Mybatis深入原始碼分析之SqlSessionFactoryBuilder原始碼分析
一:原始碼分析程式碼片段
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// 基本mybatis環境
// 1.定義mybatis_config檔案地址
String resources = "mybatis_config.xml";
// 2.獲取InputStreamReaderIo流
Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader(resources);
// 3.獲取SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
// 4.獲取Session
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
// 5.操作Mapper介面
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
UserEntity user = mapper.getUser(2);
System.out.println(user.getName());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}首先對步驟2進行分析
// 2.獲取InputStreamReaderIo流
Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader(resources);
public static Reader getResourceAsReader(String resource) throws IOException {
InputStreamReader reader;
if (charset == null) {
reader = new InputStreamReader(getResourceAsStream(resource));
} else {
reader = new InputStreamReader(getResourceAsStream(resource), charset);
}
return reader;
}通過上述程式碼可知:使用了門面模式:定義了Resource類,把複雜過程封裝起來,方便使用者使用,返回reader為InputStreamReader,指的是讀取的mybatis_config.xml檔案,斷點除錯結果如下:
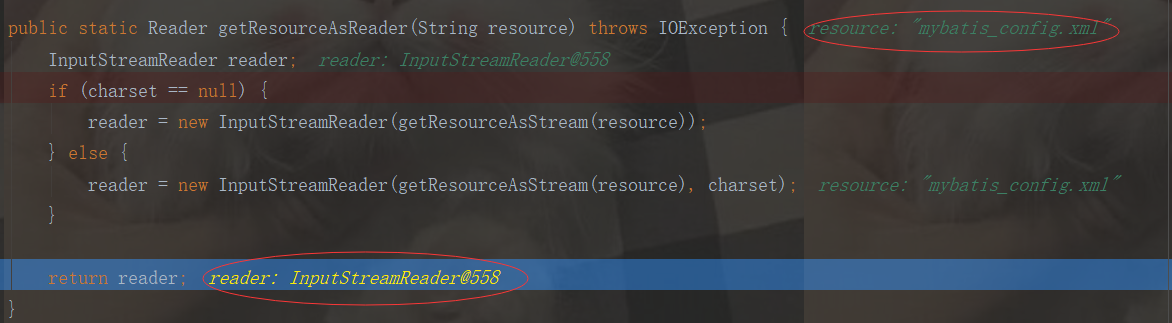
第三步原始碼分析
// 3.獲取SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
進入SqlSessionFactoryBuilder()建構函式如下:
public SqlSessionFactoryBuilder() {
}可知,無參建構函式沒用做任何事情,再進入build(reader)原始碼,reader引數為InputStream流
public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader) {
return this.build((Reader)reader, (String)null, (Properties)null);
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader, String environment, Properties properties) {
SqlSessionFactory var5;
try {
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(reader, environment, properties);
var5 = this.build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception var14) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", var14);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException var13) {
;
}
}
return var5;
}
我們來分析下XMLConfigBuilder這個類是幹嘛的,進入XMLConfigBuilder建構函式如下:
public XMLConfigBuilder(Reader reader, String environment, Properties props) {
this(new XPathParser(reader, true, props, new XMLMapperEntityResolver()), environment, props);
}
private XMLConfigBuilder(XPathParser parser, String environment, Properties props) {
super(new Configuration());
this.localReflectorFactory = new DefaultReflectorFactory();
ErrorContext.instance().resource("SQL Mapper Configuration");
this.configuration.setVariables(props);
this.parsed = false;
this.environment = environment;
this.parser = parser;
}
進入super()程式碼如下:
public BaseBuilder(Configuration configuration) {
this.configuration = configuration;
this.typeAliasRegistry = this.configuration.getTypeAliasRegistry();
this.typeHandlerRegistry = this.configuration.getTypeHandlerRegistry();
}
通過上述程式碼可知:this.parsed = false;後面有用,這裡先提下。返回原先執行處:var5 = this.build(parser.parse());
var5 = this.build(parser.parse());
進入parser.parse()這個方法,程式碼如下:
public Configuration parse() {
if (this.parsed) {
throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once.");
} else {
this.parsed = true;
this.parseConfiguration(this.parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
return this.configuration;
}
}
由前面設定了this.parsed = false,可知this.parsed為false,就進入else分支,讀者這個時候就有疑問了,為啥要設定this.parsed = false呢?
我們通過else分支可知,又設定了 this.parsed = true;說明再下一次再次進入parse方法的時候,this.parsed=true會直接丟擲異常。
這裡我們可以總結下:
為什麼XMLConfigBuilder只能被使用一次呢?
答:因為我們的Configuration是一個全域性的,所以只能被解析一次。
多次解析的話,會丟擲:Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once.異常,防止使用者私自呼叫parse()方法再去重複解析,因為配置檔案是全域性的,不能多次解析。
進入else分支的下面這個程式碼中:
this.parseConfiguration(this.parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {
try {
this.propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));
this.typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));
this.pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));
this.objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));
this.objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
this.reflectionFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectionFactory"));
this.settingsElement(root.evalNode("settings"));
this.environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));
this.databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
this.typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
this.mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
} catch (Exception var3) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + var3, var3);
}
}
我們先看看配置檔案的內容:
<configuration>
<!-- 環境配置 -->
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<!-- 資料庫連線相關配置 ,這裡動態獲取config.properties檔案中的內容-->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<!-- mapping檔案路徑配置 -->
<mappers>
<mapper resource="mappers/UserMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
我們先進入下面這行程式碼:因為這個environments在我們配置檔案中配置了,我們先分析它:
this.environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"))
private void environmentsElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
if (this.environment == null) {
this.environment = context.getStringAttribute("default");
}
Iterator i$ = context.getChildren().iterator();
while(i$.hasNext()) {
XNode child = (XNode)i$.next();
String id = child.getStringAttribute("id");
if (this.isSpecifiedEnvironment(id)) {
TransactionFactory txFactory = this.transactionManagerElement(child.evalNode("transactionManager"));
DataSourceFactory dsFactory = this.dataSourceElement(child.evalNode("dataSource"));
DataSource dataSource = dsFactory.getDataSource();
Builder environmentBuilder = (new Builder(id)).transactionFactory(txFactory).dataSource(dataSource);
this.configuration.setEnvironment(environmentBuilder.build());
}
}
}
}
通過斷點除錯environmentsElement()程式碼結果如下:
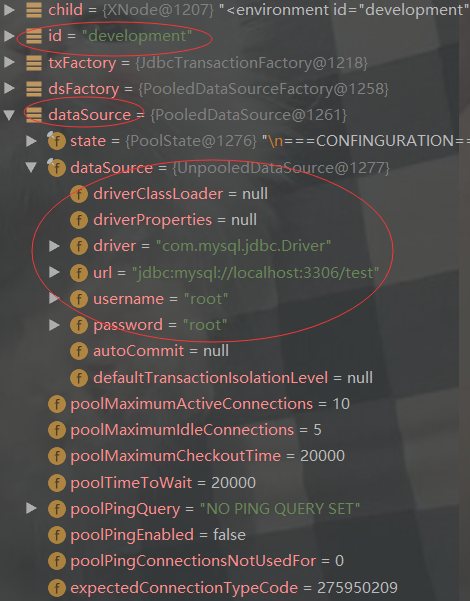
我們看下這段程式碼:
this.configuration.setEnvironment(environmentBuilder.build());
public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) {
this.environment = environment;
}
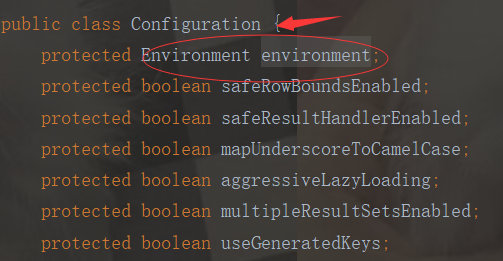
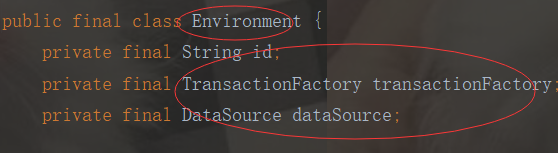
到這裡我們就明白了:這裡將解析的XML結點封裝成Environment物件,再把Environment物件設定給Configuration物件中。也就是解析XML,再把XML轉為Configuration實體類
到這裡我們再來分析:mappers結點在配置檔案中配置了,我們也來分析下
this.mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
private void mapperElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
Iterator i$ = parent.getChildren().iterator();
while(true) {
while(i$.hasNext()) {
XNode child = (XNode)i$.next();
String resource;
if ("package".equals(child.getName())) { //註解方式配置掃包package
resource = child.getStringAttribute("name");
this.configuration.addMappers(resource);
} else { //resource 方式
resource = child.getStringAttribute("resource");
String url = child.getStringAttribute("url");
String mapperClass = child.getStringAttribute("class");
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser;
InputStream inputStream;
if (resource != null && url == null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource);
inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, this.configuration, resource, this.configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
} else if (resource == null && url != null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(url);
inputStream = Resources.getUrlAsStream(url);
mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, this.configuration, url, this.configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
} else {
if (resource != null || url != null || mapperClass == null) {
throw new BuilderException("A mapper element may only specify a url, resource or class, but not more than one.");
}
Class<?> mapperInterface = Resources.classForName(mapperClass);
this.configuration.addMapper(mapperInterface);
}
}
}
return;
}
}
}
通過上述程式碼可知,配置方式有兩種:一種是註解形式掃包,第二種是resource方式
我們是resource方式的配置,所以進入else分支:
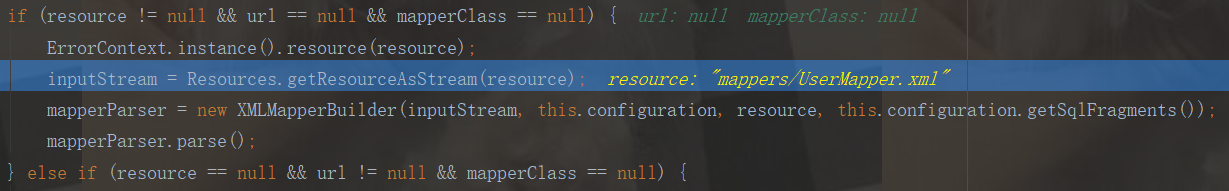
由上面斷點分析可知,這裡會讀取mapper.xml配置檔案的內容,轉化為inputStream流,再解析mapper.xml配置檔案
XMLMapperBuilder類的作用:解析mapper配置檔案得到Configuration物件,我們看下XMLMapperBuilder怎麼去解析mapper配置檔案
public XMLMapperBuilder(InputStream inputStream, Configuration configuration, String resource, Map<String, XNode> sqlFragments) {
this(new XPathParser(inputStream, true, configuration.getVariables(), new XMLMapperEntityResolver()), configuration, resource, sqlFragments);
}
private XMLMapperBuilder(XPathParser parser, Configuration configuration, String resource, Map<String, XNode> sqlFragments) {
super(configuration);
this.builderAssistant = new MapperBuilderAssistant(configuration, resource);
this.parser = parser;
this.sqlFragments = sqlFragments;
this.resource = resource;
}
最終進入:
mapperParser.parse()
public void parse() {
if (!this.configuration.isResourceLoaded(this.resource)) {
this.configurationElement(this.parser.evalNode("/mapper"));
this.configuration.addLoadedResource(this.resource);
this.bindMapperForNamespace();
}
進入addLoadedResource()方法:
public void addLoadedResource(String resource) {
this.loadedResources.add(resource);
}
protected final Set<String> loadedResources;
public Configuration() {
this.loadedResources = new HashSet();
}
通過上述程式碼可知:loadedResources存放的都是mybatis對映的檔案路徑地址【mapper.xml】, 使用HashSet集合存放
存放進去之後,斷點如下:
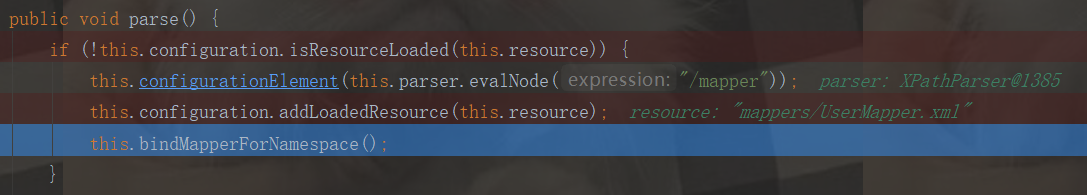
我們進入下面這個方法:
this.bindMapperForNamespace();
private void bindMapperForNamespace() {
String namespace = this.builderAssistant.getCurrentNamespace(); //拿到mapper.xml裡面配置的namespace,這裡是com.mayikt.mapper.UserMapper
if (namespace != null) {
Class boundType = null;
try {
boundType = Resources.classForName(namespace); //通過Java反射機制幫我去查詢,這裡得到interface com.mayikt.mapper.UserMapper
} catch (ClassNotFoundException var4) {
;
}
if (boundType != null && !this.configuration.hasMapper(boundType)) {//判斷mapper.xml配置檔案是否註冊過
this.configuration.addLoadedResource("namespace:" + namespace);
this.configuration.addMapper(boundType);
}
}
}
先看看addMapper方法:
this.configuration.addMapper(boundType);
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
this.mapperRegistry.addMapper(type);
}
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
if (type.isInterface()) { //判斷是否是介面型別
if (this.hasMapper(type)) { //再次判斷是否註冊過,如果註冊過,則丟擲異常
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
this.knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory(type));
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(this.config, type);
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
if (!loadCompleted) {
this.knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
this.knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory(type));
private final Map<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>> knownMappers = new HashMap();
由上述程式碼可知:mapperRegistry作用是:存放dao層mapper介面,debug結果如下:
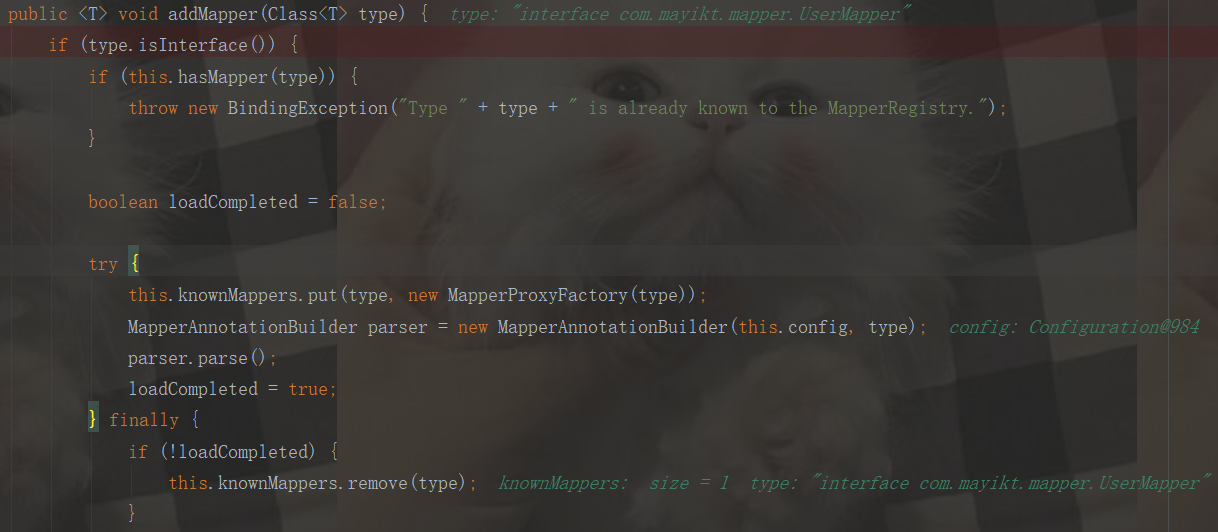
最後,我們來看看loadedResources裡面的東西:存放的是userMapper的配置檔案
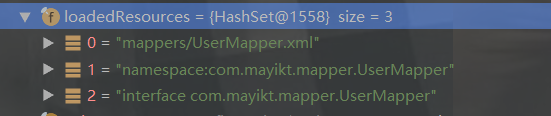
再看看mapperRegistery裡面的東西:存放的是mapper介面
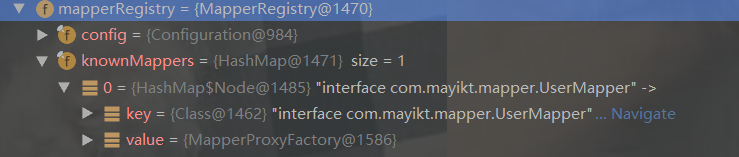
最後,我們回到開始的parse()方法,上述程式碼執行完this.parseConfiguration(this.parser.evalNode("/configuration"))方法之後,返回configuration物件
public Configuration parse() {
if (this.parsed) {
throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once.");
} else {
this.parsed = true;
this.parseConfiguration(this.parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
return this.configuration;
}
}
到這裡,我們就結束了原始碼分析,下面總結下大體流程:
總結:
- 獲取本地InputStreamReader物件(mybatis配置檔案)
- 呼叫SqlSessionFactoryBuilder
- ###再使用XMLConfigBuilder解析mybatis配置檔案,裝配到Configuration中。
- 將配置檔案中的Mapper新增到Configuration mapperRegistry實現註冊。
備註:mapperRegistry存放當前所有的mapper介面。
loadedResources裡面的東西:存放的是userMapper的配置檔案
本文參考
螞蟻課堂:http:

