Object物件之clone方法
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-02-17
克隆的目的:快速建立一個已有物件的副本。
克隆的步驟:
- 建立一個物件
- 將原有物件的資料匯入到新建立的資料中
1. Object的clone()原始碼簡介
- /**
- * Creates and returns a copy of this {@code Object}. The default
- * implementation returns a so-called "shallow" copy: It creates a new
- * instance of the same class and then copies the field values (including
- * object references) from this instance to the new instance. A "deep" copy,
- * in contrast, would also recursively clone nested objects. A subclass that
- * needs to implement this kind of cloning should call {@code super.clone()}
- * to create the new instance and then create deep copies of the nested,
- * mutable objects.
- *
- * @return a copy of this object.
- * @throws CloneNotSupportedException
- * if this object's class does not implement the {@code
- * Cloneable} interface.
- */
- protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
- if (!(this instanceof Cloneable)) {
- throw new CloneNotSupportedException("Class doesn't implement Cloneable");
- }
- return internalClone((Cloneable) this);
- }
- /*
- * Native helper method for cloning.
- */
- private native Object internalClone(Cloneable o);
clone方法首先會判物件是否實現了Cloneable介面,若無則丟擲CloneNotSupportedException, 最後會呼叫internalClone. intervalClone是一個native方法,一般來說native方法的執行效率高於非native方法。
當某個類要複寫clone方法時,要繼承Cloneable介面。通常的克隆物件都是通過super.clone()方法來克隆物件。
2.淺克隆(shadow clone)
克隆就是複製一個物件的複本.若只需要複製物件的欄位值(對於基本資料型別,如:int,long,float等,則複製值;對於複合資料型別僅複製該欄位值,如陣列變數則複製地址,對於物件變數則複製物件的reference。
例子:
- public class ShadowClone implements Cloneable{
- private int a; // 基本型別
- private int[] b; // 非基本型別
- // 重寫Object.clone()方法,並把protected改為public
- public Object clone(){
- ShadowClone sc = null;
- try
- {
- sc = (ShadowClone) super.clone();
- } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e){
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- return sc;
- }
- public int getA()
- {
- return a;
- }
- public void setA(int a)
- {
- this.a = a;
- }
- public int[] getB() {
- return b;
- }
- public void setB(int[] b) {
- this.b = b;
- }
- }
- public class Test{
- public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException{
- ShadowClone c1 = new ShadowClone();
- //對c1賦值
- c1.setA(100) ;
- c1.setB(new int[]{1000}) ;
- System.out.println("克隆前c1: a="+c1.getA()+" b="+c1.getB()[0]);
- //克隆出物件c2,並對c2的屬性A,B,C進行修改
- ShadowClone c2 = (ShadowClone) c1.clone();
- //對c2進行修改
- c2.setA(50) ;
- int []a = c2.getB() ;
- a[0]=5 ;
- c2.setB(a);
- System.out.println("克隆前c1: a="+c1.getA()+" b="+c1.getB()[0]);
- System.out.println("克隆後c2: a="+c2.getA()+ " b[0]="+c2.getB()[0]);
- }
- }
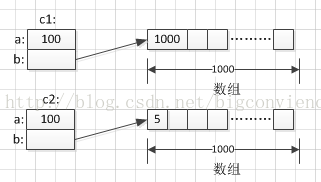
克隆前c1: a=100 b=1000
克隆前c1: a=100 b=5
克隆後c2: a=50 b[0]=5
c1和c2的物件模型:
可以看出,基本型別可以使用淺克隆,而對於引用型別,由於引用的是內容相同,所以改變c2例項物件中的屬性就會影響到c1。所以引用型別需要使用深克隆。另外,在開發一個不可變類的時候,如果這個不可變類中成員有引用型別,則就需要通過深克隆來達到不可變的目的。
3.深克隆(deep clone)
深克隆與淺克隆的區別在於對複合資料型別的複製。若物件中的某個欄位為複合型別,在克隆物件的時候,需要為該欄位重新建立一個物件。
例子:
- public class DeepClone implements Cloneable {
- private int a; // 基本型別
- private int[] b; // 非基本型別
- // 重寫Object.clone()方法,並把protected改為public
- public Object clone(){
- DeepClone sc = null;
- try
- {
- sc = (DeepClone) super.clone();
- int[] t = sc.getB();
- int[] b1 = new int[t.length];
- for (int i = 0; i < b1.length; i++) {
- b1[i] = t[i];
- }
- sc.setB(b1);
- } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e){
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- return sc;
- }
- public int getA()
- {
- return a;
- }
- public void setA(int a)
- {
- this.a = a;
- }
- public int[] getB() {
- return b;
- }
- public void setB(int[] b) {
- this.b = b;
- }
- }
結果為:
克隆前c1: a=100 b=1000
克隆前c1: a=100 b=1000克隆後c2: a=50 b[0]=5
物件模型:
4、總結:
- 克隆方法用於建立物件的拷貝,為了使用clone方法,類必須實現java.lang.Cloneable介面重寫protected方法clone,如果沒有實現Clonebale介面會丟擲CloneNotSupportedException.
- 在克隆java物件的時候不會呼叫構造器
- java提供一種叫淺拷貝(shallow copy)的預設方式實現clone,建立好物件的副本後然後通過賦值拷貝內容,意味著如果你的類包含引用型別,那麼原始物件和克隆都將指向相同的引用內容,這是很危險的,因為發生在可變的欄位上任何改變將反應到他們所引用的共同內容上。為了避免這種情況,需要對引用的內容進行深度克隆。