獲取Android裝置上的所有儲存裝置
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-02-13
Android系統提供了Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory()介面獲得儲存裝置的路徑,但是這個介面往往給出的結果並不是我們想要的,在某些裝置上它返回的是手機內部儲存,某些裝置上返回的手機外部儲存。還有就是某些Android裝置支援擴充套件多個sdcard,這個時候想要獲得所有儲存器的掛載路徑,這個介面是沒有辦法辦到的。
那麼,Android系統的檔案管理器是如何把所有掛載的儲存裝置加載出來的呢?通過檢視檔案管理器的原始碼發現是在MountPointManager類中處理的,通過呼叫StorageManager類的getVolumeList()方法獲取的。
/** * This method initializes MountPointManager. * * @param context Context to use */ public void init(Context context) { mStorageManager = (StorageManager) context.getSystemService(Context.STORAGE_SERVICE); final String defaultPath = getDefaultPath(); LogUtils.d(TAG, "init,defaultPath = " + defaultPath); if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(defaultPath)) { mRootPath = ROOT_PATH; } mMountPathList.clear(); // check media availability to init mMountPathList StorageVolume[] storageVolumeList = mStorageManager.getVolumeList(); if (storageVolumeList != null) { for (StorageVolume volume : storageVolumeList) { MountPoint mountPoint = new MountPoint(); mountPoint.mDescription = volume.getDescription(context); mountPoint.mPath = volume.getPath(); mountPoint.mIsMounted = isMounted(volume.getPath()); mountPoint.mIsExternal = volume.isRemovable(); mountPoint.mMaxFileSize = volume.getMaxFileSize(); LogUtils.d(TAG, "init,description :" + mountPoint.mDescription + ",path : " + mountPoint.mPath + ",isMounted : " + mountPoint.mIsMounted + ",isExternal : " + mountPoint.mIsExternal + ", mMaxFileSize: " + mountPoint.mMaxFileSize); mMountPathList.add(mountPoint); } } IconManager.getInstance().init(context, defaultPath + SEPARATOR); }
系統提供了StorageManager類,它有一個方法叫getVolumeList(),這個方法的返回值是一個StorageVolume陣列,StorageVolume類中封裝了掛載路徑,掛載狀態,以及是否可以移除等資訊。下面是這個方法的原始碼。
/** * Returns list of all mountable volumes. * @hide */ public StorageVolume[] getVolumeList() { if (mMountService == null) return new StorageVolume[0]; try { Parcelable[] list = mMountService.getVolumeList(); if (list == null) return new StorageVolume[0]; int length = list.length; StorageVolume[] result = new StorageVolume[length]; for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { result[i] = (StorageVolume)list[i]; } return result; } catch (RemoteException e) { Log.e(TAG, "Failed to get volume list", e); return null; } }
getVolumeList()方法是隱藏的,不能在應用程式碼中直接呼叫,所以我們只能通過反射來呼叫這個方法了。
通過反射機制獲取Android裝置的所有儲存裝置
public class StorageInfo {
public String path;
public String state;
public boolean isRemoveable;
public StorageInfo(String path) {
this.path = path;
}
public boolean isMounted() {
return "mounted".equals(state);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "StorageInfo [path=" + path + ", state=" + state
+ ", isRemoveable=" + isRemoveable + "]";
}
} public static List<StorageInfo> listAllStorage(Context context) {
ArrayList<StorageInfo> storages = new ArrayList<StorageInfo>();
StorageManager storageManager = (StorageManager) context.getSystemService(Context.STORAGE_SERVICE);
try {
Class<?>[] paramClasses = {};
Method getVolumeList = StorageManager.class.getMethod("getVolumeList", paramClasses);
Object[] params = {};
Object[] invokes = (Object[]) getVolumeList.invoke(storageManager, params);
if (invokes != null) {
StorageInfo info = null;
for (int i = 0; i < invokes.length; i++) {
Object obj = invokes[i];
Method getPath = obj.getClass().getMethod("getPath", new Class[0]);
String path = (String) getPath.invoke(obj, new Object[0]);
info = new StorageInfo(path);
Method getVolumeState = StorageManager.class.getMethod("getVolumeState", String.class);
String state = (String) getVolumeState.invoke(storageManager, info.path);
info.state = state;
Method isRemovable = obj.getClass().getMethod("isRemovable", new Class[0]);
info.isRemoveable = ((Boolean) isRemovable.invoke(obj, new Object[0])).booleanValue();
storages.add(info);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
storages.trimToSize();
return storages;
}
public static List<StorageInfo> getAvaliableStorage(List<StorageInfo> infos){
List<StorageInfo> storages = new ArrayList<StorageInfo>();
for(StorageInfo info : infos){
File file = new File(info.path);
if ((file.exists()) && (file.isDirectory()) && (file.canWrite())) {
if (info.isMounted()) {
storages.add(info);
}
}
}
return storages;
}呼叫上述方法:
List<StorageInfo> list = listAllStorage(this);
for(StorageInfo info : list){
Log.e(TAG, info.toString());
}
Log.e(TAG, "-----------------");
List<StorageInfo> infos = getAvaliableStorage(list);
for(StorageInfo info : infos){
Log.e(TAG, info.toString());
}
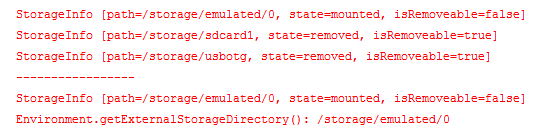
Log.e(TAG, "Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory(): " + Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory());連上手機進行驗證,輸出Log資訊:
可以看到,通過listAllStorage()方法獲取到了手機上的所有儲存裝置,通過getAvaliableStorage()方法的過濾獲取到了掛載狀態的所有儲存裝置。由於該手機只有一個可讀寫的儲存裝置,因此與Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory()方法獲取到的結果一致。
注意:由於在getAvaliableStorage()方法中我們獲取的是可寫(canWrite)的裝置,需要加上相應許可權: <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE"/> ,否則獲取不到儲存裝置。