elasticsearch 6.0java api的使用
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-02-15
elasticsearch 6.0 中java api的使用
1:使用java api建立elasticsearch客戶端

package com.search.elasticsearch; import org.elasticsearch.client.transport.TransportClient; import org.elasticsearch.common.settings.Settings; import org.elasticsearch.common.transport.TransportAddress; import org.elasticsearch.transport.client.PreBuiltTransportClient;import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.net.InetAddress; import java.util.Properties; public class ElasticsearchConfig { private static TransportClient client; public TransportClient getElasticsearchClient() { try { Settings settings = Settings.builder() .put("cluster.name", "my-esLearn") //連線的叢集名 .put("client.transport.ignore_cluster_name", true) //如果叢集名不對,也能連線 .build(); //建立client client = new PreBuiltTransportClient(settings) .addTransportAddress(new TransportAddress(InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1"), 9300)); //主機和埠號 return client; } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return null; } }

2:使用客戶端建立索引,索引中 某些欄位指定ik分詞器等
package com.search.elasticsearch;

import org.elasticsearch.action.DocWriteResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.action.admin.indices.analyze.AnalyzeRequestBuilder;
import org.elasticsearch.action.admin.indices.mapping.put.PutMappingRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.bulk.BulkItemResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.action.bulk.BulkRequestBuilder;
import org.elasticsearch.action.bulk.BulkResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.action.get.GetResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.action.index.IndexRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.index.IndexResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.action.search.SearchResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.action.search.SearchType;
import org.elasticsearch.action.update.UpdateRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.update.UpdateResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.client.IndicesAdminClient;
import org.elasticsearch.client.Requests;
import org.elasticsearch.client.transport.TransportClient;
import org.elasticsearch.common.settings.Settings;
import org.elasticsearch.common.transport.TransportAddress;
import org.elasticsearch.common.xcontent.XContentBuilder;
import org.elasticsearch.common.xcontent.XContentFactory;
import org.elasticsearch.index.query.QueryBuilders;
import org.elasticsearch.transport.client.PreBuiltTransportClient;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.ResourceBundle;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import static org.elasticsearch.common.xcontent.XContentFactory.jsonBuilder;
public class ElasticSearchUtil {
private static TransportClient client;
public ElasticSearchUtil() {
this.client=new ElasticsearchConfig().getElasticsearchClient(); //使用上面建立好的客戶端新增到類中。
}
//建立索引,並給索引某些欄位指定iK分詞,以後向該索引中查詢時,就會用ik分詞。
public void createIndex() throws IOException {
//建立對映
XContentBuilder mapping = XContentFactory.jsonBuilder()
.startObject()
.startObject("properties")
// .startObject("m_id").field("type","keyword").endObject()
//title:欄位名, type:文字型別 analyzer :分詞器型別
.startObject("title").field("type", "text").field("analyzer", "ik_smart").endObject() //該欄位新增的內容,查詢時將會使用ik_smart分詞
.startObject("content").field("type", "text").field("analyzer", "ik_max_word").endObject()
.endObject()
.endObject();
//index:索引名 type:型別名(可以自己定義)
PutMappingRequest putmap = Requests.putMappingRequest("index").type("type").source(mapping);
//建立索引
client.admin().indices().prepareCreate("index").execute().actionGet();
//為索引新增對映
client.admin().indices().putMapping(putmap).actionGet();
}
}
這個時候索引就建立好了,mapping不能掉
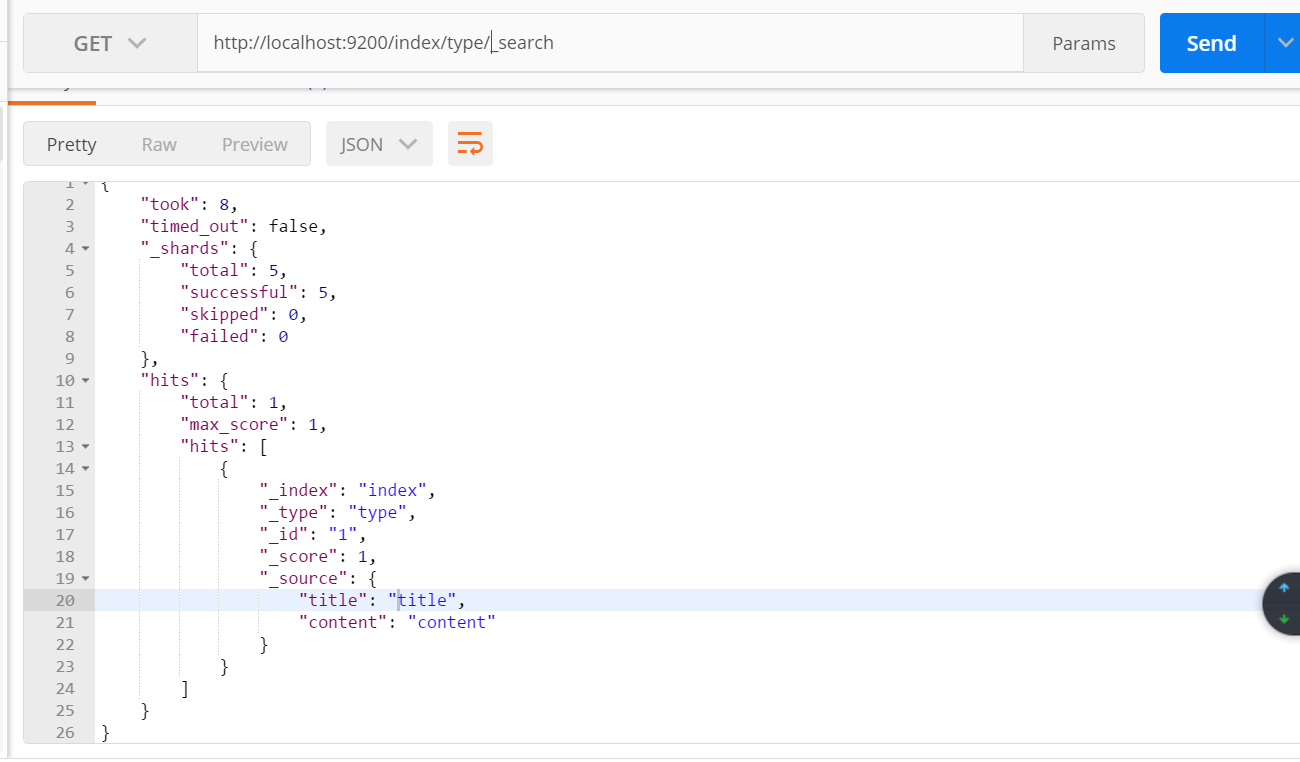
3: 向上一步建立的索引中新增內容,包括id,id不能重複

public void createIndex1() throws IOException { IndexResponse response = client.prepareIndex("index", "type", "1") //索引,型別,id .setSource(jsonBuilder() .startObject() .field("title", "title") //欄位,值 .field("content", "content") .endObject() ).get(); }

使用postman查詢該索引:
4:更新索引,更新剛才建立的索引,如果id相同將會覆蓋掉剛才的內容

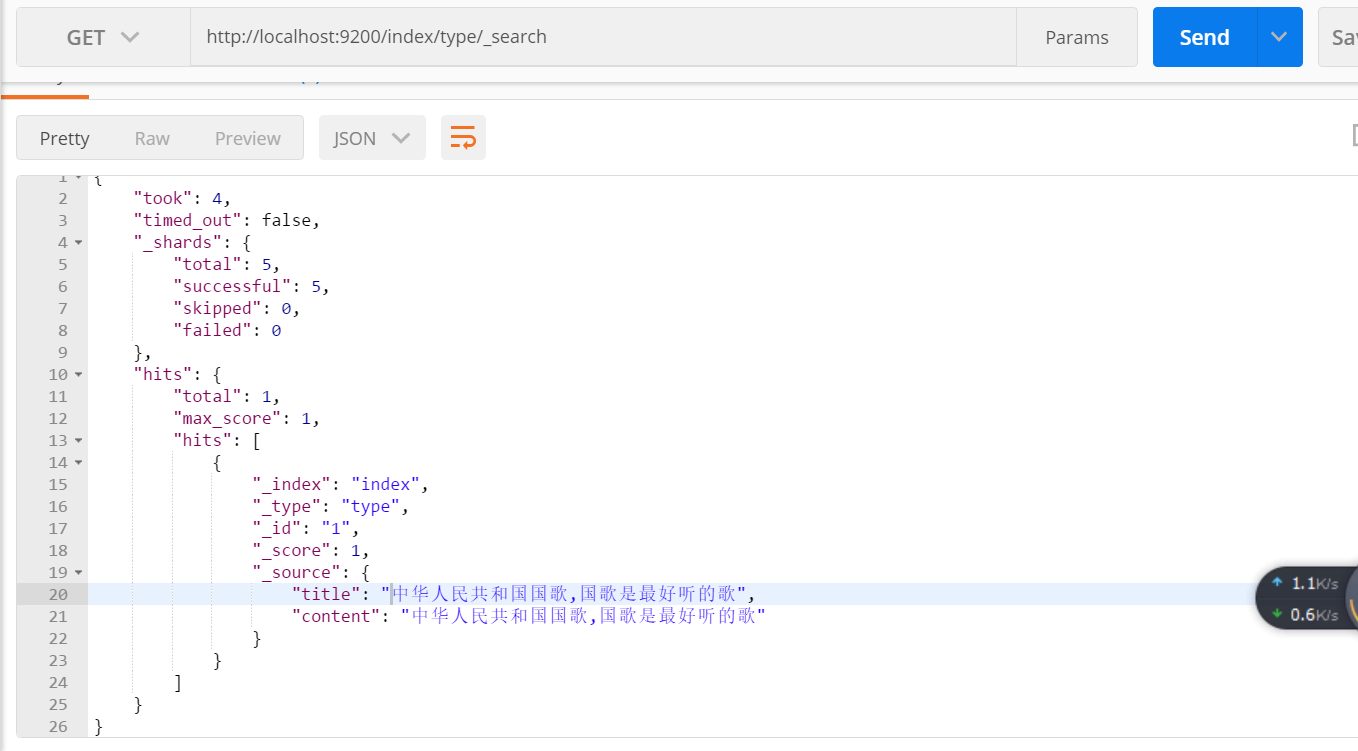
public void updateByClient() throws IOException, ExecutionException, InterruptedException { //每次新增id應該不同,相當於資料表中的主鍵,相同 的話將會進行覆蓋 UpdateResponse response = client.update(new UpdateRequest("index", "type", "1") .doc(XContentFactory.jsonBuilder() .startObject() .field("title", "中華人民共和國國歌,國歌是最好聽的歌") .field("content","中華人民共和國國歌,國歌是最好聽的歌") .endObject() )).get(); }

使用postman檢視該索引的內容
5:對索引進行查詢,因為分詞不同,分詞器將會對要查詢的內容先分詞,再在子段中查詢。
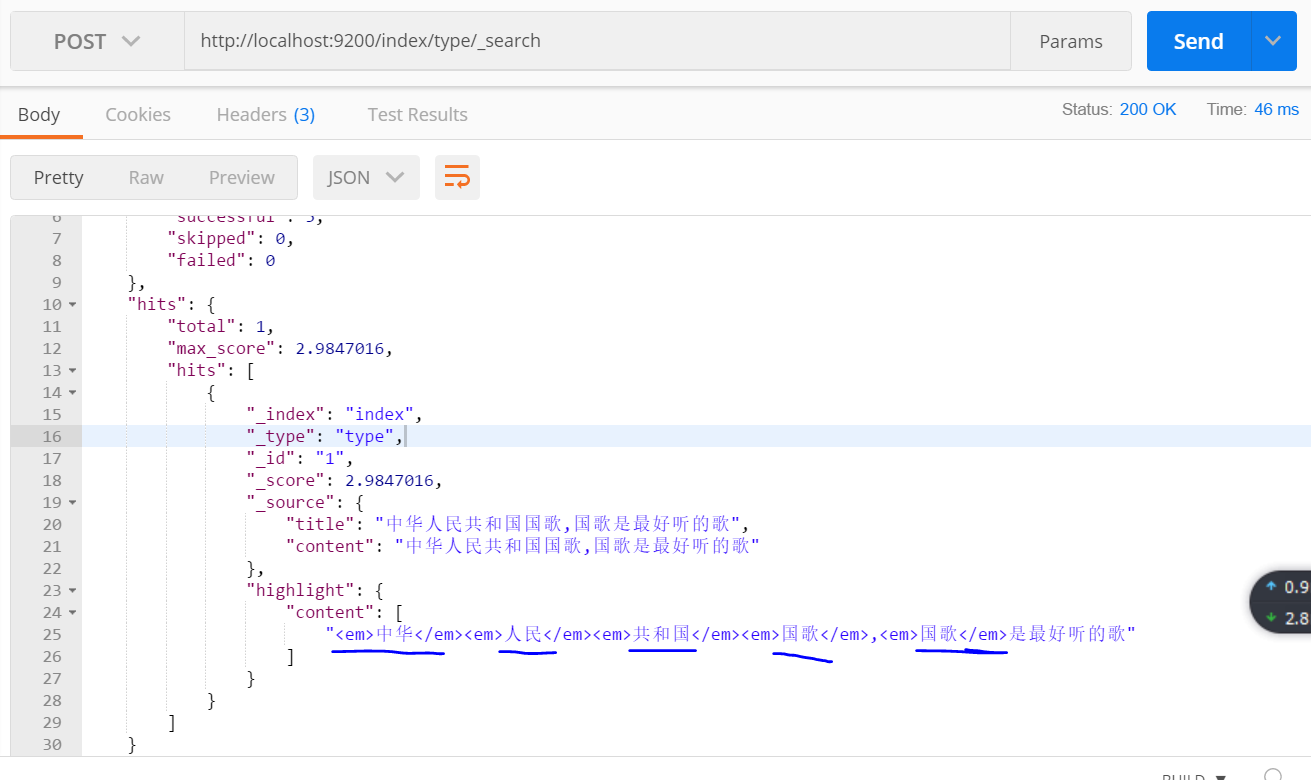
查詢 子段 content
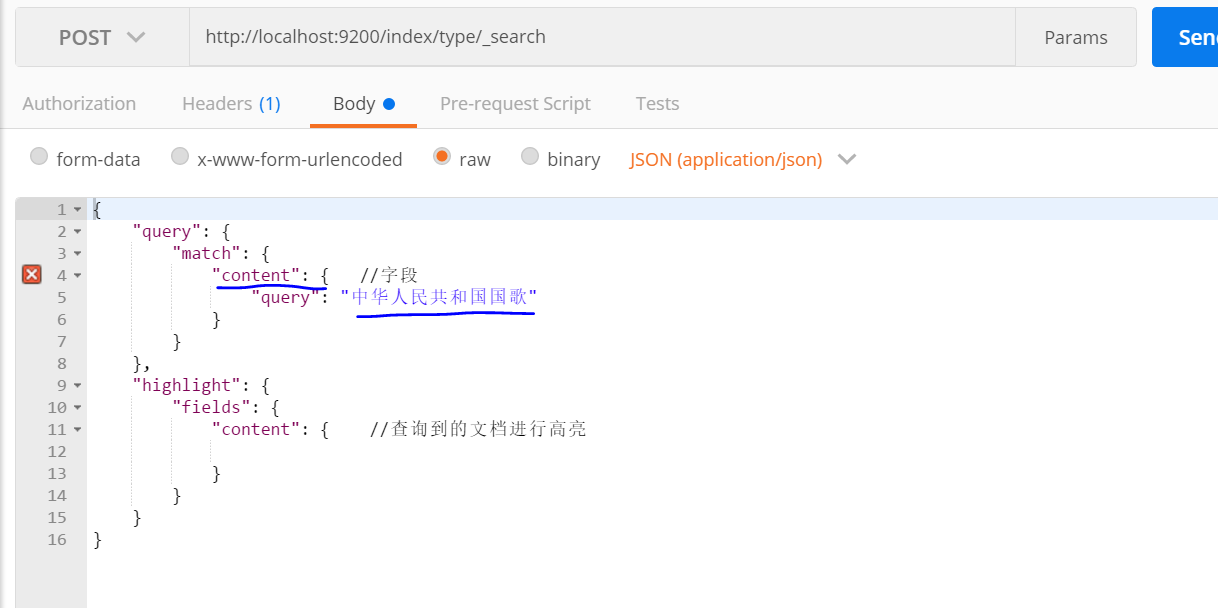
查詢結果:
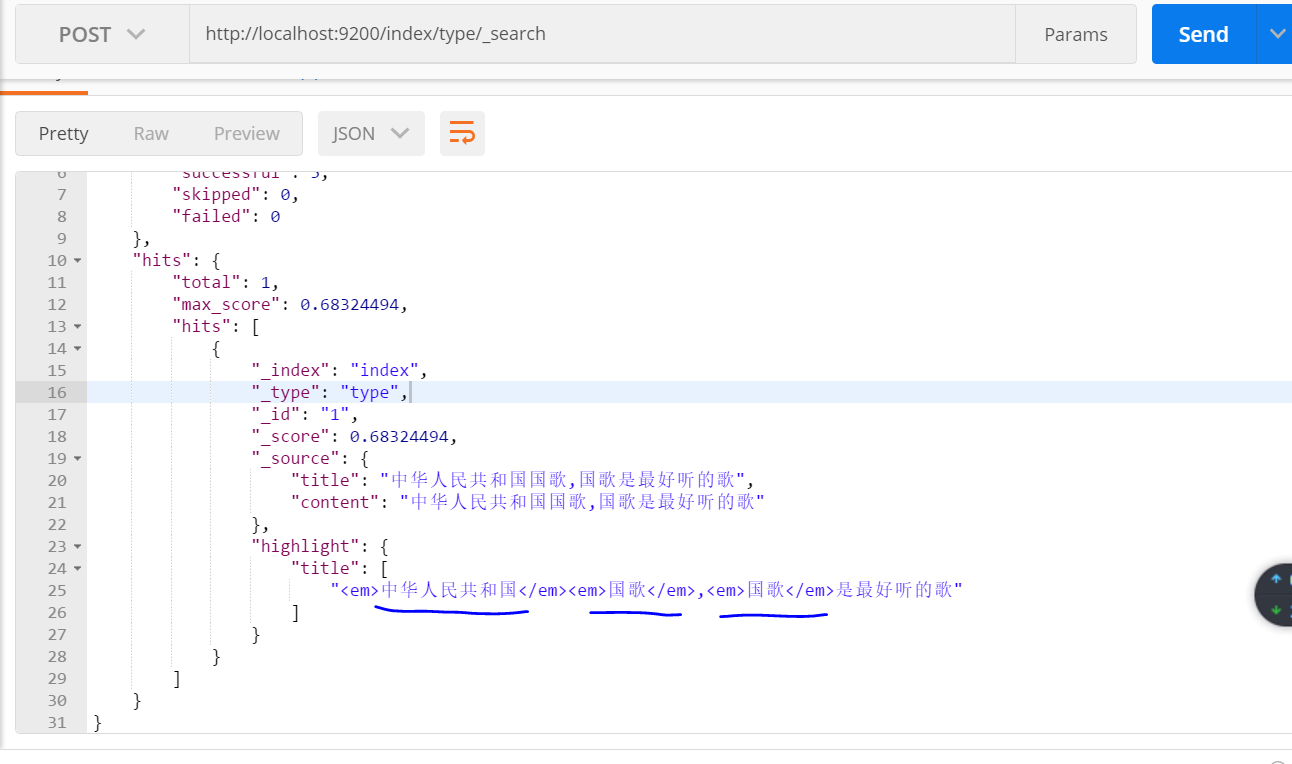
對title子段進行查詢:

查詢結果:
6:向 索引中再新增一條資料

public void createIndex2() throws IOException { IndexResponse response = client.prepareIndex("index", "type", "2") .setSource(jsonBuilder() .startObject() .field("title", "中華民族是偉大的民族") .field("content", "中華民族是偉大的民族") .endObject() ).get(); }

對欄位content進行查詢:
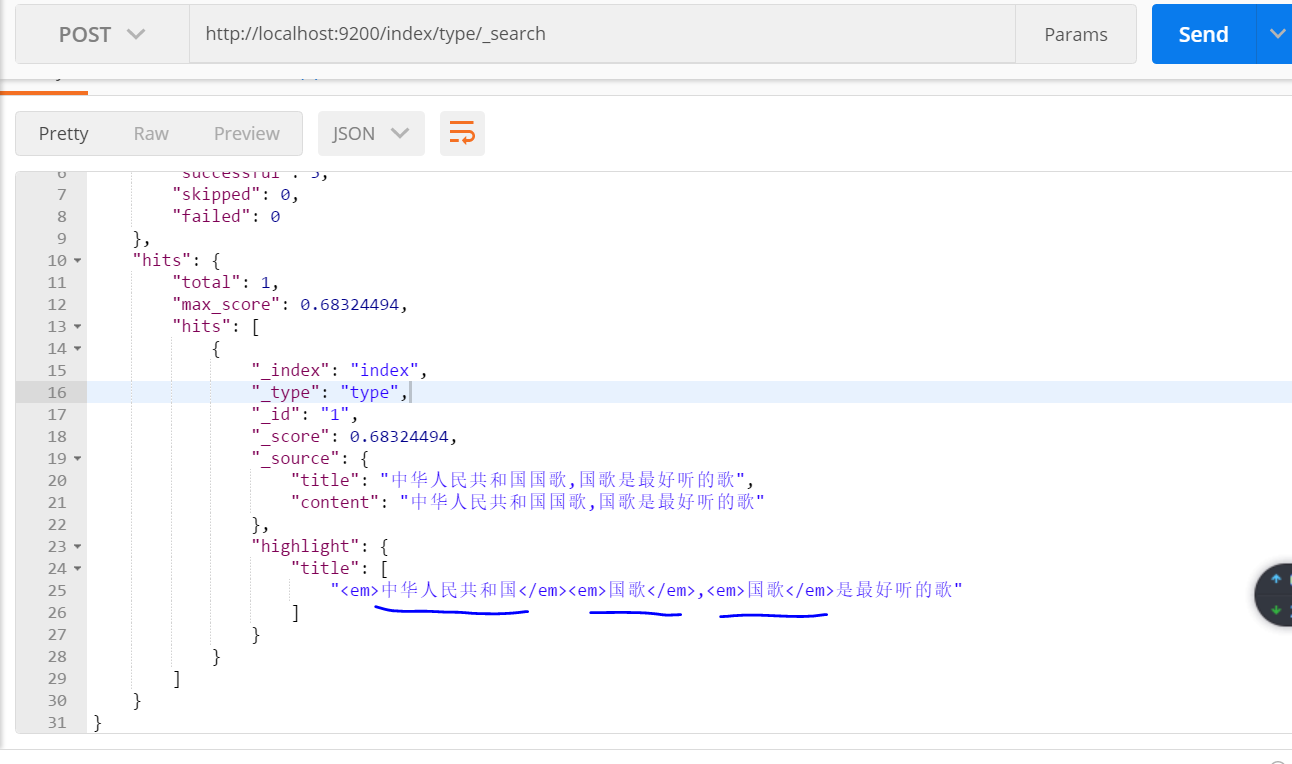
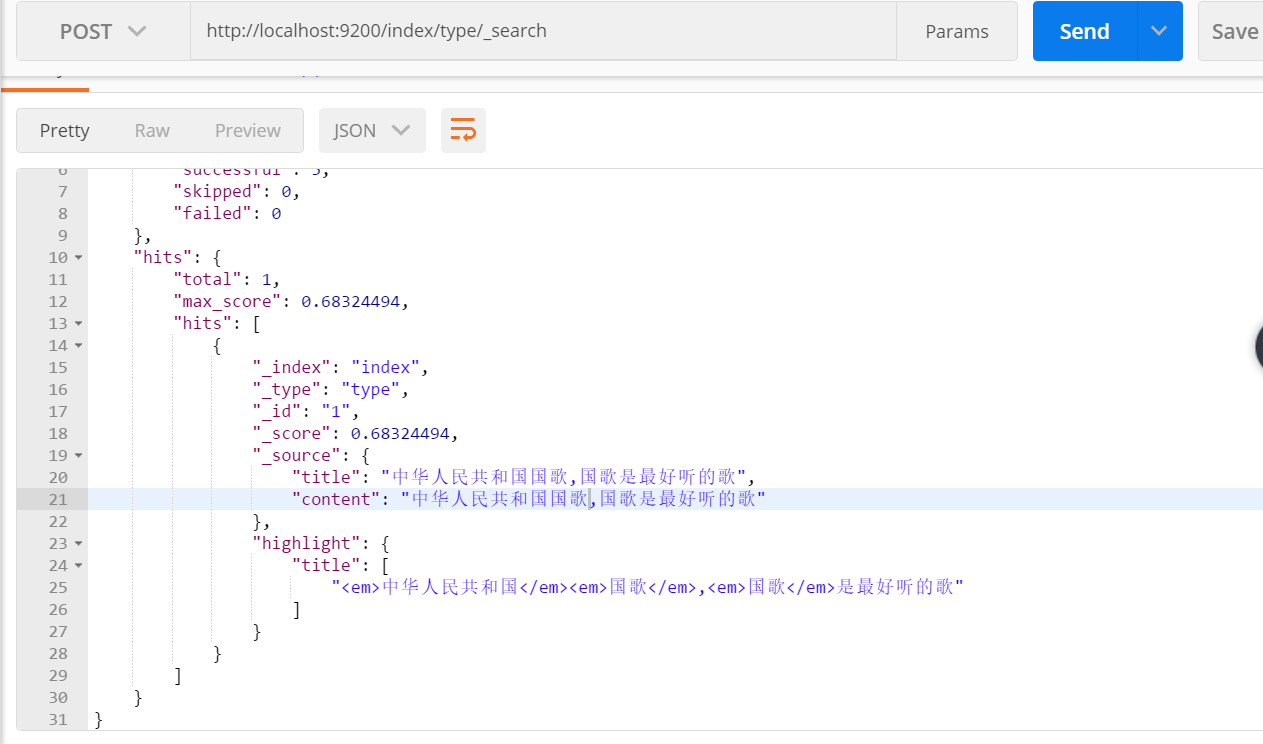
結果:兩條資料都能查到,因為對查詢內容 “中華人民共和國國歌” 進行細粒度劃分,含有“中華” 一詞,兩條資料中都包含“中華”。
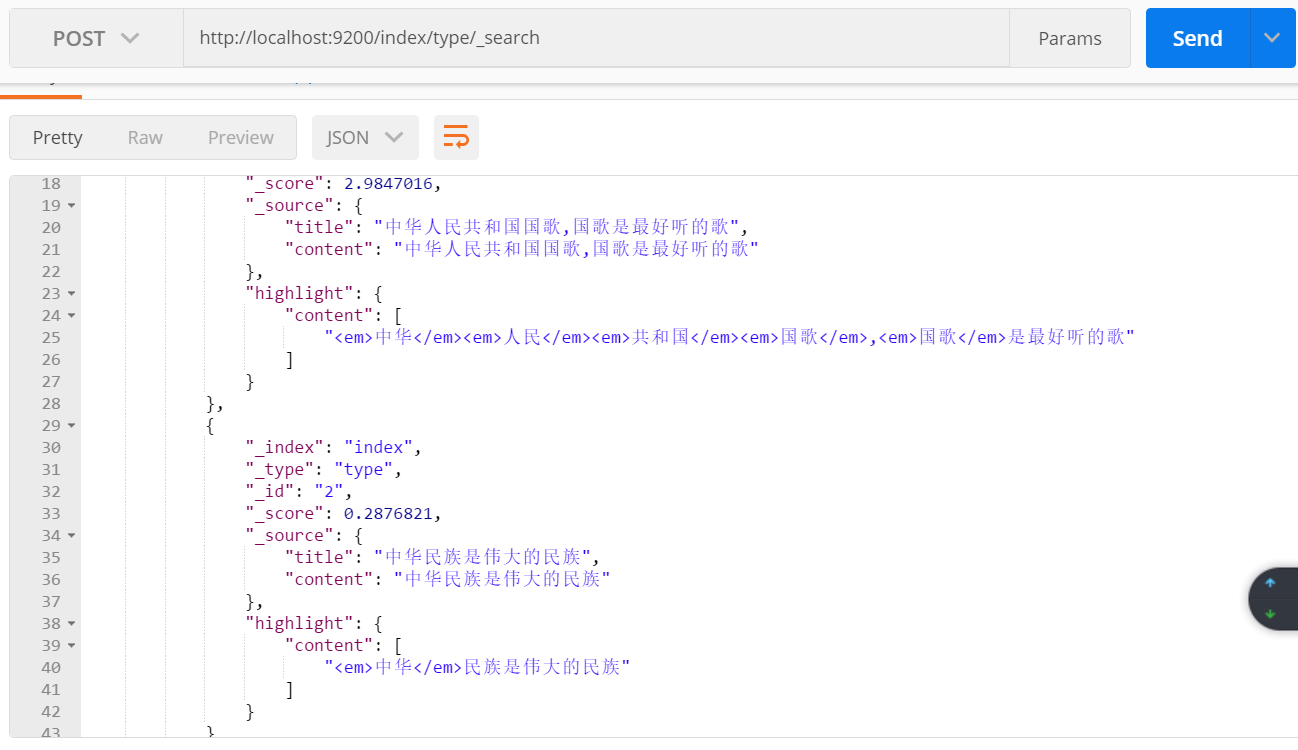
對欄位title 進行查詢:
查詢結果: 只有一條資料,因為對title 使用的是 粗粒度分詞
7:search api的操作:

public void search() {
SearchResponse response1 = client.prepareSearch("index1", "index") //指定多個索引
.setTypes("type1", "type") //指定型別
.setSearchType(SearchType.QUERY_THEN_FETCH)
.setQuery(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("title", "中華人民共和國國歌")) // Query
// .setPostFilter(QueryBuilders.rangeQuery("age").from(12).to(18)) // Filter
.setFrom(0).setSize(60).setExplain(true)
.get();
long totalHits1= response1.getHits().totalHits; //命中個數
System.out.println(totalHits1);
SearchResponse response2 = client.prepareSearch("index1", "index") //指定多個索引
.setTypes("type1", "type") //指定型別
.setSearchType(SearchType.QUERY_THEN_FETCH)
.setQuery(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("content", "中華人民共和國國歌")) // Query
// .setPostFilter(QueryBuilders.rangeQuery("age").from(12).to(18)) // Filter
.setFrom(0).setSize(60).setExplain(true)
.get();
long totalHits2 = response2.getHits().totalHits; //命中個數
System.out.println(totalHits2);
}
8:Get Api操作:

public void get() { GetResponse response = client.prepareGet("index", "type", "1").get(); Map<String, Object> source = response.getSource(); Set<String> strings = source.keySet(); Iterator<String> iterator = strings.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()) { System.out.println(source.get(iterator.next())); } }

9:bulk api 批量建立索引,並新增資料

/** * 批量建立索引,並新增資料 * @throws IOException */ public void bulkApi() throws IOException { BulkRequestBuilder bulkRequest = client.prepareBulk(); // either use client#prepare, or use Requests# to directly build index/delete requests bulkRequest.add(client.prepareIndex("twitter", "tweet", "1") .setSource(jsonBuilder() .startObject() .field("user", "kimchy") .field("postDate", new Date()) .field("message", "trying out Elasticsearch") .endObject() ) ); bulkRequest.add(client.prepareIndex("twitter", "tweet", "2") .setSource(jsonBuilder() .startObject() .field("user", "kimchy") .field("postDate", new Date()) .field("message", "another post") .endObject() ) ); BulkResponse bulkResponse = bulkRequest.get(); if (bulkResponse.hasFailures()) { // process failures by iterating through each bulk response item } }

10 將搜尋得到的資料以json資料形式返回。

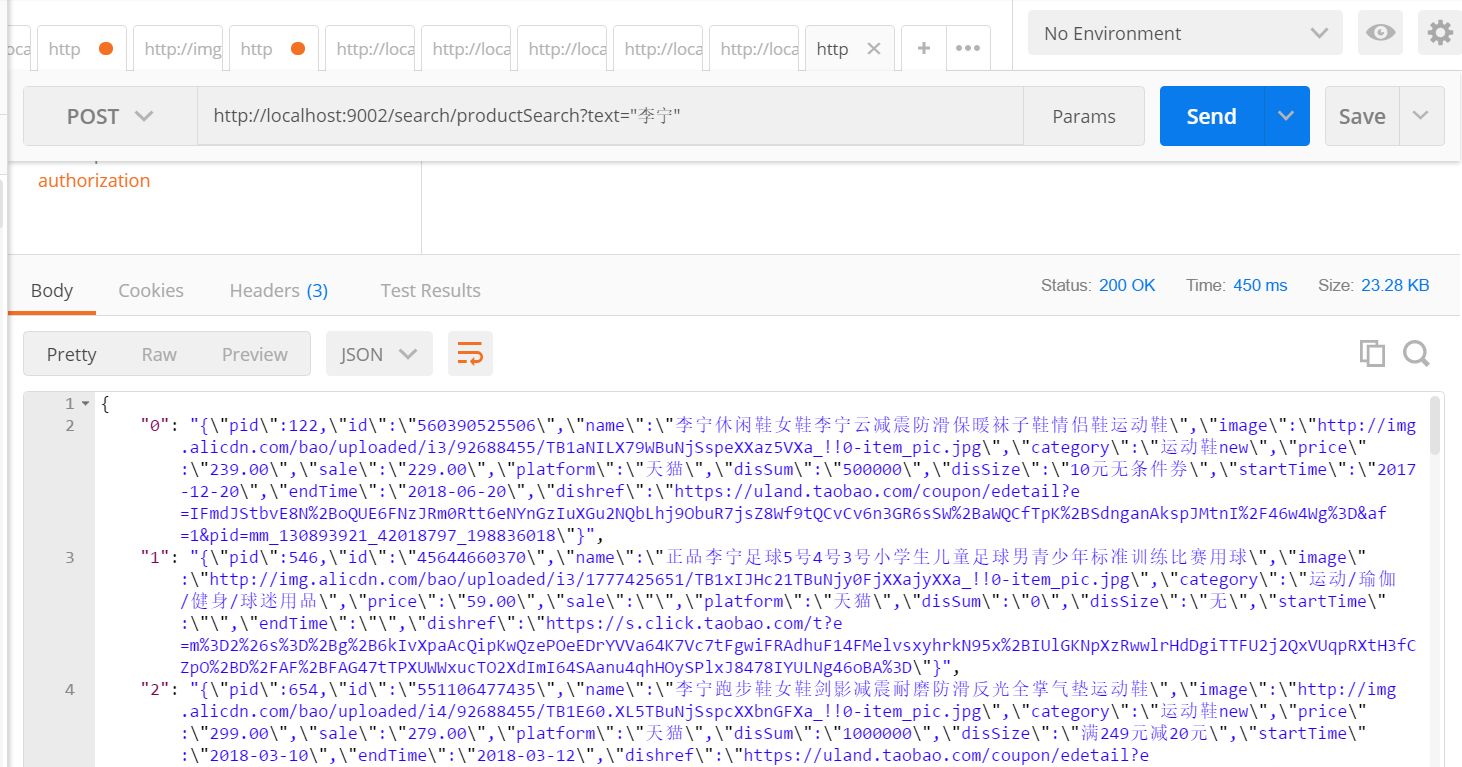
/** * 商品搜尋 */ @RequestMapping("/productSearch") @ResponseBody public JSONObject productSearch(String text) { SearchResponse response1 = client.prepareSearch("product", "index") //指定多個索引 .setTypes("product", "type") //指定型別 .setSearchType(SearchType.QUERY_THEN_FETCH) .setQuery(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("name", text)) // Query .setFrom(0).setSize(60).setExplain(true) .get(); SearchHit[] searchHits = response1.getHits().getHits();//命中個數 JSONObject jsonObject = new JSONObject(); for (int i = 0; i < searchHits.length; i++) { String sourceAsString = searchHits[i].getSourceAsString(); jsonObject.put(i+"",sourceAsString); } return jsonObject; }