一個酷炫的button變化動畫開源庫原始碼分析—Android morph Button(一)
最近很是喜愛一些酷炫的動畫效果,特意在github上找了一些,看看他們是怎麼做到的,做個分析,順便可以對自定義控制元件和動畫有進一步的認識。
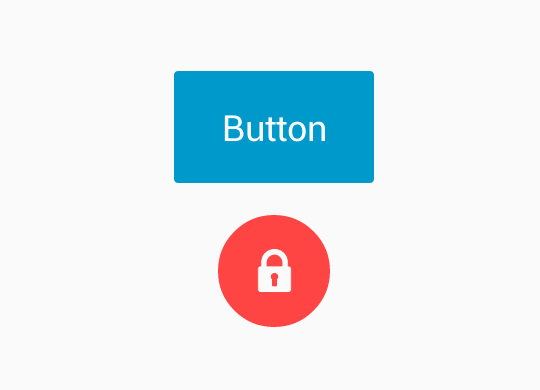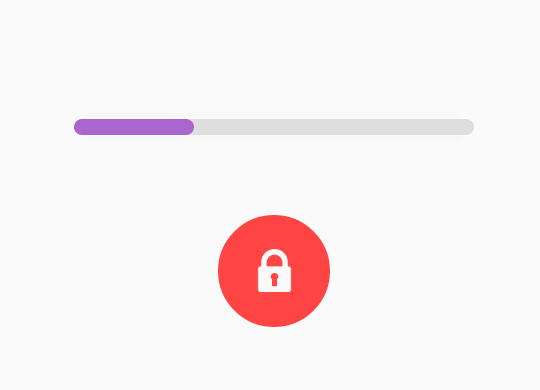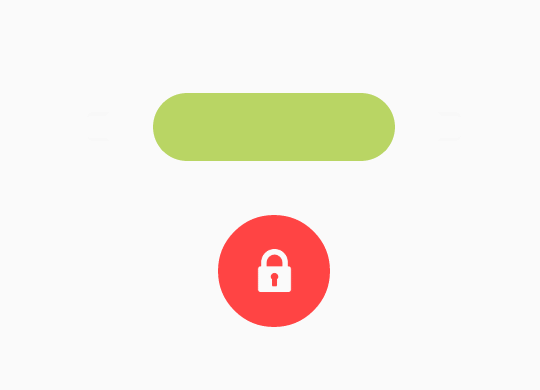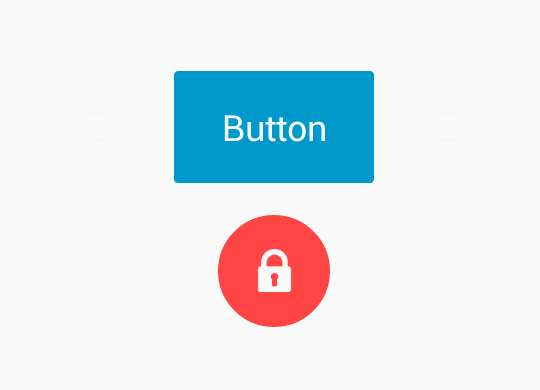
先來看下這個庫中button的變化效果是什麼樣的:
是不是很酷炫,而且中間的變化過程很舒服,沒有僵硬的感覺,應用的場景也比較廣:只要點選按鈕,執行一個操作之後,返回結果,這個結果以對錯表示,如果是一個耗時的操作還可以顯示執行的進度,有很好的使用者體驗。比如點選按鈕後,在後臺進行下載、使用者點選按鈕進行登入等。
先分析第一個動畫效果:
稍微複雜的動畫一般是用屬性動畫來做了,對多個屬性進行同時變化,仔細觀察這個動畫效果可以看到,有width的變化,由長方形變成了圓形,必然有CornerRadius的變化,變化的過程中背景顏色也有變化,最後顯示通過和沒通過的ICON,來看下ObjectAnimator使用的方法,target就是要變化的物件,propertyName就是要變化的屬性,現在要變化的屬性已經有了,就是上面說的:width、cornerRadius、color等,那麼target應該是什麼?
直接是button本身嗎?我們知道某個屬性變化(如color)是依據target中的setColor()方法來動態設定color的值,也就是button中藥提供setColor()、setCornerRadius()這樣的方法,來更新對應的值到介面上,一般最後還有呼叫invalidate()方法來重新整理介面展示變化的效果。但是這樣實現比較麻煩,這些方法都要我們自己提供。那麼Android Morphing Button這個庫是怎麼做的呢?
其實我們想象這個button動畫真的變化的其實就是它的background,這個庫就是將backgroud設定為一個GradientDrawable,然後對這個GradientDrawable進行變化,也就事target就是這個GradientDrawable,GradientDrawable本身就有setColor、setCornerRadius、setStroke這些方法,並且會自動重新整理UI,這樣就不不用我們自己去寫這些方法來重繪,大體的思路就是這樣的,接下來分析具體的程式碼。
public static ObjectAnimator ofInt(Object target, String propertyName, int... values)1. 具體使用:
// sample demonstrate how to morph button to green circle with icon
MorphingButton btnMorph = (MorphingButton) findViewById(R.id.btnMorph);
// inside on click event
MorphingButton.Params circle = MorphingButton.Params MorphingButton就是自定義的這個button,裡面有個Params的靜態內部類,設定一些引數如:cornerRadius、width,color等,表示變化到什麼引數,Icon為結束的顯示的圖示。設定好引數後,就呼叫
public void morph(@NonNull Params params) 這個方法來執行動畫,使用起來很是簡單。
接下來看下這個庫程式碼的構成,有下面幾個類:
StrokeGradientDrawable.class 這個類就是GradientDrawable就是屬性動畫要變化的物件,在GradientDrawable的基礎上加入了stroke,radius,color的設定,提供了對應set和get方法。
MorphingAnimation.class 這個類就是具體的動畫變化類了。
MorphingButton.class 這個類繼承自button,在程式碼中設定background為StrokeGradientDrawable,這樣對StrokeGradientDrawable做了屬性變化後,動畫效果就顯示在button上了。
就按照這個順序來分析具體的程式碼,先看StrokeGradientDrawable.class:
public class StrokeGradientDrawable {
private int mStrokeWidth;
private int mStrokeColor;
private GradientDrawable mGradientDrawable;
private float mRadius;
private int mColor;
public StrokeGradientDrawable(GradientDrawable drawable) {
mGradientDrawable = drawable;
}
public int getStrokeWidth() {
return mStrokeWidth;
}
public void setStrokeWidth(int strokeWidth) {
mStrokeWidth = strokeWidth;
mGradientDrawable.setStroke(strokeWidth, getStrokeColor());
}
public int getStrokeColor() {
return mStrokeColor;
}
public void setStrokeColor(int strokeColor) {
mStrokeColor = strokeColor;
mGradientDrawable.setStroke(getStrokeWidth(), strokeColor);
}
public void setCornerRadius(float radius) {
mRadius = radius;
mGradientDrawable.setCornerRadius(radius);
}
public void setColor(int color) {
mColor = color;
mGradientDrawable.setColor(color);
}
public int getColor() {
return mColor;
}
public float getRadius() {
return mRadius;
}
public GradientDrawable getGradientDrawable() {
return mGradientDrawable;
}
}
這個類就比較簡單,有mStrokeWidth、mStrokeWidth、mRadius、mColor,這幾個屬性值,還有一個GradientDrawable物件,在建構函式中傳入,然後上面幾個屬性對用的set方法,就是呼叫的GradientDrawable的對應屬性的set方法,剩下的就是get方法。這裡要注意的是:屬性動畫是在變化物件中尋找setXXXX(XXXX即為要變化的屬性)方法來進行變化,所以一定要有對應的set方法
接下來看MorphingAnimation.class,這個類
public class MorphingAnimation {
//動畫結束的回撥介面
public interface Listener {
void onAnimationEnd();
}
//內部引數類:變化的button和回撥介面,變化前的屬性和變化後的,屬性有:圓角、高度、寬度、顏色、描邊寬度和顏色
public static class Params {
private float fromCornerRadius;
private float toCornerRadius;
private int fromHeight;
private int toHeight;
private int fromWidth;
private int toWidth;
private int fromColor;
private int toColor;
private int duration;
private int fromStrokeWidth;
private int toStrokeWidth;
private int fromStrokeColor;
private int toStrokeColor;
private MorphingButton button;
private MorphingAnimation.Listener animationListener;
private Params(@NonNull MorphingButton button) {
this.button = button;
}
public static Params create(@NonNull MorphingButton button) {
return new Params(button);
}
public Params duration(int duration) {
this.duration = duration;
return this;
}
public Params listener(@NonNull MorphingAnimation.Listener animationListener) {
this.animationListener = animationListener;
return this;
}
public Params color(int fromColor, int toColor) {
this.fromColor = fromColor;
this.toColor = toColor;
return this;
}
public Params cornerRadius(int fromCornerRadius, int toCornerRadius) {
this.fromCornerRadius = fromCornerRadius;
this.toCornerRadius = toCornerRadius;
return this;
}
public Params height(int fromHeight, int toHeight) {
this.fromHeight = fromHeight;
this.toHeight = toHeight;
return this;
}
public Params width(int fromWidth, int toWidth) {
this.fromWidth = fromWidth;
this.toWidth = toWidth;
return this;
}
public Params strokeWidth(int fromStrokeWidth, int toStrokeWidth) {
this.fromStrokeWidth = fromStrokeWidth;
this.toStrokeWidth = toStrokeWidth;
return this;
}
public Params strokeColor(int fromStrokeColor, int toStrokeColor) {
this.fromStrokeColor = fromStrokeColor;
this.toStrokeColor = toStrokeColor;
return this;
}
}
private Params mParams;
public MorphingAnimation(@NonNull Params params) {
mParams = params;
}
public void start() {
StrokeGradientDrawable background = mParams.button.getDrawableNormal();
ObjectAnimator cornerAnimation =
ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(background, "cornerRadius", mParams.fromCornerRadius, mParams.toCornerRadius);
ObjectAnimator strokeWidthAnimation =
ObjectAnimator.ofInt(background, "strokeWidth", mParams.fromStrokeWidth, mParams.toStrokeWidth);
ObjectAnimator strokeColorAnimation = ObjectAnimator.ofInt(background, "strokeColor", mParams.fromStrokeColor, mParams.toStrokeColor);
strokeColorAnimation.setEvaluator(new ArgbEvaluator());
ObjectAnimator bgColorAnimation = ObjectAnimator.ofInt(background, "color", mParams.fromColor, mParams.toColor);
bgColorAnimation.setEvaluator(new ArgbEvaluator());
ValueAnimator heightAnimation = ValueAnimator.ofInt(mParams.fromHeight, mParams.toHeight);
heightAnimation.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator valueAnimator) {
int val = (Integer) valueAnimator.getAnimatedValue();
ViewGroup.LayoutParams layoutParams = mParams.button.getLayoutParams();
layoutParams.height = val;
mParams.button.setLayoutParams(layoutParams);
}
});
ValueAnimator widthAnimation = ValueAnimator.ofInt(mParams.fromWidth, mParams.toWidth);
widthAnimation.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator valueAnimator) {
int val = (Integer) valueAnimator.getAnimatedValue();
ViewGroup.LayoutParams layoutParams = mParams.button.getLayoutParams();
layoutParams.width = val;
mParams.button.setLayoutParams(layoutParams);
}
});
AnimatorSet animatorSet = new AnimatorSet();
animatorSet.setDuration(mParams.duration);
animatorSet.playTogether(strokeWidthAnimation, strokeColorAnimation, cornerAnimation, bgColorAnimation,
heightAnimation, widthAnimation);
animatorSet.addListener(new AnimatorListenerAdapter() {
@Override
public void onAnimationEnd(Animator animation) {
if (mParams.animationListener != null) {
mParams.animationListener.onAnimationEnd();
}
}
});
animatorSet.start();
}
}
裡面有一個動畫結束的回撥介面和一個動畫引數的設定內部類,主要看start()方法:
先利用
StrokeGradientDrawable background = mParams.button.getDrawableNormal();獲取到button的normal(還有按下狀態)狀態下的background,然後就是利用ObjectAnimator來對這個物件的屬性進行變化,corner、strokeWidth、strokeColor、color這幾個屬性都是類似的,以Corner為例,都是利用:
ObjectAnimator cornerAnimation =
ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(background, "cornerRadius", mParams.fromCornerRadius, mParams.toCornerRadius);
變化前後的引數就是Params中設定好的引數,然後這裡的width和height變化是利用ValueAnimator,在AnimatorUpdateListener中利用 ViewGroup.LayoutParams,根據產生的變化值動態的設定width和height。最後將這幾個動畫加入到一個AnimatorSet中,來同時顯示,並在最後設定動畫結束後回撥傳入的介面。那麼這個變化前後的引數值是哪裡得到的呢,是在這個類的構造方法中:
public MorphingAnimation(@NonNull Params params) {
mParams = params;
}
最後我們分析MorphingButton.class這個類
public class MorphingButton extends Button {
private Padding mPadding;
private int mHeight;
private int mWidth;
private int mColor;
private int mCornerRadius;
private int mStrokeWidth;
private int mStrokeColor;
protected boolean mAnimationInProgress;
private StrokeGradientDrawable mDrawableNormal;
private StrokeGradientDrawable mDrawablePressed;
public MorphingButton(Context context) {
super(context);
initView();
}
public MorphingButton(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
initView();
}
public MorphingButton(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
initView();
}
@Override
protected void onSizeChanged(int w, int h, int oldw, int oldh) {
super.onSizeChanged(w, h, oldw, oldh);
if (mHeight == 0 && mWidth == 0 && w != 0 && h != 0) {
mHeight = getHeight();
mWidth = getWidth();
}
}
public StrokeGradientDrawable getDrawableNormal() {
return mDrawableNormal;
}
public void morph(@NonNull Params params) {
if (!mAnimationInProgress) {
mDrawablePressed.setColor(params.colorPressed);
mDrawablePressed.setCornerRadius(params.cornerRadius);
mDrawablePressed.setStrokeColor(params.strokeColor);
mDrawablePressed.setStrokeWidth(params.strokeWidth);
if (params.duration == 0) {
morphWithoutAnimation(params);
} else {
morphWithAnimation(params);
}
mColor = params.color;
mCornerRadius = params.cornerRadius;
mStrokeWidth = params.strokeWidth;
mStrokeColor = params.strokeColor;
}
}
private void morphWithAnimation(@NonNull final Params params) {
mAnimationInProgress = true;
setText(null);
setCompoundDrawablesWithIntrinsicBounds(0, 0, 0, 0);
setPadding(mPadding.left, mPadding.top, mPadding.right, mPadding.bottom);
MorphingAnimation.Params animationParams = MorphingAnimation.Params.create(this)
.color(mColor, params.color)
.cornerRadius(mCornerRadius, params.cornerRadius)
.strokeWidth(mStrokeWidth, params.strokeWidth)
.strokeColor(mStrokeColor, params.strokeColor)
.height(getHeight(), params.height)
.width(getWidth(), params.width)
.duration(params.duration)
.listener(new MorphingAnimation.Listener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationEnd() {
finalizeMorphing(params);
}
});
MorphingAnimation animation = new MorphingAnimation(animationParams);
animation.start();
}
private void morphWithoutAnimation(@NonNull Params params) {
mDrawableNormal.setColor(params.color);
mDrawableNormal.setCornerRadius(params.cornerRadius);
mDrawableNormal.setStrokeColor(params.strokeColor);
mDrawableNormal.setStrokeWidth(params.strokeWidth);
if(params.width != 0 && params.height !=0) {
ViewGroup.LayoutParams layoutParams = getLayoutParams();
layoutParams.width = params.width;
layoutParams.height = params.height;
setLayoutParams(layoutParams);
}
finalizeMorphing(params);
}
private void finalizeMorphing(@NonNull Params params) {
mAnimationInProgress = false;
if (params.icon != 0 && params.text != null) {
setIconLeft(params.icon);
setText(params.text);
} else if (params.icon != 0) {
setIcon(params.icon);
} else if(params.text != null) {
setText(params.text);
}
if (params.animationListener != null) {
params.animationListener.onAnimationEnd();
}
}
public void blockTouch() {
setOnTouchListener(new OnTouchListener() {
@Override
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
return true;
}
});
}
public void unblockTouch() {
setOnTouchListener(new OnTouchListener() {
@Override
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
return false;
}
});
invalidate();
}
private void initView() {
mPadding = new Padding();
mPadding.left = getPaddingLeft();
mPadding.right = getPaddingRight();
mPadding.top = getPaddingTop();
mPadding.bottom = getPaddingBottom();
Resources resources = getResources();
int cornerRadius = (int) resources.getDimension(R.dimen.mb_corner_radius_2);
int blue = resources.getColor(R.color.mb_blue);
int blueDark = resources.getColor(R.color.mb_blue_dark);
StateListDrawable background = new StateListDrawable();
mDrawableNormal = createDrawable(blue, cornerRadius, 0);
mDrawablePressed = createDrawable(blueDark, cornerRadius, 0);
mColor = blue;
mStrokeColor = blue;
mCornerRadius = cornerRadius;
background.addState(new int[]{android.R.attr.state_pressed}, mDrawablePressed.getGradientDrawable());
background.addState(StateSet.WILD_CARD, mDrawableNormal.getGradientDrawable());
setBackgroundCompat(background);
}
private StrokeGradientDrawable createDrawable(int color, int cornerRadius, int strokeWidth) {
StrokeGradientDrawable drawable = new StrokeGradientDrawable(new GradientDrawable());
drawable.getGradientDrawable().setShape(GradientDrawable.RECTANGLE);
drawable.setColor(color);
drawable.setCornerRadius(cornerRadius);
drawable.setStrokeColor(color);
drawable.setStrokeWidth(strokeWidth);
return drawable;
}
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
private void setBackgroundCompat(@Nullable Drawable drawable) {
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT <= Build.VERSION_CODES.JELLY_BEAN) {
setBackgroundDrawable(drawable);
} else {
setBackground(drawable);
}
}
public void setIcon(@DrawableRes final int icon) {
// post is necessary, to make sure getWidth() doesn't return 0
post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
Drawable drawable = getResources().getDrawable(icon);
int padding = (getWidth() / 2) - (drawable.getIntrinsicWidth() / 2);
setCompoundDrawablesWithIntrinsicBounds(icon, 0, 0, 0);
setPadding(padding, 0, 0, 0);
}
});
}
public void setIconLeft(@DrawableRes int icon) {
setCompoundDrawablesWithIntrinsicBounds(icon, 0, 0, 0);
}首先在構造方法中呼叫了initView()方法,建立一個StateListDrawable物件,然後利用
private StrokeGradientDrawable createDrawable(int color, int cornerRadius, int strokeWidth)產生一個StrokeGradientDrawable 物件,在利用
background.addState(new int[]{android.R.attr.state_pressed}, mDrawablePressed.getGradientDrawable());
background.addState(StateSet.WILD_CARD, mDrawableNormal.getGradientDrawable());
setBackgroundCompat(background); 分別設定了按下裝填和普通狀態的背景,當前的mColor,mStrokeColor,mCornerRadius,就是對用Params中變化前的引數,然後看下morph()這個方法,這個方法就是最開始使用的方法:開始進行變換,在其中呼叫了morphWithAnimation(@NonNull final Params params) 方法,來執行具體的動畫,這個方法中傳入的params就是使用這個庫時,建立的param,代表變化後的引數,是MorphingButton類中的一個內部類,上面程式碼中沒有貼出來,然後根據變化前的引數和傳入的變化的param構造 MorphingAnimation.Params這個引數,就是變化前和變化後的引數animationParams,最後利用
MorphingAnimation animation = new MorphingAnimation(animationParams);
animation.start();在建立MorphingAnimation 時,將這個animationParams引數傳入,呼叫start()方法開始動畫。可以看到在動畫結束後的回撥介面中呼叫了
finalizeMorphing(params);這個方法裡面有個 setIconLeft(params.icon),setText()來設定動畫結束後的顯示的圖示和文字,需要注意的是在setIconLeft()方法中,是利用:
// post is necessary, to make sure getWidth() doesn't return 0
post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
Drawable drawable = getResources().getDrawable(icon);
int padding = (getWidth() / 2) - (drawable.getIntrinsicWidth() / 2);
setCompoundDrawablesWithIntrinsicBounds(icon, 0, 0, 0);
setPadding(padding, 0, 0, 0);
}
});setCompoundDrawablesWithIntrinsicBounds()方法來設定ICON,並且設定一個padding來留出ICON的位置,這裡使用的Post(Runnable runbable)方法是為了避免獲取獲取的getWidth()為0,。
相信說到這裡,應該已經明白第一個動畫效果是怎麼實現的,其實關於button的動畫大多數是應該對background的drawable做變換,這個庫程式碼我覺得寫得還是不錯的,看著比較清晰,對於設定引數這塊的程式碼還是寫得挺好的,,在外部呼叫很直觀。
但這只是一個最簡單的動畫效果,還有一個更加酷炫的動畫效果:
這個動畫效果和第二個動畫效果放到下一篇部落格中進行解析。