SpringFramework之@Controller/@RequestMapping解析
分析版本Spring5.0.9.release,Springboot2.0.3.release
spring-webmvc的META-INFO/spring.handles檔案中,有MvcNamespaceHandler,這是用來解析標籤的,來看下MvcNamespaceHandler的init(),如下List-1,我們暫時只關注AnnotationDrivenBeanDefinitionParser。
List-1
@Override public void init() { registerBeanDefinitionParser("annotation-driven", new AnnotationDrivenBeanDefinitionParser()); registerBeanDefinitionParser("default-servlet-handler", new DefaultServletHandlerBeanDefinitionParser()); registerBeanDefinitionParser("interceptors", new InterceptorsBeanDefinitionParser()); registerBeanDefinitionParser("resources", new ResourcesBeanDefinitionParser()); registerBeanDefinitionParser("view-controller", new ViewControllerBeanDefinitionParser()); registerBeanDefinitionParser("redirect-view-controller", new ViewControllerBeanDefinitionParser()); registerBeanDefinitionParser("status-controller", new ViewControllerBeanDefinitionParser()); registerBeanDefinitionParser("view-resolvers", new ViewResolversBeanDefinitionParser()); registerBeanDefinitionParser("tiles-configurer", new TilesConfigurerBeanDefinitionParser()); registerBeanDefinitionParser("freemarker-configurer", new FreeMarkerConfigurerBeanDefinitionParser()); registerBeanDefinitionParser("groovy-configurer", new GroovyMarkupConfigurerBeanDefinitionParser()); registerBeanDefinitionParser("script-template-configurer", new ScriptTemplateConfigurerBeanDefinitionParser()); registerBeanDefinitionParser("cors", new CorsBeanDefinitionParser()); }
AnnotationDrivenBeanDefinitionParser的parse方法裡面有很多程式碼,但是我們只關注倆個,如下List-2:
- 用RootBeanDefinition將RequestMappingHandlerMapping註冊到spring容器中。
- MvcNamespaceUtils.registerDefaultComponents中,將BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping註冊到spring容器中、將HttpRequestHandlerAdapter註冊到spring容器中、將SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter註冊到spring容器中、將HandlerMappingIntrospector註冊到容器中。
List-2
@Override @Nullable public BeanDefinition parse(Element element, ParserContext context) { ... RootBeanDefinition handlerMappingDef = new RootBeanDefinition(RequestMappingHandlerMapping.class); ... // Ensure BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping (SPR-8289) and default HandlerAdapters are not "turned off" MvcNamespaceUtils.registerDefaultComponents(context, source); return null; }
RequestMappingHandlerMapping的繼承圖如下圖1所示:
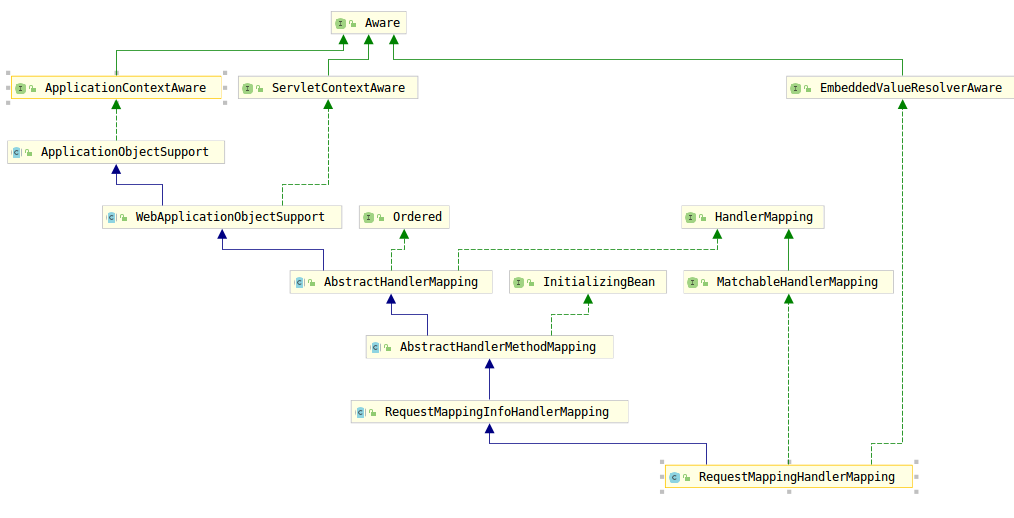
圖1
圖1中,AbstractHandlerMethodMapping實現了介面InitializingBean,實現了afterPropertiesSet(),如果瞭解SpringIOC,應該知道這個方法意味著什麼,Spring在建立Bean的時候會呼叫這個方法。
List-3
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
initHandlerMethods();
}由List-3知道afterPropertiesSet呼叫了initHandlerMethods(),如下List-4,首先從ApplicationContext或者所有的beanName,之後迴圈它們。isHandler方法由子類RequestMappingHandlerMapping實現,判斷類上是否有Controller或者RequestMapping註解,所以即使不加上@Controller,只是用@RequestMapping註解也可以。List-4中的handlerMethodsInitialized是空方法,不用管。
List-4
protected void initHandlerMethods() {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Looking for request mappings in application context: " + getApplicationContext());
}
String[] beanNames = (this.detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts ?
BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(obtainApplicationContext(), Object.class) :
obtainApplicationContext().getBeanNamesForType(Object.class));
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
if (!beanName.startsWith(SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX)) {
Class<?> beanType = null;
try {
beanType = obtainApplicationContext().getType(beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// An unresolvable bean type, probably from a lazy bean - let's ignore it.
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Could not resolve target class for bean with name '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
}
if (beanType != null && isHandler(beanType)) {
detectHandlerMethods(beanName);
}
}
}
handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods());
}來看List-4中的方法detectHandlerMethods,傳入的是String型別的bean name,如下List-5,首先獲取bean name對應的Class,getMappingForMethod在RequestMappingHandlerMapping中實現,如List-6所示,判斷方法上是否有RequestMapping註解,如果有,則獲取引數、path、header等資訊,用builder模式構造出RequestMappingInfo。MethodIntrospector.selectMethods會遍歷類上的方法,所以整體上對類的所有方法進行是否有RequestMapping的檢查。需要注意的是,類似GetMapping等是組合註解,它們還是基於RequestMapping,所以方法上有GetMapping/PostMapping等都會會掃描並創建出對應的RequestMappingInfo。
List-5
protected void detectHandlerMethods(Object handler) {
Class<?> handlerType = (handler instanceof String ?
obtainApplicationContext().getType((String) handler) : handler.getClass());
if (handlerType != null) {
Class<?> userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType);
Map<Method, T> methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(userType,
(MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<T>) method -> {
try {
return getMappingForMethod(method, userType);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Invalid mapping on handler class [" +
userType.getName() + "]: " + method, ex);
}
});
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(methods.size() + " request handler methods found on " + userType + ": " + methods);
}
methods.forEach((method, mapping) -> {
Method invocableMethod = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(method, userType);
registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping);
});
}
}List-6
@Override
@Nullable
protected RequestMappingInfo getMappingForMethod(Method method, Class<?> handlerType) {
RequestMappingInfo info = createRequestMappingInfo(method);
if (info != null) {
RequestMappingInfo typeInfo = createRequestMappingInfo(handlerType);
if (typeInfo != null) {
info = typeInfo.combine(info);
}
}
return info;
}
@Nullable
private RequestMappingInfo createRequestMappingInfo(AnnotatedElement element) {
RequestMapping requestMapping = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(element, RequestMapping.class);
RequestCondition<?> condition = (element instanceof Class ?
getCustomTypeCondition((Class<?>) element) : getCustomMethodCondition((Method) element));
return (requestMapping != null ? createRequestMappingInfo(requestMapping, condition) : null);
}
protected RequestMappingInfo createRequestMappingInfo(
RequestMapping requestMapping, @Nullable RequestCondition<?> customCondition) {
RequestMappingInfo.Builder builder = RequestMappingInfo
.paths(resolveEmbeddedValuesInPatterns(requestMapping.path()))
.methods(requestMapping.method())
.params(requestMapping.params())
.headers(requestMapping.headers())
.consumes(requestMapping.consumes())
.produces(requestMapping.produces())
.mappingName(requestMapping.name());
if (customCondition != null) {
builder.customCondition(customCondition);
}
return builder.options(this.config).build();
}List-5中的registerHandlerMethod,會將得到的Mapper資訊註冊到mappingRegistry到,這個mappingRegistry後面在DispatcherServlet中使用到。注意傳入到registerHandlerMethod方法的handler是String型別的bean name。
Springboot中,RequestMappingHandlerMapping是通過@Configuration方式注入的,如下List-7
List-7
@Bean
public RequestMappingHandlerMapping requestMappingHandlerMapping() {
RequestMappingHandlerMapping mapping = createRequestMappingHandlerMapping();
...