Java實現可視化迷宮
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-03-05
lower block oca 算法優化 結構 ring return 項目 stack
代碼地址如下:
http://www.demodashi.com/demo/14547.html
需求
使用深度優先算法求解迷宮路徑,使用Java實現求解過程的可視化,可單步運行,形象直觀。
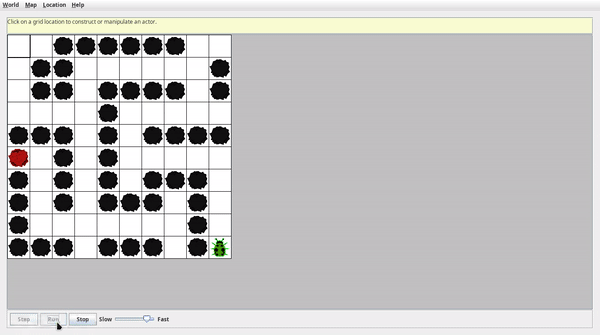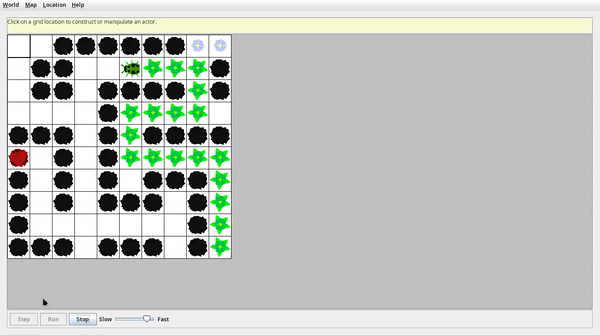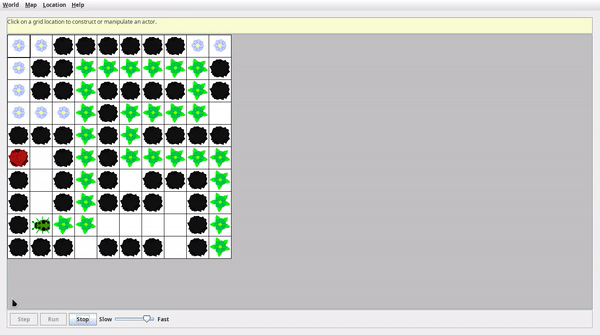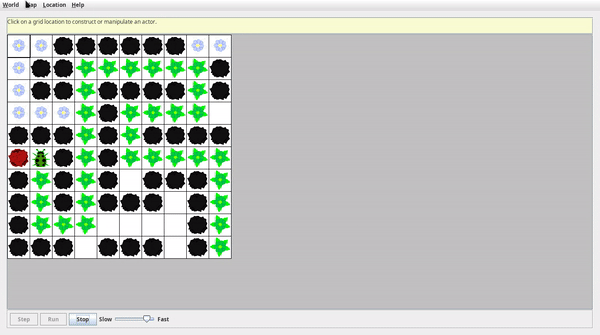
演示效果
紅色格子為迷宮終點,迷宮可放大縮小,為了錄屏選擇了較小的尺寸,有多種不同難度的迷宮可以加載。
- 簡單迷宮
- 復雜迷宮

項目運行
文件中有兩個運行腳本,Windows下直接雙擊win運行.bat即可,linux和Mac運行sh文件中的命令即可,喜歡用IDE的也可自行創建項目。
運行項目後,點擊菜單欄左上角的Map加載迷宮地圖, 點擊右下角的Run開始解迷宮,Step可單步運行,可通過速度進度條調節速度。
項目結構
Maze ├── classes # 存放編譯生成的class文件 ├── lib.jar # 打包好的gui庫 ├── map # 迷宮地圖文件 │ ├── EasyMaze.txt │ ├── FinalMaze01.txt │ ├── FinalMaze02.txt │ ├── FinalMaze03.txt │ ├── FinalMaze04.txt │ └── FinalMaze05.txt ├── src │ ├── MazeBug.java │ └── MazeBugRunner.java ├── linux運行.sh # 運行腳本 └── win運行.bat # 運行腳本
原理方法
使用深度優先算法,每個格子下一步都有上下左右4種走法,但是這4種走法並不是都是合法的,比如有些格子有障礙物,有些格式在邊界之外,去掉這些剩下的才是合法的走法。
深度優先算法的思想就是:
- 找出當前位置A下一步合法的的格子,選擇其中一個,往前走一步到達B。
- 如果B相鄰的有合法格子,重復第1步;如果沒有合法的,後退一步回到A,選擇A的其他合法格子走;
- 重復以上方法,直到找到迷宮終點;
算法優化:上面的方法選擇下一步走的方向是隨機的,或者按照上下左右的順序選擇。但是很多迷宮都有偏向性,比如如果有右偏向性,那麽每次都優先往右走可以更快走出迷宮。所以在實現的時候,記錄每個方向走的次數,每往一個方向走一步就加1,如果回退就該方向減1,每次走都優先走次數最多的方向,當迷宮有偏向性時,該方法效率更高。
以項目中的迷宮為例,大部分情況下偏向性所需步數更少。
普通方法: 534 1175 350 973 1052
偏向性: 552 761 330 175 420代碼實現
/*
* 節點:存儲方向和該方向所走的次數
* 往一個方向前進則加1,後退則減1
*/
class Node {
private int dir; // 方向,角度值
private int ct; // 該方向所走次數
public Node(int initdir, int initct) {
dir = initdir;
ct = initct;
}
public int getDir() {
return dir;
}
public int getCt() {
return ct;
}
public void setCt(int deta) {
ct += deta;
}
}
// 深度優先算法解迷宮,並且以小甲蟲的形式呈現
public class MazeBug extends Bug {
private Location next; // 下一步要走的格子
private Integer stepCount = 0; // 所走的步數
private boolean isEnd = false; // 是否到達迷宮出口
private boolean hasShown = false; // 是否顯示了結束信息
private Stack<Location> path = new Stack<>(); // 存儲走過的路徑
private ArrayList<Node> arr = new ArrayList<>();
public MazeBug() {
setColor(Color.GREEN);
arr.add(new Node(0, 0));
arr.add(new Node(90, 0));
arr.add(new Node(270, 0));
arr.add(new Node(180, 0));
}
// 周期性執行
public void act() {
boolean willMove = canMove(); // 是否還能繼續移動
if (isEnd) { // 是否結束
if (!hasShown) { // 是否顯示結束消息
String msg = stepCount.toString() + " steps";
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, msg);
hasShown = true;
}
return;
} else if (willMove) { // 向前移動一個,步數加1
move();
++stepCount;
} else { // 不能移動,後退一步,將該方向的計數器減1
Grid<Actor> grid = getGrid();
Location loc = this.getLocation();
Location top = path.pop();
++stepCount;
grid.remove(top);
this.setDirection(loc.getDirectionToward(top));
this.moveTo(top);
// 在走過的死路留下一朵白花
Flower flower = new Flower(Color.WHITE);
flower.putSelfInGrid(getGrid(), loc);
// 方向計數器減1
int dir = 180 + ((getDirection() / 90) % 2) * 180 - getDirection();
for (Node node : arr)
if (node.getDir() == dir) {
node.setCt(-1);
return;
}
}
}
// 找出和當前位置相鄰的、合法的並且從未走過的格子
public Location getValid(Location loc) {
Grid<Actor> gr = getGrid();
if (gr == null)
return null;
// 將每個方向走過的次數從大到小排序,下一步優先選次數多的方向走
Location adjLocation;
arr.sort(new Comparator<Node>() {
@Override
public int compare(Node a, Node b) {
return (a.getCt() < b.getCt()) ? 1 : -1;
}
});
for (Node node : arr) {
adjLocation = this.getLocation().getAdjacentLocation(node.getDir());
if (gr.isValid(adjLocation)
&& (gr.get(adjLocation) == null || gr.get(adjLocation).getColor().equals(Color.RED))) {
node.setCt(1);
return adjLocation;
}
}
return null;
}
// 判斷當前位置是否可以繼續移動
public boolean canMove() {
Grid<Actor> gr = getGrid();
Actor adj;
Location loc = this.getValid(this.getLocation());
if (loc != null) {
adj = gr.get(loc);
next = loc;
isEnd = adj != null && adj.getColor().equals(Color.RED);
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 將甲蟲的方向轉向下一格,往前移動一步,將原來的位置壓棧,並放置一朵綠花,表示走過的路徑
public void move() {
Grid<Actor> gr = getGrid();
if (gr == null)
return;
Location loc = this.getLocation();
path.push(loc);
this.setDirection(loc.getDirectionToward(next));
this.moveTo(next);
Flower flower = new Flower(this.getColor());
flower.putSelfInGrid(gr, loc);
}
}其他:
跟算法無關的代碼,比如GUI方面的都打包成lib.jar了,如果想要自己更改可以自行解壓。Java實現可視化迷宮
代碼地址如下:
http://www.demodashi.com/demo/14547.html
註:本文著作權歸作者,由demo大師代發,拒絕轉載,轉載需要作者授權
Java實現可視化迷宮
