蟻群演算法(詳解)python
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-02-20
only integers, slices (`:`), ellipsis (`...`), numpy.newaxis (`None`) and integer or boolean arrays are valid indices
因為要做數學建模,所以學一下蟻群演算法。在CSDN中看到這個部落格,但是不是很詳細,基於此程式碼為模板,詳解一下。
旅行商問題(travelling salesman problem,TSP)是物流領域的典型問題。螞蟻演算法求解TSP問題的過程如下:
(1)初始化,設迭代的次數為NC,初始NC=0。(2)將numant只螞蟻置於numcity個頂點上。(3)numant只螞蟻按概率函式選擇下一個城市,完成各自的周遊。(4)記錄本次迭代最佳路線。(5)全域性更新資訊素值。(6)終止,若終止條件滿足,則結束;否則iter=iter+1,轉入步驟(2)進行下一代優化。終止條件可指定進化的代數,也可限定執行的時間,或設定最短路長的下限。(7)輸出結果。
下面是兩個關鍵公式:
第一個是轉移城市概率公式:
第二個公式是:資訊素更新公式
程式碼與解釋如下:
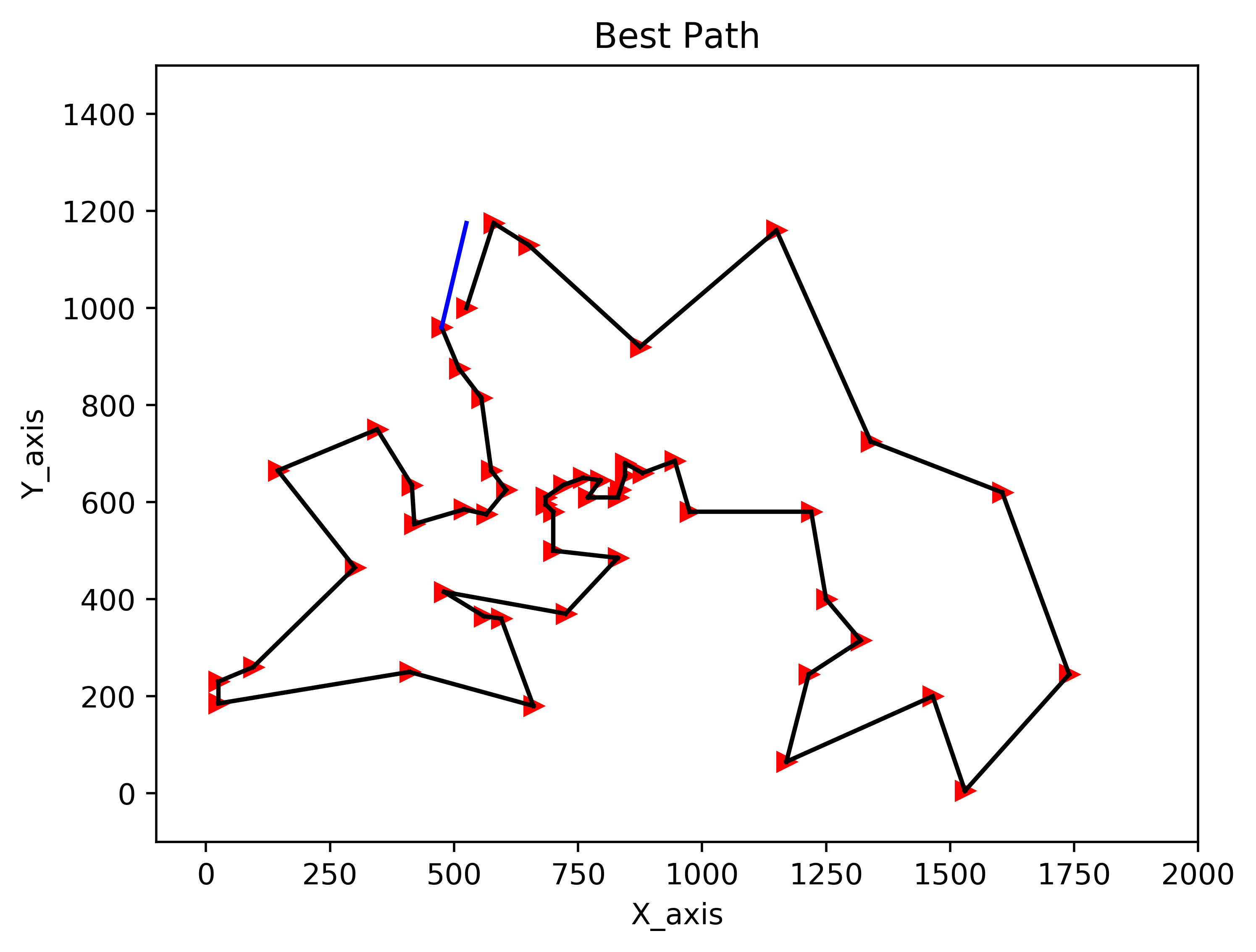
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """ Created on Wed Jun 16 15:21:03 2018 @author: SYSTEM """ import os os.getcwd() #返回當前工作目錄 import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # % pylab #初始化城市座標,總共52個城市 coordinates = np.array([[565.0, 575.0], [25.0, 185.0], [345.0, 750.0], [945.0, 685.0], [845.0, 655.0], [880.0, 660.0], [25.0, 230.0], [525.0, 1000.0], [580.0, 1175.0], [650.0, 1130.0], [1605.0, 620.0], [1220.0, 580.0], [1465.0, 200.0], [1530.0, 5.0], [845.0, 680.0], [725.0, 370.0], [145.0, 665.0], [415.0, 635.0], [510.0, 875.0], [560.0, 365.0], [300.0, 465.0], [520.0, 585.0], [480.0, 415.0], [835.0, 625.0], [975.0, 580.0], [1215.0, 245.0], [1320.0, 315.0], [1250.0, 400.0], [660.0, 180.0], [410.0, 250.0], [420.0, 555.0], [575.0, 665.0], [1150.0, 1160.0], [700.0, 580.0], [685.0, 595.0], [685.0, 610.0], [770.0, 610.0], [795.0, 645.0], [720.0, 635.0], [760.0, 650.0], [475.0, 960.0], [95.0, 260.0], [875.0, 920.0], [700.0, 500.0], [555.0, 815.0], [830.0, 485.0], [1170.0, 65.0], [830.0, 610.0], [605.0, 625.0], [595.0, 360.0], [1340.0, 725.0], [1740.0, 245.0]]) #計算52個城市間的歐式距離 def getdistmat(coordinates): num = coordinates.shape[0] distmat = np.zeros((52, 52)) # 初始化生成52*52的矩陣 for i in range(num): for j in range(i, num): distmat[i][j] = distmat[j][i] = np.linalg.norm(coordinates[i] - coordinates[j]) return distmat #返回城市距離矩陣 distmat = getdistmat(coordinates) numant = 60 # 螞蟻個數 numcity = coordinates.shape[0] # shape[0]=52 城市個數,也就是任務個數 alpha = 1 # 資訊素重要程度因子 beta = 5 # 啟發函式重要程度因子 rho = 0.1 # 資訊素的揮發速度 Q = 1 # 完成率 iter = 0 #迭代初始 itermax = 150 #迭代總數 etatable = 1.0 / (distmat + np.diag([1e10] * numcity)) #diag(),將一維陣列轉化為方陣 啟發函式矩陣,表示螞蟻從城市i轉移到城市j的期望程度 pheromonetable = np.ones((numcity, numcity)) # 資訊素矩陣 52*52 pathtable = np.zeros((numant, numcity)).astype(int) # 路徑記錄表,轉化成整型 40*52 distmat = getdistmat(coordinates) # 城市的距離矩陣 52*52 lengthaver = np.zeros(itermax) # 迭代50次,存放每次迭代後,路徑的平均長度 50*1 lengthbest = np.zeros(itermax) # 迭代50次,存放每次迭代後,最佳路徑長度 50*1 pathbest = np.zeros((itermax, numcity)) # 迭代50次,存放每次迭代後,最佳路徑城市的座標 50*52 while iter < itermax: #迭代總數 #40個螞蟻隨機放置於52個城市中 if numant <= numcity: # 城市數比螞蟻數多,不用管 pathtable[:, 0] = np.random.permutation(range(numcity))[:numant] #返回一個打亂的40*52矩陣,但是並不改變原來的陣列,把這個陣列的第一列(40個元素)放到路徑表的第一列中 #矩陣的意思是哪個螞蟻在哪個城市,矩陣元素不大於52 else: # 螞蟻數比城市數多,需要有城市放多個螞蟻 pathtable[:numcity, 0] = np.random.permutation(range(numcity))[:] # 先放52個 pathtable[numcity:, 0] = np.random.permutation(range(numcity))[:numant - numcity] # 再把剩下的放完 # print(pathtable[:,0]) length = np.zeros(numant) # 1*40的陣列 #本段程式算出每隻/第i只螞蟻轉移到下一個城市的概率 for i in range(numant): # i=0 visiting = pathtable[i, 0] # 當前所在的城市 # set()建立一個無序不重複元素集合 # visited = set() #已訪問過的城市,防止重複 # visited.add(visiting) #增加元素 unvisited = set(range(numcity)) #未訪問的城市集合 #剔除重複的元素 unvisited.remove(visiting) # 刪除已經訪問過的城市元素 for j in range(1, numcity): # 迴圈numcity-1次,訪問剩餘的所有numcity-1個城市 # j=1 # 每次用輪盤法選擇下一個要訪問的城市 listunvisited = list(unvisited) #未訪問城市數,list probtrans = np.zeros(len(listunvisited)) #每次迴圈都初始化轉移概率矩陣1*52,1*51,1*50,1*49.... #以下是計算轉移概率 for k in range(len(listunvisited)): probtrans[k] = np.power(pheromonetable[visiting][listunvisited[k]], alpha) \ * np.power(etatable[visiting][listunvisited[k]], alpha) #eta-從城市i到城市j的啟發因子 這是概率公式的分母 其中[visiting][listunvis[k]]是從本城市到k城市的資訊素 cumsumprobtrans = (probtrans / sum(probtrans)).cumsum() #求出本只螞蟻的轉移到各個城市的概率斐波衲挈數列 cumsumprobtrans -= np.random.rand() # 隨機生成下個城市的轉移概率,再用區間比較 # k = listunvisited[find(cumsumprobtrans > 0)[0]] k = listunvisited[list(cumsumprobtrans > 0).index(True)] # k = listunvisited[np.where(cumsumprobtrans > 0)[0]] # where 函式選出符合cumsumprobtans>0的數 # 下一個要訪問的城市 pathtable[i, j] = k #採用禁忌表來記錄螞蟻i當前走過的第j城市的座標,這裡走了第j個城市.k是中間值 unvisited.remove(k) # visited.add(k) #將未訪問城市列表中的K城市刪去,增加到已訪問城市列表中 length[i] += distmat[visiting][k] #計算本城市到K城市的距離 visiting = k length[i] += distmat[visiting][pathtable[i, 0]] # 計算本只螞蟻的總的路徑距離,包括最後一個城市和第一個城市的距離 # print("ants all length:",length) # 包含所有螞蟻的一個迭代結束後,統計本次迭代的若干統計引數 lengthaver[iter] = length.mean() #本輪的平均路徑 #本部分是為了求出最佳路徑 if iter == 0: lengthbest[iter] = length.min() pathbest[iter] = pathtable[length.argmin()].copy() #如果是第一輪路徑,則選擇本輪最短的路徑,並返回索引值下標,並將其記錄 else: #後面幾輪的情況,更新最佳路徑 if length.min() > lengthbest[iter - 1]: lengthbest[iter] = lengthbest[iter - 1] pathbest[iter] = pathbest[iter - 1].copy() # 如果是第一輪路徑,則選擇本輪最短的路徑,並返回索引值下標,並將其記錄 else: lengthbest[iter] = length.min() pathbest[iter] = pathtable[length.argmin()].copy() #此部分是為了更新資訊素 changepheromonetable = np.zeros((numcity, numcity)) for i in range(numant):#更新所有的螞蟻 for j in range(numcity - 1): changepheromonetable[pathtable[i, j]][pathtable[i, j + 1]] += Q / distmat[pathtable[i, j]][pathtable[i, j + 1]] #根據公式更新本只螞蟻改變的城市間的資訊素 Q/d 其中d是從第j個城市到第j+1個城市的距離 changepheromonetable[pathtable[i, j + 1]][pathtable[i, 0]] += Q / distmat[pathtable[i, j + 1]][pathtable[i, 0]] #首城市到最後一個城市 所有螞蟻改變的資訊素總和 #資訊素更新公式p=(1-揮發速率)*現有資訊素+改變的資訊素 pheromonetable = (1 - rho) * pheromonetable + changepheromonetable iter += 1 # 迭代次數指示器+1 print("this iteration end:",iter) # 觀察程式執行進度,該功能是非必須的 if (iter - 1) % 20 == 0: print("schedule:",iter - 1) #迭代完成 #以下是做圖部分 #做出平均路徑長度和最優路徑長度 fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=2, ncols=1, figsize=(12, 10)) axes[0].plot(lengthaver, 'k', marker='*') axes[0].set_title('Average Length') axes[0].set_xlabel(u'iteration') #線條顏色black https://blog.csdn.net/ywjun0919/article/details/8692018 axes[1].plot(lengthbest, 'k', marker='<') axes[1].set_title('Best Length') axes[1].set_xlabel(u'iteration') fig.savefig('Average_Best.png', dpi=500, bbox_inches='tight') plt.close() fig.show() # 作出找到的最優路徑圖 bestpath = pathbest[-1] plt.plot(coordinates[:, 0], coordinates[:, 1], 'r.', marker='>') plt.xlim([-100, 2000]) #x範圍 plt.ylim([-100, 1500]) #y範圍 for i in range(numcity - 1): #按座標繪出最佳兩兩城市間路徑 m, n = int(bestpath[i]), int(bestpath[i + 1]) print("best_path:",m, n) plt.plot([coordinates[m][0],coordinates[n][0]], [coordinates[m][1], coordinates[n][1]], 'k') plt.plot([coordinates[int(bestpath[0])][0],coordinates[int(bestpath[51])][0]], [coordinates[int(bestpath[0])][1],coordinates[int(bestpath[50])][1]] ,'b') ax = plt.gca() ax.set_title("Best Path") ax.set_xlabel('X_axis') ax.set_ylabel('Y_axis') plt.savefig('Best Path.png', dpi=500, bbox_inches='tight') plt.close()
輸出圖片:
後期,還會補充的。
希望有志同道合的小夥伴關注我的公眾平臺,歡迎您的批評指正,共同交流進步。