通過micrometer實時監控線程池的各項指標
通過micrometer實時監控線程池的各項指標
前提
最近的一個項目中涉及到文件上傳和下載,使用到JUC的線程池ThreadPoolExecutor,在生產環境中出現了某些時刻線程池滿負載運作,由於使用了CallerRunsPolicy拒絕策略,導致滿負載情況下,應用接口調用無法響應,處於假死狀態。考慮到之前用micrometer + prometheus + grafana搭建過監控體系,於是考慮使用micrometer做一次主動的線程池度量數據采集,最終可以相對實時地展示在grafana的面板中。
實踐過程
下面通過真正的實戰過程做一個仿真的例子用於復盤。
代碼改造
首先我們要整理一下ThreadPoolExecutor
- 線程池名稱,Tag:
thread.pool.name,這個很重要,用於區分各個線程池的數據,如果使用IOC容器管理,可以使用BeanName代替。 int getCorePoolSize():核心線程數,Tag:thread.pool.core.size。int getLargestPoolSize():歷史峰值線程數,Tag:thread.pool.largest.size。int getMaximumPoolSize():最大線程數(線程池線程容量),Tag:thread.pool.max.size。int getActiveCount():當前活躍線程數,Tag:thread.pool.active.size。int getPoolSize():當前線程池中運行的線程總數(包括核心線程和非核心線程),Tag:thread.pool.thread.count。- 當前任務隊列中積壓任務的總數,Tag:
thread.pool.queue.size,這個需要動態計算得出。
接著編寫具體的代碼,實現的功能如下:
- 1、建立一個
ThreadPoolExecutor實例,核心線程和最大線程數為10,任務隊列長度為10,拒絕策略為AbortPolicy。 - 2、提供兩個方法,分別使用線程池實例模擬短時間耗時的任務和長時間耗時的任務。
- 3、提供一個方法用於清空線程池實例中的任務隊列。
- 4、提供一個單線程的調度線程池用於定時收集
ThreadPoolExecutor實例中上面列出的度量項,保存到micrometer內存態的收集器中。
由於這些統計的值都會跟隨時間發生波動性變更,可以考慮選用Gauge類型的Meter進行記錄。
// ThreadPoolMonitor
import io.micrometer.core.instrument.Metrics;
import io.micrometer.core.instrument.Tag;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
/**
* @author throwable
* @version v1.0
* @description
* @since 2019/4/7 21:02
*/
@Service
public class ThreadPoolMonitor implements InitializingBean {
private static final String EXECUTOR_NAME = "ThreadPoolMonitorSample";
private static final Iterable<Tag> TAG = Collections.singletonList(Tag.of("thread.pool.name", EXECUTOR_NAME));
private final ScheduledExecutorService scheduledExecutor = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor();
private final ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(10, 10, 0, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(10), new ThreadFactory() {
private final AtomicInteger counter = new AtomicInteger();
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
Thread thread = new Thread(r);
thread.setDaemon(true);
thread.setName("thread-pool-" + counter.getAndIncrement());
return thread;
}
}, new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
private Runnable monitor = () -> {
//這裏需要捕獲異常,盡管實際上不會產生異常,但是必須預防異常導致調度線程池線程失效的問題
try {
Metrics.gauge("thread.pool.core.size", TAG, executor, ThreadPoolExecutor::getCorePoolSize);
Metrics.gauge("thread.pool.largest.size", TAG, executor, ThreadPoolExecutor::getLargestPoolSize);
Metrics.gauge("thread.pool.max.size", TAG, executor, ThreadPoolExecutor::getMaximumPoolSize);
Metrics.gauge("thread.pool.active.size", TAG, executor, ThreadPoolExecutor::getActiveCount);
Metrics.gauge("thread.pool.thread.count", TAG, executor, ThreadPoolExecutor::getPoolSize);
// 註意如果阻塞隊列使用無界隊列這裏不能直接取size
Metrics.gauge("thread.pool.queue.size", TAG, executor, e -> e.getQueue().size());
} catch (Exception e) {
//ignore
}
};
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
// 每5秒執行一次
scheduledExecutor.scheduleWithFixedDelay(monitor, 0, 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
public void shortTimeWork() {
executor.execute(() -> {
try {
// 5秒
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
//ignore
}
});
}
public void longTimeWork() {
executor.execute(() -> {
try {
// 500秒
Thread.sleep(5000 * 100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
//ignore
}
});
}
public void clearTaskQueue() {
executor.getQueue().clear();
}
}
//ThreadPoolMonitorController
import club.throwable.smp.service.ThreadPoolMonitor;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @author throwable
* @version v1.0
* @description
* @since 2019/4/7 21:20
*/
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@RestController
public class ThreadPoolMonitorController {
private final ThreadPoolMonitor threadPoolMonitor;
@GetMapping(value = "/shortTimeWork")
public ResponseEntity<String> shortTimeWork() {
threadPoolMonitor.shortTimeWork();
return ResponseEntity.ok("success");
}
@GetMapping(value = "/longTimeWork")
public ResponseEntity<String> longTimeWork() {
threadPoolMonitor.longTimeWork();
return ResponseEntity.ok("success");
}
@GetMapping(value = "/clearTaskQueue")
public ResponseEntity<String> clearTaskQueue() {
threadPoolMonitor.clearTaskQueue();
return ResponseEntity.ok("success");
}
}配置如下:
server:
port: 9091
management:
server:
port: 9091
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: '*'
base-path: /managementprometheus的調度Job也可以適當調高頻率,這裏默認是15秒拉取一次/prometheus端點,也就是會每次提交3個收集周期的數據。項目啟動之後,可以嘗試調用/management/prometheus查看端點提交的數據:
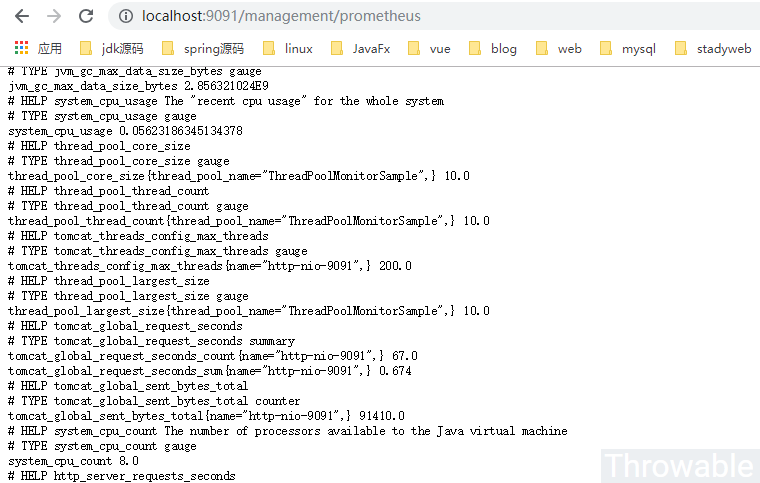
因為ThreadPoolMonitorSample是我們自定義命名的Tag,看到相關字樣說明數據收集是正常的。如果prometheus的Job沒有配置錯誤,在本地的spring-boot項目起來後,可以查下prometheus的後臺:

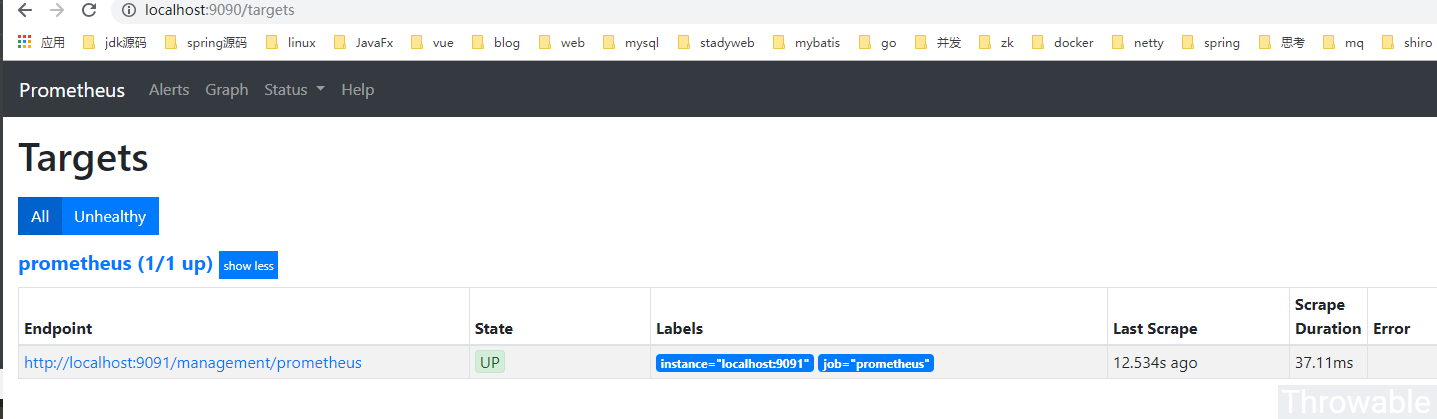
OK,完美,可以進行下一步。
grafana面板配置
確保JVM應用和prometheus的調度Job是正常的情況下,接下來重要的一步就是配置grafana面板。如果暫時不想認真學習一下prometheus的PSQL的話,可以從prometheus後臺的/graph面板直接搜索對應的樣本表達式拷貝進去grafana配置中就行,當然最好還是去看下prometheus的文檔系統學習一下怎麽編寫PSQL。
- 基本配置:
- 可視化配置,把右邊的標簽勾選,寬度盡量調大點:
- 查詢配置,這個是最重要的,最終圖表就是靠查詢配置展示的:
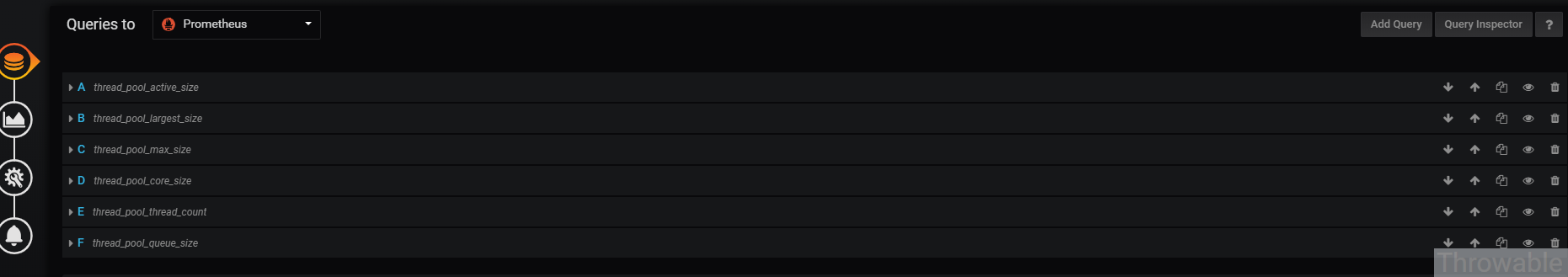
查詢配置具體如下:
- A:thread_pool_active_size,Legend:
{{instance}}-{{thread_pool_name}}線程池活躍線程數。 - B:thread_pool_largest_size,Legend:
{{instance}}-{{thread_pool_name}}線程池歷史峰值線程數。 - C:thread_pool_max_size,Legend:
{{instance}}-{{thread_pool_name}}線程池容量。 - D:thread_pool_core_size,Legend:
{{instance}}-{{thread_pool_name}}線程池核心線程數。 - E:thread_pool_thread_count,Legend:
{{instance}}-{{thread_pool_name}}線程池運行中的線程數。 - F:thread_pool_queue_size,Legend:
{{instance}}-{{thread_pool_name}}線程池積壓任務數。
最終效果
多調用幾次例子中提供的幾個接口,就能得到一個監控線程池呈現的圖表:
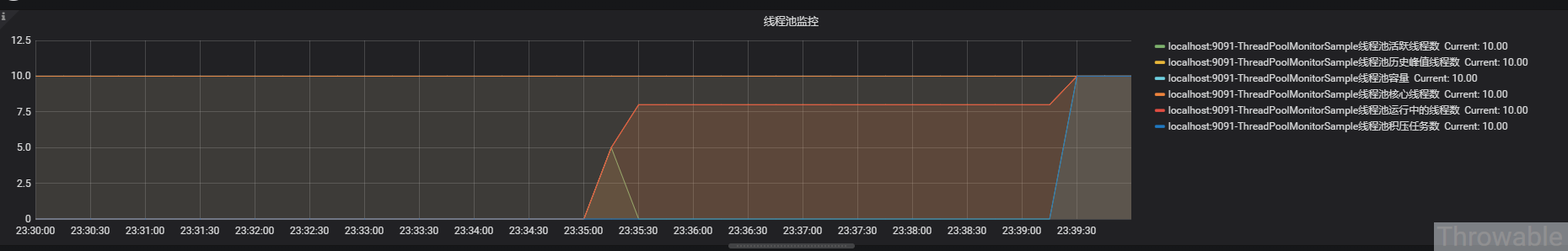
小結
針對線程池ThreadPoolExecutor的各項數據進行監控,有利於及時發現使用線程池的接口的異常,如果想要快速恢復,最有效的途徑是:清空線程池中任務隊列中積壓的任務。具體的做法是:可以把ThreadPoolExecutor委托到IOC容器管理,並且把ThreadPoolExecutor的任務隊列清空的方法暴露成一個REST端點即可。像HTTP客戶端的連接池如Apache-Http-Client或者OkHttp等的監控,可以用類似的方式實現,數據收集的時候可能由於加鎖等原因會有少量的性能損耗,不過這些都是可以忽略的,如果真的怕有性能影響,可以嘗試用反射API直接獲取ThreadPoolExecutor實例內部的屬性值,這樣就可以避免加鎖的性能損耗。
個人博客原文鏈接:http://www.throwable.club/2019/04/14/jvm-micrometer-thread-pool-monitor
(本文完 c-2-d 20190414)
通過micrometer實時監控線程池的各項指標
