_batch; /* incremented when batch uncharge started */
struct mem_cgroup *memcg; /* target memcg of uncharge */
unsigned long bytes; /* uncharged usage */
unsigned long memsw_bytes; /* uncharged mem+swap usage */
} memcg_batch;
#endif
#endif
};
參考: