Android實戰——GreenDao3.2的使用,愛不釋手
GreenDao3.2的使用,愛不釋手
前言
GreenDao是一款操作資料庫的神器,經過了2.0版本的升級後,已經被廣泛的開發者使用。確實是很好用,入門簡單,可以剩去了資料庫的建表操作和資料庫SQL的編寫,博主用了一次之後愛不釋手,和以前的資料庫操作一大堆的程式碼將它縮成了一句話,舒服
GreenDao3.2的簡介
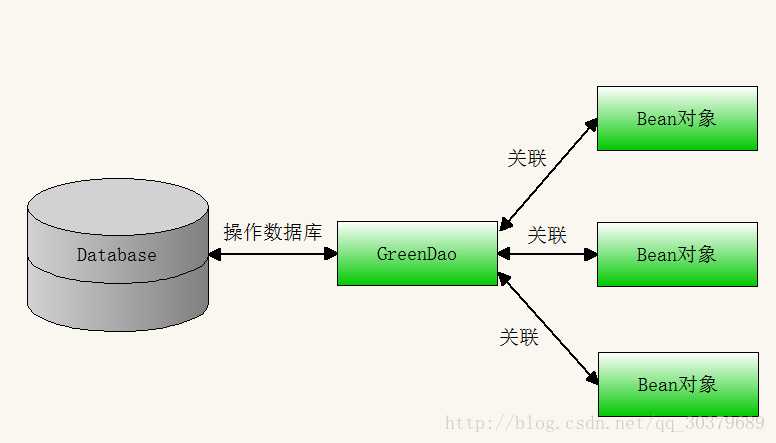
認識GreenDao之前必須知道ORM(Object Relation Mapping物件關係對映),其表現形式就是通過GreenDao將資料庫和Bean物件關聯起來,其表現形式如下圖
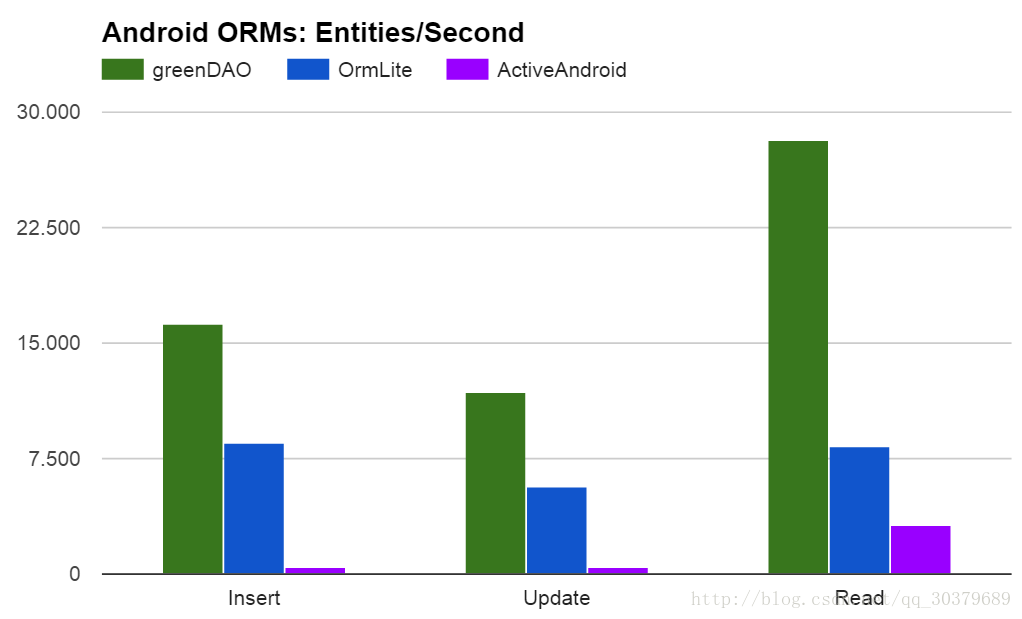
GreenDao之所以很流行,跟它的優點是息息相關的,從官網中可以看到這樣一張圖,其表示了在主流的ORM第三方庫中,其對資料庫操作的速度是最快的
不僅如此,其優點還包括有以下幾點
- 存取速度快
- 支援資料庫加密
- 輕量級
- 啟用實體
- 支援快取
- 程式碼自動生成
GreenDao3.2的配置
GreenDao的配置很簡單,不過需要注意的是,有些人按照正確的配置後卻頻頻出錯,個人也經歷過,最後的原因是網路有問題。因為校園網的DNS服務很差,所以解析不到GreenDao的依賴網站
一、需要在工程(Project)的build.gradle中新增依賴
buildscript {
repositories {
jcenter()
}
dependencies {
classpath 'com.android.tools.build:gradle:2.0.0' 二、在專案(Module)的build.gradle中新增依賴
apply plugin: 'com.android.application'
//使用greendao
apply plugin: 'org.greenrobot.greendao'
android {
compileSdkVersion 23
buildToolsVersion "23.0.2"
defaultConfig {
applicationId "com.handsome.didi" 到這裡就配置成功了
GreenDao3.2的使用
配置完成後,最重要的就是GreenDao的使用了,或許使用過Bmob第三方後端雲的同學會知道,他們的API有些相像,都是通過API來拼裝SQL語句的
下面就以購物車的實戰來使用GreenDao,這裡的購物車展示圖如下
我們所知道的資料庫操作需要:資料庫名、表名、欄位名,缺一不可,下面就是這三項的建立
一、建立Bean物件(表名和欄位名)
GreenDao需要建立Bean物件之後,該Bean物件就是表名,而它的屬性值就是欄位名,其實現是通過註釋的方式來實現的,下面是購物車的Bean物件(每個Bean物件對應一張表)
@Entity
public class Shop{
//表示為購物車列表
public static final int TYPE_CART = 0x01;
//表示為收藏列表
public static final int TYPE_LOVE = 0x02;
//不能用int
@Id(autoincrement = true)
private Long id;
//商品名稱
@Unique
private String name;
//商品價格
@Property(nameInDb = "price")
private String price;
//已售數量
private int sell_num;
//圖示url
private String image_url;
//商家地址
private String address;
//商品列表型別
private int type;
}這裡需要注意的是,建立完成之後,需要build gradle來完成我們的程式碼自動生成。自動生成的程式碼有
- Bean實體的構造方法和get、set方法
- DaoMaster、DaoSession、DAOS類
這裡對Bean物件的註釋進行解釋
- @Entity:告訴GreenDao該物件為實體,只有被@Entity註釋的Bean類才能被dao類操作
- @Id:物件的Id,使用Long型別作為EntityId,否則會報錯。(autoincrement = true)表示主鍵會自增,如果false就會使用舊值
- @Property:可以自定義欄位名,注意外來鍵不能使用該屬性
- @NotNull:屬性不能為空
- @Transient:使用該註釋的屬性不會被存入資料庫的欄位中
- @Unique:該屬性值必須在資料庫中是唯一值
- @Generated:編譯後自動生成的建構函式、方法等的註釋,提示建構函式、方法等不能被修改
二、建立資料庫(資料庫名)
資料庫的表名和欄位都建好了,下面差個數據庫的建立,下面通過傳統和GreenDao的比較來體驗其優點
① 傳統的資料庫建立
public class CommonOpenHelper extends SQLiteOpenHelper {
private static CommonOpenHelper helper;
public static CommonOpenHelper getInstance(Context context) {
if (helper == null) {
helper = new CommonOpenHelper(context, "common.db", null, 1);
}
return helper;
}
private CommonOpenHelper(Context context, String name, SQLiteDatabase.CursorFactory factory, int version) {
super(context, name, factory, version);
}
@Override
public void onCreate(SQLiteDatabase db) {
//建立love表
db.execSQL("create table love(" +
"id integer primary key autoincrement, " +
"name varchar, " +
"price varchar, " +
"sell_num integer, " +
"image_url varchar, " +
"address varchar" +
")");
}
@Override
public void onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase db, int oldVersion, int newVersion) {
}
}② GreenDao資料庫建立
public class BaseApplication extends Application {
private static DaoSession daoSession;
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
//配置資料庫
setupDatabase();
}
/**
* 配置資料庫
*/
private void setupDatabase() {
//建立資料庫shop.db"
DaoMaster.DevOpenHelper helper = new DaoMaster.DevOpenHelper(this, "shop.db", null);
//獲取可寫資料庫
SQLiteDatabase db = helper.getWritableDatabase();
//獲取資料庫物件
DaoMaster daoMaster = new DaoMaster(db);
//獲取Dao物件管理者
daoSession = daoMaster.newSession();
}
public static DaoSession getDaoInstant() {
return daoSession;
}
}可以發現,GreenDao已經將我們的資料庫建立縮成幾句話,程式碼會自動將Bean物件建立成表,不再是傳統的手寫SQL語句。這裡的資料庫建立只需要在Application中執行一次即可,這裡對幾個類進行解釋
- DevOpenHelper:建立SQLite資料庫的SQLiteOpenHelper的具體實現
- DaoMaster:GreenDao的頂級物件,作為資料庫物件、用於建立表和刪除表
- DaoSession:管理所有的Dao物件,Dao物件中存在著增刪改查等API
由於我們已經建立好了DaoSession和Shop的Bean物件,編譯後會自動生成我們的ShopDao物件,可通過DaoSession獲得
ShopDao dao = daoSession.getShopDao();這裡的Dao(Data Access Object)是指資料訪問介面,即提供了資料庫操作一些API介面,可通過dao進行增刪改查操作
三、資料庫的增刪改查
資料庫的表名、欄位、資料庫都建好了,下面就通過傳統和GreenDao對資料庫的操作來比較體驗其優點
① 傳統的增刪改查
/**
* 採用ContentProvider進行增刪改查
*/
public class CartDao {
/**
* 新增資料
*
* @param resolver
* @param shop
* @return
*/
public static boolean insertCart(ContentResolver resolver, Shop shop) {
ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
values.put("name", shop.getName());
values.put("price", shop.getPrice());
values.put("sell_num", shop.getSell_num());
values.put("image_url", shop.getImage_url());
values.put("address", shop.getAddress());
resolver.insert(MyCartProvider.URI.CODE_CART_INSERT, values);
BaseApplication.getDaoInstant().getShopDao().insert(shop);
return true;
}
/**
* 刪除資料
*
* @param resolver
* @param id
*/
public static void deleteCart(ContentResolver resolver, int id) {
resolver.delete(MyCartProvider.URI.CODE_CART_DELETE, "id = " + id, null);
}
/**
* 查詢資料
*
* @param resolver
* @return
*/
public static List<Shop> queryCart(ContentResolver resolver) {
List<Shop> list = new ArrayList<Shop>();
String[] projection = {"id", "name", "price", "sell_num", "image_url", "address"};
Cursor cursor = resolver.query(MyCartProvider.URI.CODE_CART_QUERY, projection, null, null, null);
while (cursor.moveToNext()) {
Shop shop = new Shop();
shop.setId(cursor.getLong(cursor.getColumnIndex("id")));
shop.setName(cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("name")));
shop.setPrice(cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("price")));
shop.setSell_num(cursor.getInt(cursor.getColumnIndex("sell_num")));
shop.setImage_url(cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("image_url")));
shop.setAddress(cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("address")));
list.add(shop);
}
return list;
}
/**
* 省略更新資料
*/
}② GreenDao增刪改查
public class LoveDao {
/**
* 新增資料,如果有重複則覆蓋
*
* @param shop
*/
public static void insertLove(Shop shop) {
BaseApplication.getDaoInstant().getShopDao().insertOrReplace(shop);
}
/**
* 刪除資料
*
* @param id
*/
public static void deleteLove(long id) {
BaseApplication.getDaoInstant().getShopDao().deleteByKey(id);
}
/**
* 更新資料
*
* @param shop
*/
public static void updateLove(Shop shop) {
BaseApplication.getDaoInstant().getShopDao().update(shop);
}
/**
* 查詢條件為Type=TYPE_LOVE的資料
*
* @return
*/
public static List<Shop> queryLove() {
return BaseApplication.getDaoInstant().getShopDao().queryBuilder().where(ShopDao.Properties.Type.eq(Shop.TYPE_LOVE)).list();
}
/**
* 查詢全部資料
*/
public static List<Shop> queryAll() {
return BaseApplication.getDaoInstant().getShopDao().loadAll();
}
}效果很明顯,GreenDao的封裝更加短小精悍,語義明朗,下面對GreenDao中Dao物件其他API的介紹
- 增加單個數據
- getShopDao().insert(shop);
- getShopDao().insertOrReplace(shop);
- 增加多個數據
- getShopDao().insertInTx(shopList);
- getShopDao().insertOrReplaceInTx(shopList);
- 查詢全部
- List< Shop> list = getShopDao().loadAll();
- List< Shop> list = getShopDao().queryBuilder().list();
- 查詢附加單個條件
- .where()
- .whereOr()
- 查詢附加多個條件
- .where(, , ,)
- .whereOr(, , ,)
- 查詢附加排序
- .orderDesc()
- .orderAsc()
- 查詢限制當頁個數
- .limit()
- 查詢總個數
- .count()
- 修改單個數據
- getShopDao().update(shop);
- 修改多個數據
- getShopDao().updateInTx(shopList);
- 刪除單個數據
- getTABUserDao().delete(user);
- 刪除多個數據
- getUserDao().deleteInTx(userList);
- 刪除資料ByKey
- getTABUserDao().deleteByKey();
結語
關於GreenDao的的基本概念與基本操作就講到這裡,更多對於GreenDao的資料庫操作還需要多多從實戰中去探索,這裡只是一個快速入門的引導.GreenDao高階操作還包括有:多表查詢、多表關聯、session快取等用法,可以到GreenDao的官網進行學習