詳述Spring對資料校驗支援的核心API:SmartValidator
每篇一句
要致富,先修路。要使用,先...基礎是需要壘砌的,做技術切勿空中樓閣
相關閱讀
【小家Java】深入瞭解資料校驗:Java Bean Validation 2.0(JSR303、JSR349、JSR380)Hibernate-Validation 6.x使用案例
【小家Java】深入瞭解資料校驗(Bean Validation):基礎類打點(ValidationProvider、ConstraintDescriptor、ConstraintValidator)
前言
浩浩蕩蕩的把一般程式設計師都不太關注的Bean Validation
Spring中的使用啊。我想若不出意外,這應該是眾多小夥伴的共同心聲吧,但路漫漫其修遠兮,也得上下求索,本文將切入到最關心的Spring中來~
要想深入瞭解Spring對Bean Validation的支援,org.springframework.validation.beanvalidation這個包裡面的這幾個關鍵API必須搞明白嘍,這樣再使用起@Valid結合Spring時時才能更加的收放自如~
說明:這個包所在的jar是
spring-context,屬於Spring上下文的核心功能模組
我把這個包內的類圖截圖如下,供以參考:
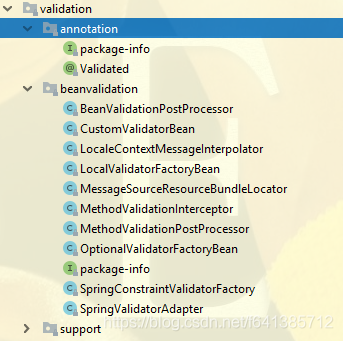
Spring雖然沒有直接實現Bean校驗這塊的JSR規範,但是從Spring3.0開始,Spring就提供了對Bean Validation的支援。
- 3.0提供了Bean級別的校驗
- 3.1提供了更加強大的
方法級別的校驗
BeanValidationPostProcessor
它就是個普通的BeanPostProcessor。它能夠去校驗Spring容器中的Bean,從而決定允不允許它初始化完成。
比如我們有些Bean某些欄位是不允許為空的,比如資料的連結,使用者名稱密碼等等,這個時候用上它處理就非常的優雅和高階了~
若校驗不通過,在違反約束的情況下就會丟擲異常,阻止容器的正常啟動~
public class BeanValidationPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor, InitializingBean {
// 這就是我們熟悉的校驗器
// 請注意這裡是javax.validation.Validator,而不是org.springframework.validation.Validator
@Nullable
private Validator validator;
// true:表示在Bean初始化之後完成校驗
// false:表示在Bean初始化之前就校驗
private boolean afterInitialization = false;
... // 省略get/set
// 由此可見使用的是預設的校驗器(當然還是Hibernate的)
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
if (this.validator == null) {
this.validator = Validation.buildDefaultValidatorFactory().getValidator();
}
}
// 這個實現太簡單了~~~
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (!this.afterInitialization) {
doValidate(bean);
}
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (this.afterInitialization) {
doValidate(bean);
}
return bean;
}
protected void doValidate(Object bean) {
Assert.state(this.validator != null, "No Validator set");
Object objectToValidate = AopProxyUtils.getSingletonTarget(bean);
if (objectToValidate == null) {
objectToValidate = bean;
}
Set<ConstraintViolation<Object>> result = this.validator.validate(objectToValidate);
// 拼接錯誤訊息最終丟擲
if (!result.isEmpty()) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("Bean state is invalid: ");
for (Iterator<ConstraintViolation<Object>> it = result.iterator(); it.hasNext();) {
ConstraintViolation<Object> violation = it.next();
sb.append(violation.getPropertyPath()).append(" - ").append(violation.getMessage());
if (it.hasNext()) {
sb.append("; ");
}
}
throw new BeanInitializationException(sb.toString());
}
}
}這個BeanValidationPostProcessor實現的功能確實非常的簡單,無非就是對所有的Bean在初始化前/後進行校驗。
我們若是對Spring Bean想做約束的話(比如對屬性、構造器等等),使用它就非常的方便~
備註:
BeanValidationPostProcessor預設可是沒有被裝配進容器的~
==org.springframework.validation.Validator==
應用程式特定物件的驗證器,這是Spring自己的抽象,注意區別於javax.validation.Validator。這個介面完全脫離了任何基礎設施或上下文,也就是說,它沒有耦合到只驗證Web層、資料訪問層或任何層中的物件。它支援應用於程式內的任何層
// 注意:它可不是Spring3後才推出的 最初就有
public interface Validator {
// 此clazz是否可以被validate
boolean supports(Class<?> clazz);
// 執行校驗,錯誤訊息放在Errors 裝著
// 可以參考ValidationUtils這個工具類,它能幫助你很多
void validate(Object target, Errors errors);
}它的繼承樹如下:
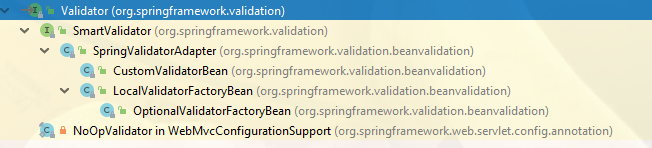
SmartValidator
這個子介面它擴充套件增加了校驗分組:hints。
// @since 3.1 這個出現得比較晚
public interface SmartValidator extends Validator {
// 注意:這裡的Hints最終都會被轉化到JSR的分組裡去~~
// 所以這個可變引數,傳介面Class物件即可~
void validate(Object target, Errors errors, Object... validationHints);
// @since 5.1 簡單的說,這個方法子類請複寫 否則不能使用
default void validateValue(Class<?> targetType, String fieldName, @Nullable Object value, Errors errors, Object... validationHints) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot validate individual value for " + targetType);
}
}SpringValidatorAdapter:校驗介面卡(重要)
這個實現類Class是非常重要的,它是javax.validation.Validator到Spring的Validator的適配,通過它就可以對接到JSR的校驗器來完成校驗工作了~
在Spring5.0後,此實現類已完美支援到
Bean Validation 2.0
// @since 3.0
public class SpringValidatorAdapter implements SmartValidator, javax.validation.Validator {
// 通用的三個約束註解都需要有的屬性
private static final Set<String> internalAnnotationAttributes = new HashSet<>(4);
static {
internalAnnotationAttributes.add("message");
internalAnnotationAttributes.add("groups");
internalAnnotationAttributes.add("payload");
}
// 最終都是委託給它來完成校驗的~~~
@Nullable
private javax.validation.Validator targetValidator;
public SpringValidatorAdapter(javax.validation.Validator targetValidator) {
Assert.notNull(targetValidator, "Target Validator must not be null");
this.targetValidator = targetValidator;
}
// 簡單的說:預設支援校驗所有的Bean型別~~~
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> clazz) {
return (this.targetValidator != null);
}
// processConstraintViolations做的事一句話解釋:
// 把ConstraintViolations錯誤訊息,全都適配放在Errors(BindingResult)裡面儲存著
@Override
public void validate(Object target, Errors errors) {
if (this.targetValidator != null) {
processConstraintViolations(this.targetValidator.validate(target), errors);
}
}
@Override
public void validate(Object target, Errors errors, Object... validationHints) {
if (this.targetValidator != null) {
processConstraintViolations(this.targetValidator.validate(target, asValidationGroups(validationHints)), errors);
}
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
public void validateValue(Class<?> targetType, String fieldName, @Nullable Object value, Errors errors, Object... validationHints) {
if (this.targetValidator != null) {
processConstraintViolations(this.targetValidator.validateValue(
(Class) targetType, fieldName, value, asValidationGroups(validationHints)), errors);
}
}
// 把validationHints都轉換為group (支識別Class型別哦)
private Class<?>[] asValidationGroups(Object... validationHints) {
Set<Class<?>> groups = new LinkedHashSet<>(4);
for (Object hint : validationHints) {
if (hint instanceof Class) {
groups.add((Class<?>) hint);
}
}
return ClassUtils.toClassArray(groups);
}
// 關於Implementation of JSR-303 Validator interface 省略...
}這個介面卡它把所有的Spring介面的校驗方法,最終都委託給了org.springframework.validation.Validator,這樣就可以完美的和JSR結合起來使用了,功能更加的強大~
雖然本類它是個Class實體類,但是一般來說不建議直接使用它
CustomValidatorBean
可配置(Custom)的Bean類,也同樣的實現了雙介面。它可以配置ValidatorFactory驗證器工廠、MessageInterpolator插值器等...
public class CustomValidatorBean extends SpringValidatorAdapter implements Validator, InitializingBean {
// javax.validation.ValidatorFactory
@Nullable
private ValidatorFactory validatorFactory;
@Nullable
private MessageInterpolator messageInterpolator;
@Nullable
private TraversableResolver traversableResolver;
... // 省略所有set方法(木有get方法)
// 預設設定~~~~初始化
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
if (this.validatorFactory == null) {
this.validatorFactory = Validation.buildDefaultValidatorFactory();
}
// 這一句就是new ValidatorContextImpl( this )
ValidatorContext validatorContext = this.validatorFactory.usingContext();
// 插值器
MessageInterpolator targetInterpolator = this.messageInterpolator;
if (targetInterpolator == null) {
targetInterpolator = this.validatorFactory.getMessageInterpolator();
}
validatorContext.messageInterpolator(new LocaleContextMessageInterpolator(targetInterpolator));
if (this.traversableResolver != null) {
validatorContext.traversableResolver(this.traversableResolver);
}
// 把已經配置好的這個Validator設定進去~
setTargetValidator(validatorContext.getValidator());
}
}命名中就能可以看出,它是一個Bean,所以可以配合Spring容器一起使用。Spring內部雖然沒有直接使用到它,但我們自己有需求的話自己可以使用它(其實更多的還是使用更強的子類)~
==LocalValidatorFactoryBean==
它和CustomValidatorBean平級,都是繼承自SpringValidatorAdapter,但是它提供的能力更加的強大,比如Spring處理校驗這塊最重要的處理器MethodValidationPostProcessor就是依賴於它來給提供驗證器~
它是Spring上下文中javax.validation的中心配置類。
// @since 3.0 這個類非常的豐富 實現了介面javax.validation.ValidatorFactory
// 實現了ApplicationContextAware拿到Spring上下文...
// 但其實,它的實際工作都是委託式,自己只提供了各式各樣的配置~~~(主要是配置JSR)
public class LocalValidatorFactoryBean extends SpringValidatorAdapter implements ValidatorFactory, ApplicationContextAware, InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
... // 省略所有的配置屬性
... // 省略所有的get/set
... // 省略afterPropertiesSet()進行的預設配置初始化 最終呼叫setTargetValidator(this.validatorFactory.getValidator());
// 備註:還記得上文嗎?上文的validator校驗器是從上下文拿的,這裡是從工廠拿的
// 省略所有對ValidatorFactory介面的方法實現~
}這個類是非常重要的,雖然它也不被Spring直接使用,但是它是基石。
備註:雖然命名字尾是
FactoryBean,但它並不是org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean這個介面的子類。
其實這是斷句問題,正確斷句方式是:LocalValidatorFactoryBean~
OptionalValidatorFactoryBean
@since 4.0.1提供的,它做的唯一一件事:讓org.springframework.validation.Validator成為可選(即使沒有初始化成功,也不會報錯,相當於把異常吃了嘛~)
// @since 4.0.1
public class OptionalValidatorFactoryBean extends LocalValidatorFactoryBean {
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
try {
super.afterPropertiesSet();
} catch (ValidationException ex) {
LogFactory.getLog(getClass()).debug("Failed to set up a Bean Validation provider", ex);
}
}
}綜上,若你想使用org.springframework.validation.SmartValidator來完成對Bean的校驗,那就手動定義一個這樣的Bean,然後自行呼叫API校驗完成校驗~
若你想這一切能面向註解程式設計,自動完成校驗,那就聽下文分解吧(也是最為關心,最為重要的內容)~
SpringConstraintValidatorFactory
ConstraintValidatorFactory整個API前問有講過,本類就是Spring對它的擴充套件,從而和Spring容器整合了~
public class SpringConstraintValidatorFactory implements ConstraintValidatorFactory {
private final AutowireCapableBeanFactory beanFactory;
public SpringConstraintValidatorFactory(AutowireCapableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
Assert.notNull(beanFactory, "BeanFactory must not be null");
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
// 注意:此處是直接呼叫了create方法,放進容器
@Override
public <T extends ConstraintValidator<?, ?>> T getInstance(Class<T> key) {
return this.beanFactory.createBean(key);
}
// Bean Validation 1.1 releaseInstance method
public void releaseInstance(ConstraintValidator<?, ?> instance) {
this.beanFactory.destroyBean(instance);
}
}MessageSourceResourceBundleLocator
這個類也非常有意思,它擴充套件了Hibernate包的ResourceBundleLocator國際化,而使用
Spring自己的國際化資源:org.springframework.context.MessageSource
說明:
ResourceBundleLocator是它Hibernate的一個SPI,Hibernate內部自己對它可是也有實現的哦~(Bean Validation內部大量的用到了SPI技術,有興趣的可以瞭解)
public class MessageSourceResourceBundleLocator implements ResourceBundleLocator {
private final MessageSource messageSource;
public MessageSourceResourceBundleLocator(MessageSource messageSource) {
Assert.notNull(messageSource, "MessageSource must not be null");
this.messageSource = messageSource;
}
@Override
public ResourceBundle getResourceBundle(Locale locale) {
return new MessageSourceResourceBundle(this.messageSource, locale);
}
}關於MessageSourceResourceBundle它,就相對比較熟悉點了,它不是校驗專用的,是Spring整體上用來處理國際化資源:MessageSource,java.util.ResourceBundl的幫助類~
//@since 27.02.2003 java.util.ResourceBundle 它是JDK提供來讀取國際化的屬性配置檔案的 是個抽象類
public class MessageSourceResourceBundle extends ResourceBundle {
private final MessageSource messageSource;
private final Locale locale;
public MessageSourceResourceBundle(MessageSource source, Locale locale) {
Assert.notNull(source, "MessageSource must not be null");
this.messageSource = source;
this.locale = locale;
}
public MessageSourceResourceBundle(MessageSource source, Locale locale, ResourceBundle parent) {
this(source, locale);
setParent(parent);
}
@Override
@Nullable
protected Object handleGetObject(String key) {
try {
return this.messageSource.getMessage(key, null, this.locale);
} catch (NoSuchMessageException ex) {
return null;
}
}
// @since 1.6
@Override
public boolean containsKey(String key) {
try {
this.messageSource.getMessage(key, null, this.locale);
return true;
}
catch (NoSuchMessageException ex) {
return false;
}
}
@Override
public Enumeration<String> getKeys() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("MessageSourceResourceBundle does not support enumerating its keys");
}
@Override
public Locale getLocale() {
return this.locale;
}
}Spring環境下不僅可以使用Hibernate的國際化檔案,也可以藉助MessageSourceResourceBundleLocator搞自己的。
LocaleContextMessageInterpolator
它是個javax.validation.MessageInterpolator插值器,Spring把它和自己的LocaleContext結合起來了~
// @since 3.0
// org.springframework.context.i18n.LocaleContextHolder#getLocale()
public class LocaleContextMessageInterpolator implements MessageInterpolator {
private final MessageInterpolator targetInterpolator;
public LocaleContextMessageInterpolator(MessageInterpolator targetInterpolator) {
Assert.notNull(targetInterpolator, "Target MessageInterpolator must not be null");
this.targetInterpolator = targetInterpolator;
}
@Override
public String interpolate(String message, Context context) {
return this.targetInterpolator.interpolate(message, context, LocaleContextHolder.getLocale());
}
@Override
public String interpolate(String message, Context context, Locale locale) {
return this.targetInterpolator.interpolate(message, context, locale);
}
}Demo Show
想來想去,還是給個Demo非常簡單的操作一把吧,此處我以CustomValidatorBean為例對Bean進行校驗:
@Getter
@Setter
@ToString
public class Person {
// 錯誤訊息message是可以自定義的
@NotNull(message = "{message} -> 名字不能為null", groups = Simple.class)
public String name;
@Max(value = 10, groups = Simple.class)
@Positive(groups = Default.class) // 內建的分組:default
public Integer age;
@NotNull(groups = Complex.class)
@NotEmpty(groups = Complex.class)
private List<@Email String> emails;
@Future(groups = Complex.class)
private Date start;
// 定義兩個組 Simple組和Complex組
public interface Simple {
}
public interface Complex {
}
}想容器放入一個校驗器:
@Configuration
public class RootConfig {
@Bean
public CustomValidatorBean customValidatorBean() {
return new CustomValidatorBean();
}
}使用此校驗器校驗Person物件(本文為了簡單就直接new了哈,當然你也可以是容器內的Bean物件)
@Slf4j
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes = {RootConfig.class})
public class TestSpringBean {
@Autowired
private SmartValidator smartValidator;
@Test
public void test1() {
Person person = new Person();
person.setAge(-1);
person.setStart(new Date());
Errors errors = new DirectFieldBindingResult(person, "person");
ValidationUtils.invokeValidator(smartValidator, person, errors, Person.Complex.class);
System.out.println(errors);
}
}列印輸出:
org.springframework.validation.DirectFieldBindingResult: 3 errors
Field error in object 'person' on field 'emails': rejected value [null]; codes [NotEmpty.person.emails,NotEmpty.emails,NotEmpty.java.util.List,NotEmpty]; arguments [org.springframework.context.support.DefaultMessageSourceResolvable: codes [person.emails,emails]; arguments []; default message [emails]]; default message [不能為空]
Field error in object 'person' on field 'start': rejected value [Fri Jul 26 11:12:21 CST 2019]; codes [Future.person.start,Future.start,Future.java.util.Date,Future]; arguments [org.springframework.context.support.DefaultMessageSourceResolvable: codes [person.start,start]; arguments []; default message [start]]; default message [需要是一個將來的時間]
Field error in object 'person' on field 'emails': rejected value [null]; codes [NotNull.person.emails,NotNull.emails,NotNull.java.util.List,NotNull]; arguments [org.springframework.context.support.DefaultMessageSourceResolvable: codes [person.emails,emails]; arguments []; default message [emails]]; default message [不能為null]符合預期。
說明:因為前面說了
Bean Validation內的校驗類大都是執行緒安全的,包括校驗器javax.validation.Validator也是執行緒安全的~
總結
從這篇文章開始,關於Bean Validation這塊就切入進Spring的應用裡了。本文主要描述的是一些支援類,我們瞭解了它可以通過手動完成對Spring Bean的校驗,但是在實際應用中顯然不會這麼去做,畢竟一切都需要崇尚自動化嘛~
==下一篇,也就是整個Bean Validation的主菜,也就是真正在企業級·Spring·應用中使用的校驗方式分析,也就是大家熟悉的@Valid,@Validated以及級聯屬性的校驗問題,歡迎點贊關注~==
知識交流
若文章格式混亂,可點選:原文連結-原文連結-原文連結-原文連結-原文連結
==The last:如果覺得本文對你有幫助,不妨點個讚唄。當然分享到你的朋友圈讓更多小夥伴看到也是被作者本人許可的~==
若對技術內容感興趣可以加入wx群交流:Java高工、架構師3群。
若群二維碼失效,請加wx號:fsx641385712(或者掃描下方wx二維碼)。並且備註:"java入群" 字樣,會手動邀請入
