TCP校驗和的原理和實現
概述
TCP校驗和是一個端到端的校驗和,由傳送端計算,然後由接收端驗證。其目的是為了發現TCP首部和資料在傳送端到
接收端之間發生的任何改動。如果接收方檢測到校驗和有差錯,則TCP段會被直接丟棄。
TCP校驗和覆蓋TCP首部和TCP資料,而IP首部中的校驗和只覆蓋IP的首部,不覆蓋IP資料報中的任何資料。
TCP的校驗和是必需的,而UDP的校驗和是可選的。
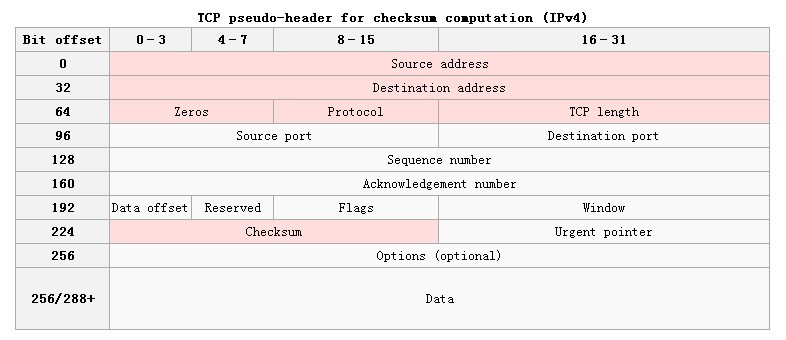
TCP和UDP計算校驗和時,都要加上一個12位元組的偽首部。
Author : zhangskd @ csdn blog
偽首部
偽首部共有12位元組,包含如下資訊:源IP地址、目的IP地址、保留位元組(置0)、傳輸層協議號(TCP是6)、TCP報文長度(報頭+資料)。
偽首部是為了增加TCP校驗和的檢錯能力:如檢查TCP報文是否收錯了(目的IP地址)、傳輸層協議是否選對了(傳輸層協議號)等。
定義
(1) RFC 793的TCP校驗和定義
The checksum field is the 16 bit one's complement of the one's complement sum of all 16-bit words in the header and text.
If a segment contains an odd number of header and text octets to be checksummed, the last octet is padded on the right
with zeros to form a 16-bit word for checksum purposes. The pad is not transmitted as part of the segment. While computing
the checksum, the checksum field itself is replaced with zeros.
上述的定義說得很明確:
首先,把偽首部、TCP報頭、TCP資料分為16位的字,如果總長度為奇數個位元組,則在最後增添一個位都為0的位元組。
把TCP報頭中的校驗和欄位置為0(否則就陷入雞生蛋還是蛋生雞的問題)。
其次,用反碼相加法累加所有的16位字(進位也要累加)。
最後,對計算結果取反,作為TCP的校驗和。
(2) RFC 1071的IP校驗和定義
1. Adjacent octets to be checksummed are paired to form 16-bit integers, and the 1's complement sum of these
16-bit integers is formed.
2. To generate a checksum, the checksum field itself is cleared, the 16-bit 1's complement sum is computed over
the octets concerned, and the 1's complement of this sum is placed in the checksum field.
3. To check a checksum, the 1's complement sum is computed over the same set of octets, including the checksum
field. If the result is all 1 bits (-0 in 1's complement arithmetic), the check succeeds.
可以看到,TCP校驗和、IP校驗和的計算方法是基本一致的,除了計算的範圍不同。
實現
基於2.6.18、x86_64。
csum_tcpudp_nofold()按4位元組累加偽首部到sum中。
static inline unsigned long csum_tcpudp_nofold (unsigned long saddr, unsigned long daddr,
unsigned short len, unsigned short proto,
unsigned int sum)
{
asm("addl %1, %0\n" /* 累加daddr */
"adcl %2, %0\n" /* 累加saddr */
"adcl %3, %0\n" /* 累加len(2位元組), proto, 0*/
"adcl $0, %0\n" /*加上進位 */
: "=r" (sum)
: "g" (daddr), "g" (saddr), "g" ((ntohs(len) << 16) + proto*256), "0" (sum));
return sum;
} csum_tcpudp_magic()產生最終的校驗和。
首先,按4位元組累加偽首部到sum中。
其次,累加sum的低16位、sum的高16位,並且對累加的結果取反。
最後,擷取sum的高16位,作為校驗和。
static inline unsigned short int csum_tcpudp_magic(unsigned long saddr, unsigned long daddr,
unsigned short len, unsigned short proto,
unsigned int sum)
{
return csum_fold(csum_tcpudp_nofold(saddr, daddr, len, proto, sum));
}
static inline unsigned int csum_fold(unsigned int sum)
{
__asm__(
"addl %1, %0\n"
"adcl 0xffff, %0"
: "=r" (sum)
: "r" (sum << 16), "0" (sum & 0xffff0000)
/* 將sum的低16位,作為暫存器1的高16位,暫存器1的低16位補0。
* 將sum的高16位,作為暫存器0的高16位,暫存器0的低16位補0。
* 這樣,addl %1, %0就累加了sum的高16位和低16位。
*
* 還要考慮進位。如果有進位,adcl 0xfff, %0為:0x1 + 0xffff + %0,暫存器0的高16位加1。
* 如果沒有進位,adcl 0xffff, %0為:0xffff + %0,對暫存器0的高16位無影響。
*/
);
return (~sum) >> 16; /* 對sum取反,返回它的高16位,作為最終的校驗和 */
}傳送校驗
#define CHECKSUM_NONE 0 /* 需要由傳輸層自己計算校驗和 */
#define CHECKSUM_HW 1 /* 由硬體計算報頭和首部的校驗和 */
#define CHECKSUM_UNNECESSARY 2 /* 表示不需要校驗,或者已經成功校驗了 */
#define CHECKSUM_PARTIAL CHECKSUM_HW
#define CHECKSUM_COMPLETE CHECKSUM_HW
@tcp_transmit_skb()
icsk->icsk_af_ops->send_check(sk, skb->len, skb); /* 計算校驗和 */
void tcp_v4_send_check(struct sock *sk, int len, struct sk_buff *skb)
{
struct inet_sock *inet = inet_sk(sk);
struct tcphdr *th = skb->h.th;
if (skb->ip_summed == CHECKSUM_HW) {
/* 只計算偽首部,TCP報頭和TCP資料的累加由硬體完成 */
th->check = ~tcp_v4_check(th, len, inet->saddr, inet->daddr, 0);
skb->csum = offsetof(struct tcphdr, check); /* 校驗和值在TCP首部的偏移 */
} else {
/* tcp_v4_check累加偽首部,獲取最終的校驗和。
* csum_partial累加TCP報頭。
* 那麼skb->csum應該是TCP資料部分的累加,這是在從使用者空間複製時順便累加的。
*/
th->check = tcp_v4_check(th, len, inet->saddr, inet->daddr,
csum_partial((char *)th, th->doff << 2, skb->csum));
}
}unsigned csum_partial(const unsigned char *buff, unsigned len, unsigned sum)
{
return add32_with_carry(do_csum(buff, len), sum);
}
static inline unsigned add32_with_carry(unsigned a, unsigned b)
{
asm("addl %2, %0\n\t"
"adcl $0, %0"
: "=r" (a)
: "0" (a), "r" (b));
return a;
}
do_csum()用於計算一段記憶體的校驗和,這裡用於累加TCP報頭。
具體計算時用到一些技巧:
1. 反碼累加時,按16位、32位、64位來累加的效果是一樣的。
2. 使用記憶體對齊,減少記憶體操作的次數。
static __force_inline unsigned do_csum(const unsigned char *buff, unsigned len)
{
unsigned odd, count;
unsigned long result = 0;
if (unlikely(len == 0))
return result;
/* 使起始地址為XXX0,接下來可按2位元組對齊 */
odd = 1 & (unsigned long) buff;
if (unlikely(odd)) {
result = *buff << 8; /* 因為機器是小端的 */
len--;
buff++;
}
count = len >> 1; /* nr of 16-bit words,這裡可能餘下1位元組未算,最後會處理*/
if (count) {
/* 使起始地址為XX00,接下來可按4位元組對齊 */
if (2 & (unsigned long) buff) {
result += *(unsigned short *)buff;
count--;
len -= 2;
buff += 2;
}
count >>= 1; /* nr of 32-bit words,這裡可能餘下2位元組未算,最後會處理 */
if (count) {
unsigned long zero;
unsigned count64;
/* 使起始地址為X000,接下來可按8位元組對齊 */
if (4 & (unsigned long)buff) {
result += *(unsigned int *)buff;
count--;
len -= 4;
buff += 4;
}
count >>= 1; /* nr of 64-bit words,這裡可能餘下4位元組未算,最後會處理*/
/* main loop using 64byte blocks */
zero = 0;
count64 = count >> 3; /* 64位元組的塊數,這裡可能餘下56位元組未算,最後會處理 */
while (count64) { /* 反碼累加所有的64位元組塊 */
asm ("addq 0*8(%[src]), %[res]\n\t" /* b、w、l、q分別對應8、16、32、64位操作 */
"addq 1*8(%[src]), %[res]\n\t" /* [src]為指定暫存器的別名,效果應該等同於0、1等 */
"adcq 2*8(%[src]), %[res]\n\t"
"adcq 3*8(%[src]), %[res]\n\t"
"adcq 4*8(%[src]), %[res]\n\t"
"adcq 5*8(%[src]), %[res]\n\t"
"adcq 6*8(%[src]), %[res]\n\t"
"adcq 7*8(%[src]), %[res]\n\t"
"adcq %[zero], %[res]"
: [res] "=r" (result)
: [src] "r" (buff), [zero] "r" (zero), "[res]" (result));
buff += 64;
count64--;
}
/* 從這裡開始,反序處理之前可能漏算的位元組 */
/* last upto 7 8byte blocks,前面按8個8位元組做計算單位,所以最多可能剩下7個8位元組 */
count %= 8;
while (count) {
asm ("addq %1, %0\n\t"
"adcq %2, %0\n"
: "=r" (result)
: "m" (*(unsigned long *)buff), "r" (zero), "0" (result));
--count;
buff += 8;
}
/* 帶進位累加result的高32位和低32位 */
result = add32_with_carry(result>>32, result&0xffffffff);
/* 之前始按8位元組對齊,可能有4位元組剩下 */
if (len & 4) {
result += *(unsigned int *) buff;
buff += 4;
}
}
/* 更早前按4位元組對齊,可能有2位元組剩下 */
if (len & 2) {
result += *(unsigned short *) buff;
buff += 2;
}
}
/* 最早之前按2位元組對齊,可能有1位元組剩下 */
if (len & 1)
result += *buff;
/* 再次帶進位累加result的高32位和低32位 */
result = add32_with_carry(result>>32, result & 0xffffffff);
/* 這裡涉及到一個技巧,用於處理初始地址為奇數的情況 */
if (unlikely(odd)) {
result = from32to16(result); /* 累加到result的低16位 */
/* result為:0 0 a b
* 然後交換a和b,result變為:0 0 b a
*/
result = ((result >> 8) & 0xff) | ((result & oxff) << 8);
}
return result; /* 返回result的低32位 */
}
static inline unsigned short from32to16(unsigned a)
{
unsigned short b = a >> 16;
asm ("addw %w2, %w0\n\t"
"adcw $0, %w0\n"
: "=r" (b)
: "0" (b), "r" (a));
return b;
}csum_partial_copy_from_user()用於拷貝使用者空間資料到核心空間,同時計算使用者資料的校驗和,
結果儲存到skb->csum中(X86_64)。
/**
* csum_partial_copy_from_user - Copy and checksum from user space.
* @src: source address (user space)
* @dst: destination address
* @len: number of bytes to be copied.
* @isum: initial sum that is added into the result (32bit unfolded)
* @errp: set to -EFAULT for an bad source address.
*
* Returns an 32bit unfolded checksum of the buffer.
* src and dst are best aligned to 64bits.
*/
unsigned int csum_partial_copy_from_user(const unsigned char __user *src,
unsigned char *dst, int len, unsigned int isum, int *errp)
{
might_sleep();
*errp = 0;
if (likely(access_ok(VERIFY_READ, src, len))) {
/* Why 6, not 7? To handle odd addresses aligned we would need to do considerable
* complications to fix the checksum which is defined as an 16bit accumulator. The fix
* alignment code is primarily for performance compatibility with 32bit and that will handle
* odd addresses slowly too.
* 處理X010、X100、X110的起始地址。不處理X001,因為這會使複雜度大增加。
*/
if (unlikely((unsigned long)src & 6)) {
while (((unsigned long)src & 6) && len >= 2) {
__u16 val16;
*errp = __get_user(val16, (__u16 __user *)src);
if (*errp)
return isum;
*(__u16 *)dst = val16;
isum = add32_with_carry(isum, val16);
src += 2;
dst += 2;
len -= 2;
}
}
/* 計算函式是用純彙編實現的,應該是因為效率吧 */
isum = csum_parial_copy_generic((__force void *)src, dst, len, isum, errp, NULL);
if (likely(*errp == 0))
return isum; /* 成功 */
}
*errp = -EFAULT;
memset(dst, 0, len);
return isum;
}
上述的實現比較複雜,來看下最簡單的csum_partial_copy_from_user()實現(um)。
unsigned int csum_partial_copy_from_user(const unsigned char *src,
unsigned char *dst, int len, int sum,
int *err_ptr)
{
if (copy_from_user(dst, src, len)) { /* 拷貝使用者空間資料到核心空間 */
*err_ptr = -EFAULT; /* bad address */
return (-1);
}
return csum_partial(dst, len, sum); /* 計算使用者資料的校驗和,會存到skb->csum中 */
}
接收校驗
@tcp_v4_rcv
/* 檢查校驗和 */
if (skb->ip_summed != CHECKSUM_UNNECESSARY && tcp_v4_checksum_init(skb))
goto bad_packet;
接收校驗的第一部分,主要是計算偽首部。
static int tcp_v4_checksum_init(struct sk_buff *skb)
{
/* 如果TCP報頭、TCP資料的反碼累加已經由硬體完成 */
if (skb->ip_summed == CHECKSUM_HW) {
/* 現在只需要再累加上偽首部,取反獲取最終的校驗和。
* 校驗和為0時,表示TCP資料報正確。
*/
if (! tcp_v4_check(skb->h.th, skb->len, skb->nh.iph->saddr, skb->nh.iph->daddr, skb->csum)) {
skb->ip_summed = CHECKSUM_UNNECESSARY;
return 0; /* 校驗成功 */
} /* 沒有else失敗退出嗎?*/
}
/* 對偽首部進行反碼累加,主要用於軟體方法 */
skb->csum = csum_tcpudp_nofold(skb->nh.iph->saddr, skb->nh.iph->daddr, skb->len, IPPROTO_TCP, 0);
/* 對於長度小於76位元組的小包,接著累加TCP報頭和報文,完成校驗;否則,以後再完成檢驗。*/
if (skb->len <= 76) {
return __skb_checksum_complete(skb);
}
}
接收校驗的第二部分,計算報頭和報文。
tcp_v4_rcv、tcp_v4_do_rcv()
| --> tcp_checksum_complete()
| --> __tcp_checksum_complete()
| --> __skb_checksum_complete()
tcp_rcv_established()
| --> tcp_checksum_complete_user()
| --> __tcp_checksum_complete_user()
| --> __tcp_checksum_complete()
| --> __skb_checksum_complete()
unsigned int __skb_checksum_complete(struct sk_buff *skb)
{
unsigned int sum;
sum = (u16) csum_fold(skb_checksum(skb, 0, skb->len, skb->csum));
if (likely(!sum)) { /* sum為0表示成功了 */
/* 硬體檢測失敗,軟體檢測成功了,說明硬體檢測有誤 */
if (unlikely(skb->ip_summed == CHECKSUM_HW))
netdev_rx_csum_fault(skb->dev);
skb->ip_summed = CHECKSUM_UNNECESSARY;
}
return sum;
}
計算skb包的校驗和時,可以指定相對於skb->data的偏移量offset。
由於skb包可能由分頁和分段,所以需要考慮skb->data + offset是位於此skb段的線性區中、
還是此skb的分頁中,或者位於其它分段中。這個函式邏輯比較複雜。
/* Checksum skb data. */
unsigned int skb_checksum(const struct sk_buff *skb, int offset, int len, unsigned int csum)
{
int start = skb_headlen(skb); /* 線性區域長度 */
/* copy > 0,說明offset線上性區域中。
* copy < 0,說明offset在此skb的分頁資料中,或者在其它分段skb中。
*/
int i, copy = start - offset;
int pos = 0; /* 表示校驗了多少資料 */
/* Checksum header. */
if (copy > 0) { /* 說明offset在本skb的線性區域中 */
if (copy > len)
copy = len; /* 不能超過指定的校驗長度 */
/* 累加copy長度的線性區校驗 */
csum = csum_partial(skb->data + offset, copy, csum);
if ((len -= copy) == 0)
return csum;
offset += copy; /* 接下來從這裡繼續處理 */
pos = copy; /* 已處理資料長 */
}
/* 累加本skb分頁資料的校驗和 */
for (i = 0; i < skb_shinfo(skb)->nr_frags; i++) {
int end;
BUG_TRAP(start <= offset + len);
end = start + skb_shinfo(skb)->frags[i].size;
if ((copy = end - offset) > 0) { /* 如果offset位於本頁中,或者線性區中 */
unsigned int csum2;
u8 *vaddr; /* 8位夠嗎?*/
skb_frag_t *frag = &skb_shinfo(skb)->frags[i];
if (copy > len)
copy = len;
vaddr = kmap_skb_frag(frag); /* 把物理頁對映到核心空間 */
csum2 = csum_partial(vaddr + frag->page_offset + offset - start, copy, 0);
kunmap_skb_frag(vaddr); /* 解除對映 */
/* 如果pos為奇數,需要對csum2進行處理。
* csum2:a, b, c, d => b, a, d, c
*/
csum = csum_block_add(csum, csum2, pos);
if (! (len -= copy))
return csum;
offset += copy;
pos += copy;
}
start = end; /* 接下來從這裡處理 */
}
/* 如果此skb是個大包,還有其它分段 */
if (skb_shinfo(skb)->frag_list) {
struct sk_buff *list = skb_shinfo(skb)->frag_list;
for (; list; list = list->next) {
int end;
BUG_TRAP(start <= offset + len);
end = start + list->len;
if ((copy = end - offset) > 0) { /* 如果offset位於此skb分段中,或者分頁,或者線性區 */
unsigned int csum2;
if (copy > len)
copy = len;
csum2 = skb_checksum(list, offset - start, copy, 0); /* 遞迴呼叫 */
csum = csum_block_add(csum, csum2, pos);
if ((len -= copy) == 0)
return csum;
offset += copy;
pos += copy;
}
start = end;
}
}
BUG_ON(len);
return csum;
}