Spring原始碼學習筆記(三)AOP實現
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-02-15
- Spring-AOP入口
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy />這一段程式碼,是實現AOP的具體入口,發現不是bean標籤則會使用不同的類進行解析,http\://www.springframework.org/schema/aop=org.springframeworl.aop.config.AopNamespaceHandler在XML的頭部可以看到這樣的配置,標誌著 AOP的解析 使用AopNamespaceHandler類來解析。
AopNamespaceHandler.java
public void init() {
// In 2.0 XSD as well as in 2.1 XSD. AspectJAutoProxyBeanDefinitionParser.java
public BeanDefinition parse(Element element, ParserContext parserContext) {
//註冊AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator AopNamespaceUtils.java
public static void registerAspectJAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(
ParserContext parserContext, Element sourceElement) {
//註冊AutoProxyCreator beanName :org.Springframework.aop.config.internalAutoProxyCreator
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = AopConfigUtils.registerAspectJAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(
parserContext.getRegistry(), parserContext.extractSource(sourceElement));
//對於proxy-target-class expose-proxy解析處理
useClassProxyingIfNecessary(parserContext.getRegistry(), sourceElement);
// 註冊元件並通知,便於監聽器作進一步處理
// 其中 beanDefinition 的 className 為 AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
registerComponentIfNecessary(beanDefinition, parserContext);
}AopConfiugUtils.java
private static BeanDefinition registerOrEscalateApcAsRequired(Class<?> cls, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Object source) {
Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null");
//判斷是否存在自動建立代理器,若存在,則判斷優先順序,誰優先順序高用誰
if (registry.containsBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
BeanDefinition apcDefinition = registry.getBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME);
if (!cls.getName().equals(apcDefinition.getBeanClassName())) {
//已註冊的Bean當前優先順序
int currentPriority = findPriorityForClass(apcDefinition.getBeanClassName());
//傳入的Bean優先順序
int requiredPriority = findPriorityForClass(cls);
if (currentPriority < requiredPriority) {
//替換
apcDefinition.setBeanClassName(cls.getName());
}
}
return null;
}
RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(cls);
beanDefinition.setSource(source);
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().add("order", Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE);
beanDefinition.setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE);
//註冊建立器
registry.registerBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME, beanDefinition);
return beanDefinition;
}
到此自動代理建立器註冊完成。
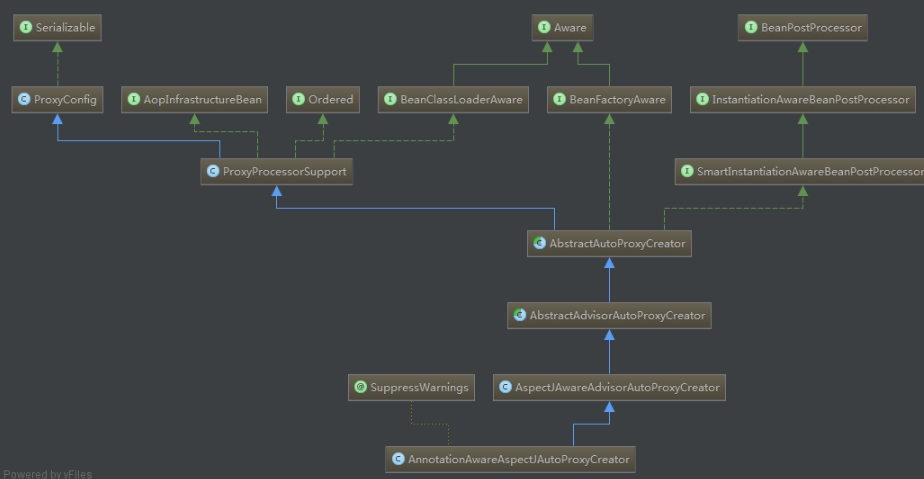
- 自動代理建立器如何工作?
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxy的介面、父類如上圖,其中BeanPostProcessor是實現代理的,AOP邏輯分析也是由BeanPostProcessor中PostprocessAfterInitialization開始。
BeanPostProcessor.java
//應用此前置處理器給新的bean例項
Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException;
//應用此後置處理器給新的bean例項
Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException;
AbstractAutoProxyCreator.java
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (bean != null) {
//獲取一個key 格式:classname_beanname
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
if (!this.earlyProxyReferences.contains(cacheKey)) {
// 如果它適合被代理,則需要封裝指定 bean。
return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
}
}
return bean;
}
//獲取key
protected Object getCacheKey(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
return beanClass.getName() + "_" + beanName;
}
//代理生成Bean
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
//判斷快取
if (beanName != null && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {
return bean;
}
//判斷是否需要增強
if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) {
return bean;
}
if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
// 若存在增強,則建立代理,(下一張詳細解析如何獲取增強)
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);
if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);
Object proxy = createProxy(bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
}
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
//生成代理
protected Object createProxy(
Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) {
//代理工廠
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.copyFrom(this);
//判斷使用 JDK動態代理 OR CGLIB
if (!proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) {
if (shouldProxyTargetClass(beanClass, beanName)) {
proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true);
}
else {
evaluateProxyInterfaces(beanClass, proxyFactory);
}
}
//裝配代理工廠 引數
Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors);
for (Advisor advisor : advisors) {
proxyFactory.addAdvisor(advisor);
}
proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource);
customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory);
proxyFactory.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy);
if (advisorsPreFiltered()) {
proxyFactory.setPreFiltered(true);
}
//生成代理 首先根據目標類的屬性,選擇 JDK動態代理 或者 CGLIB動態代理,再通過引數進行代理生成
return proxyFactory.getProxy(getProxyClassLoader());
}
@Override
//代理實現核心邏輯
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
MethodInvocation invocation;
Object oldProxy = null;
boolean setProxyContext = false;
TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.targetSource;
Class<?> targetClass = null;
Object target = null;
try {
if (!this.equalsDefined && AopUtils.isEqualsMethod(method)) {
// The target does not implement the equals(Object) method itself.
return equals(args[0]);
}
if (!this.hashCodeDefined && AopUtils.isHashCodeMethod(method)) {
// The target does not implement the hashCode() method itself.
return hashCode();
}
if (!this.advised.opaque && method.getDeclaringClass().isInterface() &&
method.getDeclaringClass().isAssignableFrom(Advised.class)) {
// Service invocations on ProxyConfig with the proxy config...
return AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(this.advised, method, args);
}
Object retVal;
if (this.advised.exposeProxy) {
// Make invocation available if necessary.
oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy);
setProxyContext = true;
}
// May be null. Get as late as possible to minimize the time we "own" the target,
// in case it comes from a pool.
target = targetSource.getTarget();
if (target != null) {
targetClass = target.getClass();
}
// Get the interception chain for this method.
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
// Check whether we have any advice. If we don't, we can fallback on direct
// reflective invocation of the target, and avoid creating a MethodInvocation.
if (chain.isEmpty()) {
// We can skip creating a MethodInvocation: just invoke the target directly
// Note that the final invoker must be an InvokerInterceptor so we know it does
// nothing but a reflective operation on the target, and no hot swapping or fancy proxying.
retVal = AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(target, method, args);
}
else {
// We need to create a method invocation...
invocation = new ReflectiveMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain);
// Proceed to the joinpoint through the interceptor chain.
retVal = invocation.proceed();
}
// Massage return value if necessary.
Class<?> returnType = method.getReturnType();
if (retVal != null && retVal == target && returnType.isInstance(proxy) &&
!RawTargetAccess.class.isAssignableFrom(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
// Special case: it returned "this" and the return type of the method
// is type-compatible. Note that we can't help if the target sets
// a reference to itself in another returned object.
retVal = proxy;
}
else if (retVal == null && returnType != Void.TYPE && returnType.isPrimitive()) {
throw new AopInvocationException(
"Null return value from advice does not match primitive return type for: " + method);
}
return retVal;
}
finally {
if (target != null && !targetSource.isStatic()) {
// Must have come from TargetSource.
targetSource.releaseTarget(target);
}
if (setProxyContext) {
// Restore old proxy.
AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy);
}
}
}
CglibAopProxy.java
//Cglib獲取代理 (先了解下CGLIB工作原理,以及實現方式)
public Object getProxy(ClassLoader classLoader) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Creating CGLIB proxy: target source is " + this.advised.getTargetSource());
}
try {
Class<?> rootClass = this.advised.getTargetClass();
Assert.state(rootClass != null, "Target class must be available for creating a CGLIB proxy");
Class<?> proxySuperClass = rootClass;
//判斷是否是CGLIB生成的類
if (ClassUtils.isCglibProxyClass(rootClass)) {
proxySuperClass = rootClass.getSuperclass();
Class<?>[] additionalInterfaces = rootClass.getInterfaces();
for (Class<?> additionalInterface : additionalInterfaces) {
this.advised.addInterface(additionalInterface);
}
}
// 驗證類是否可以使用Cglib(Final修飾的不允許繼承)
validateClassIfNecessary(proxySuperClass, classLoader);
// CGLIB 關鍵
Enhancer enhancer = createEnhancer();
if (classLoader != null) {
enhancer.setClassLoader(classLoader);
if (classLoader instanceof SmartClassLoader &&
((SmartClassLoader) classLoader).isClassReloadable(proxySuperClass)) {
enhancer.setUseCache(false);
}
}
enhancer.setSuperclass(proxySuperClass);
enhancer.setInterfaces(AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised));
enhancer.setNamingPolicy(SpringNamingPolicy.INSTANCE);
enhancer.setStrategy(new UndeclaredThrowableStrategy(UndeclaredThrowableException.class));
Callback[] callbacks = getCallbacks(rootClass);
Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[callbacks.length];
for (int x = 0; x < types.length; x++) {
types[x] = callbacks[x].getClass();
}
// fixedInterceptorMap only populated at this point, after getCallbacks call above
enhancer.setCallbackFilter(new ProxyCallbackFilter(
this.advised.getConfigurationOnlyCopy(), this.fixedInterceptorMap, this.fixedInterceptorOffset));
enhancer.setCallbackTypes(types);
// 建立代理
return createProxyClassAndInstance(enhancer, callbacks);
}
catch (CodeGenerationException ex) {
throw new AopConfigException("Could not generate CGLIB subclass of class [" +
this.advised.getTargetClass() + "]: " +
"Common causes of this problem include using a final class or a non-visible class",
ex);
}
catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new AopConfigException("Could not generate CGLIB subclass of class [" +
this.advised.getTargetClass() + "]: " +
"Common causes of this problem include using a final class or a non-visible class",
ex);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
// TargetSource.getTarget() failed
throw new AopConfigException("Unexpected AOP exception", ex);
}
}JdkDynamicAopProxy.java
//JDK動態代理生成
public Object getProxy(ClassLoader classLoader) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Creating JDK dynamic proxy: target source is " + this.advised.getTargetSource());
}
Class<?>[] proxiedInterfaces = AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised);
findDefinedEqualsAndHashCodeMethods(proxiedInterfaces);
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, proxiedInterfaces, this);
}
private void findDefinedEqualsAndHashCodeMethods(Class<?>[] proxiedInterfaces) {
for (Class<?> proxiedInterface : proxiedInterfaces) {
Method[] methods = proxiedInterface.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
if (AopUtils.isEqualsMethod(method)) {
this.equalsDefined = true;
}
if (AopUtils.isHashCodeMethod(method)) {
this.hashCodeDefined = true;
}
if (this.equalsDefined && this.hashCodeDefined) {
return;
}
}
}
}