c#基礎入門(5)——File、FileStream、StreamReader、StreamWriter
File
File的用法如下:
public void OperateFile()
{
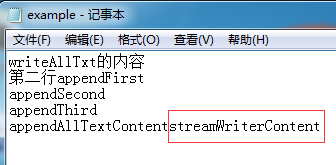
//example檔案初始內容截圖如圖一
string filePath = @"e:\Study\test\example.txt";
if (File.Exists(filePath))
{
//allText="蟈蟈first\r\n蟈蟈second\r\n蟈蟈third"
string allText =
File.ReadAllText(filePath,Encoding.Default);
//allLines[0]="蟈蟈first" 
FileStream
FileStream物件表示在磁碟或網路路徑上指向檔案的流。這個類提供了在檔案中讀寫位元組的方法,但經常使用StreamReader或StreamWriter執行這些功能。這是因為FileStream類操作的是位元組和位元組陣列(不僅可以讀寫txt還能讀寫.mp3……),而Stream類操作的是字元資料(只能是文字)。
檔案的訪問方式(FileAccess),包括三個列舉:
FileAccess.Read(對檔案讀訪問)
FileAccess.Write(對檔案進行寫操作)
FileAccess.ReadWrite(對檔案讀或寫操作)
在FileStream建構函式不使用FileAccess列舉引數的版本中,使用預設值FileAccess. ReadWrite,即有檔案的讀寫許可權。
注意:
檔案流使用結束後,一定要Close或Dispose,using(){}方法在使用完檔案流物件後會自動將其釋放
public void OperateFileStream()
{
string [email protected]"E:\Study\test\example.txt";
byte[] byteArray= new byte[1024];
using (FileStream sReader = new FileStream(filePath, FileMode.Open))
{
//length=32,漢字佔2個位元組、英文佔1個位元組2*6+5+6+5+2*2=32
int length = sReader.Read(byteArray, 0, byteArray.Length);
//result="蟈蟈first\r\n蟈蟈second\r\n蟈蟈third"
string result = System.Text.Encoding.Default.GetString(byteArray, 0, length);
//result="蟈蟈first\r\n蟈蟈second\r\n蟈蟈third\0\0\0\0\0......"
//"\0"指的是空字元
//byteArray的長度是1024資料不夠1024byte時用"\0"填充
result = System.Text.Encoding.Default.GetString(byteArray);
}
using (FileStream sReader = new FileStream(filePath, FileMode.Open))
{
//sReader.Length=32
byte[] buffer = new byte[sReader.Length];
//length=32,漢字佔2個位元組、英文佔1個位元組2*6+5+6+5+2*2=32
int length = sReader.Read(buffer, 0, buffer.Length);
//result="蟈蟈first\r\n蟈蟈second\r\n蟈蟈third"
string result = System.Text.Encoding.Default.GetString(buffer, 0, length);
//result="蟈蟈first\r\n蟈蟈second\r\n蟈蟈third"
result = System.Text.Encoding.Default.GetString(buffer);
}
using (FileStream sWriter = new FileStream(filePath, FileMode.Create))
{
string content = "fileStream寫入";
byte[] buffer = System.Text.Encoding.Default.GetBytes(content);
sWriter.Write(buffer, 0, buffer.Length);
//清空緩衝區,將緩衝區的資料寫入到檔案
sWriter.Flush();
//example檔案中的內容變為"fileStream寫入"
}
using (FileStream sAppender = new FileStream(filePath, FileMode.Append))
{
string content = "fileStream追加";
byte[] buffer = System.Text.Encoding.Default.GetBytes(content);
sAppender.Write(buffer, 0, buffer.Length);
//清空緩衝區,將緩衝區的資料寫入到檔案
sAppender.Flush();
//example檔案中的內容變為"fileStream寫入fileStream寫入的內容fileStream追加"
}
}StreamReader&StreamWriter
StreamReader實現了抽象基類TextReader,而StreamWriter實現了抽象基類TextWriter,兩者分別用於對流的讀取與寫入。
StreamReader類:
1、公共屬性
BaseStream 返回基礎流。
CurrentEncoding 獲取當前 StreamReader 物件正在使用的當前字元編碼。
EndOfStream 獲取一個值,該值表示當前的流位置是否在流的末尾。2、公共方法
Close, 關閉 StreamReader 物件和基礎流,並釋放與讀取器關聯的所有系統資源。 (重寫 TextReader..::.Close()()()。)
CreateObjRef, 建立一個物件,該物件包含生成用於與遠端物件進行通訊的代理所需的全部相關資訊。 (繼承自 MarshalByRefObject。)
DiscardBufferedData, 允許 StreamReader 物件丟棄其當前資料。
Dispose 已過載。
GetLifetimeService, 檢索控制此例項的生存期策略的當前生存期服務物件。 (繼承自 MarshalByRefObject。)
InitializeLifetimeService, 獲取控制此例項的生存期策略的生存期服務物件。 (繼承自 MarshalByRefObject。)
MemberwiseClone, 已過載。
Peek, 返回下一個可用的字元,但不使用它。 (重寫 TextReader..::.Peek()()()。)
Read, 已過載。 讀取輸入流中的下一個字元或下一組字元。
ReadBlock, 從當前流中讀取最大 count 的字元並從 index 開始將該資料寫入 buffer。 (繼承自 TextReader。)
ReadLine, 從當前流中讀取一行字元並將資料作為字串返回。 (重寫 TextReader..::.ReadLine()()()。)
ReadToEnd, 從流的當前位置到末尾讀取流。 (重寫 TextReader..::.ReadToEnd()()()。)StreamReader例項程式碼如下:
public void OperateStream()
{
string filePath = @"e:\Study\test\example.txt";
string errorMsg = string.Empty;
string msg=string.Empty;
try
{
//生成StreamReader例項物件,方法一
StreamReader sReader = new StreamReader(filePath);
//成StreamReader例項物件,方法二
//FileStream fileStream = new FileStream(filePath, FileMode.Open);
//StreamReader sReaderFromFileStream = new StreamReader(fileStream);
//每次只讀一行
msg = sReader.ReadLine();
while (msg!=null)
{
Console.WriteLine("msg=" + msg);
msg = sReader.ReadLine();
}
sReader.Close();
sReader = new StreamReader(filePath);
//EndOfStream判斷當前的流位置是否在流的末尾
//如果檔案中沒有內容,EndOfStream為true
while (!sReader.EndOfStream)
{
//每次只讀一行
msg = sReader.ReadLine();
Console.WriteLine("msg=" + msg);
}
sReader.Close();
sReader = new StreamReader(filePath);
//EndOfStream判斷當前的流位置是否在流的末尾
//如果檔案中沒有內容,EndOfStream為true
while (!sReader.EndOfStream)
{
//讀取檔案中所有內容
//此處為:蟈蟈first\r\n蟈蟈second\r\n蟈蟈third
msg = sReader.ReadToEnd();
Console.WriteLine("msg=" + msg);
}
sReader.Close();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
errorMsg = ex.Message;
}
}StreamWriter例項程式碼如下:
public void OperateStream()
{
string filePath = @"e:\Study\test\example.txt";
string errorMsg = string.Empty;
string msg=string.Empty;
try
{
//生成StreamWriter例項物件,方法一
StreamWriter sWriter = new StreamWriter(filePath);
//生成StreamWriter例項物件,方法二
//FileStream fileStream = new FileStream(filePath, FileMode.Create);
//StreamWriter sWriterFromFileStream = new StreamWriter(fileStream);
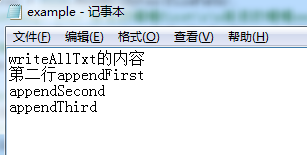
//會替換原有內容
sWriter.Write("Write內容");
sWriter.Close();
sWriter = new StreamWriter(filePath);
//會替換原有內容
sWriter.WriteLine("WriteLine內容");
sWriter.Close();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
errorMsg = ex.Message;
}
try
{
//生成StreamWriter追加內容例項物件,方法一
StreamWriter sAppender = new StreamWriter(filePath, true);
//生成StreamWriter追加內容例項物件,方法二
//FileStream fileStream = new FileStream(filePath, FileMode.Append);
//StreamWriter sAppenderFromFileStream = new StreamWriter(fileStream);
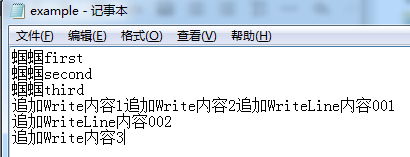
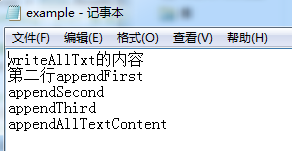
sAppender.Write("追加Write內容1");
sAppender.Write("追加Write內容2");
//WriteLine會在內容之後加上"\r\n"
sAppender.WriteLine("追加WriteLine內容001");
sAppender.WriteLine("追加WriteLine內容002");
sAppender.Write("追加Write內容3");
//追加後文件截圖如下
sAppender.Close();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
errorMsg = ex.Message;
}
}相關推薦
c#基礎入門(5)——File、FileStream、StreamReader、StreamWriter
File File的用法如下: public void OperateFile() { //example檔案初始內容截圖如圖一 string filePath = @"e:\Study\test\example.txt"; if (F
Unity/C#基礎複習(5) 之 淺析觀察者、中介者模式在遊戲中的應用與delegate原理
參考資料 【1】 《Unity 3D指令碼程式設計 使用C#語言開發跨平臺遊戲》陳嘉棟著 【2】 @張子陽【C#中的委託和事件 - Part.1】 http://www.tracefact.net/tech/009.html 【3】 @張子陽【C#中的委託和事件 - Part.2】 http://www.t
【WEB基礎】HTML & CSS 基礎入門(5)邊框與背景
前面(HTML圖片) 漂亮的網頁肯定少不了邊框與背景的修飾,本篇筆記就是說明如何為網頁上的元素設定邊框或者背景(背景顏色和背景圖片)。 之前,先了解一下HTML中的圖片元素,因為圖片標籤的使用非常簡單,所以就插在這裡說明一下。 HTML中的圖片,我們只需要掌握它的標籤寫法以及它的三個屬性就基本OK了。
JDBC入門(5)--- 時間類型、大數據
服務器 setting fun exceptio finall trace rep rest bytes 一、時間類型 數據庫類型與Java中類型的對應關系: DATE->java.sql.Date:表示日期,只有年月日,沒有時分秒,會丟失時間。 TIME->j
c#基礎入門(數據類型)
文字 直接 種類型 常用 log 數據類型 logs 基礎 cnblogs 字符類型 char ,存儲用‘’(英文單引號)括起來的一個單個字符。例如: char Size=‘大‘;//存儲大小 字符串類型 string ,存儲用“”(英文雙引號)括起來的一串字符,不限量
c#基礎入門(算術運算符++ --)
-1 clas num strong ron ack col line 操作符 運算符又名操作符是用於運算的符號,作用於一個或多個的操作數。(操作數:參與運算的數據。) 運算符++和-- ++,叫做自加運算符。比如今天22號,明年長了一天,用代碼寫出來是這樣: int
08-Linux基礎入門(六)-文件和目錄的屬性及權限之文件類型、文件擴展名及文件權限基礎
ins tmp first 串口 .py 都是 公眾平臺 cond .com 一、Linux中的文件類型在Linux系統中,可以說一切(包括目錄、普通文件、設備文件等)皆為文件。文件類型包含有普通文件、目錄、字符設備文件、設備文件、符號鏈接文件、管道文件等等,當執行ls
canvas基礎入門(一)繪制線條、三角形、七巧板
java i++ rip BE lin scrip 瀏覽器 返回 函數 復雜的內容都是有簡單的線條結合而成的,想要繪制出復雜好看的內容先從畫直線開始 canvas繪制直線先認識幾個函數 beginPath();開始一條路徑,或重置當前的路徑 moveTo(x,y);用於規定
C語言入門(四)之switch、迴圈語句
switch格式 switch格式: switch (條件表示式) { case 整數: // case可以有一個或多個 語句; break; case 整數: // case可以有一個或多個 語句;
C語言入門(六)之include、多檔案開發
include基本概念 #include <stdio.h> // 告訴系統printf函式是存在的, 告訴系統printf函式的格式(宣告printf函式) // include的作用
Scala基礎入門(二) Scala下載、安裝教程
Windows中Scala執行環境的安裝配置 第二步安裝 Scala: 下載 Scala SCALA_HOME 環境變數, 指定 D:\217JobSoftwares\scala-2.12.3\scala-2.12.3; 新增到 系
關於iOS基礎總結(5)--tableView的優化、cell高度優化、記憶體優化
1、tableView的優化 iOS平臺因為UIKit本身的特性,需要將所有的UI操作都放在主執行緒執行,所以有時候就習慣將一些執行緒安全性不確定的邏輯,以及它執行緒結束後的彙總工作等等放到了主執行緒,所以主執行緒包含大量計算、IO、繪製都有可能造成卡頓。
C語言入門(4)——常量、變數與賦值
對於基本資料型別量,按其取值是否可改變又分為常量和變數兩種。在程式執行過程中,其值不發生改變的量稱為常量,其值可變的量稱為變數。它們可與資料型別結合起來分類。常量常量有字元常量(CharacterConstant)、數字常量和列舉常量。列舉常量以後再介紹,現在我們看看如何使用
Performanced C++ 經驗規則(5):再談過載、覆蓋和隱藏
在C++中,無論在類作用域內還是外,兩個(或多個)同名的函式,可能且僅可能是以下三種關係:過載(Overload)、覆蓋(Override)和隱藏(Hide),因為同名,區分這些關係則是根據引數是否相同、是否帶有const成員函式性質、是否有virtual關鍵字修飾以及是否在同一作用域來判斷。在第四
c、c++ 基礎試題(2)
#include <stdio.h> int main() { char c; FILE *file; file = fopen("test.txt", "w+"); fprintf(file, "%c", 'a'); fprintf
c、c++ 基礎試題(3)
#include <stdio.h> struct s1 { int a : 1; int b : 1; }; struct s2 { int a : 20; int b : 12; }; struct s3 { i
c、c++ 基礎試題(1)
1、以下程式的輸出結果是什麼? main() { char *p1 = "name"; char *p2; p2 = (char*)malloc(20); memset(p2, 0, 20); while(*p2++ = *p1++); pr
C語言入門(三)之運算子、sizeof運算子、if表示式
型別轉換、型別提升 #include <stdio.h> void test(); int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) { // 1.型別轉換 /* // int 佔用4個位元組 double
maven入門(5)使用eclipse構建maven項目
org 菜單欄 ini tag 界面 java 我們 core comm 1. 安裝m2eclipse插件 要用Eclipse構建Maven項目,我們需要先安裝meeclipse插件 點擊eclipse菜單欄Help->Eclipse Marketplac
c#基礎知識(2)
alt 實現 height over 聯系 c# 覆蓋 tro strong 一,繼承與派生 原來的類——基類或父類 新定義的類——派生類 引入原因:擴展原有類的功能 派生類的成員: (1)會吸收基類的所有成員(包括私有成