golang開發:類庫篇(五)go測試工具goconvey的使用
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-09-17
為什麼要使用goconvey測試程式
goconvey 整合go test,go test 無縫接入。管理執行測試用例,而且提供了豐富的函式斷言、非常友好的WEB介面,直觀的檢視測試結果。
如果沒有goconvey的話,編寫一個測試結果,首先執行被測試函式,然後判斷被測試函式的執行結果,各種if判斷,各種輸出提示資訊,而且迴歸測試也比較麻煩。但是如果使用了goconvey這些都就變得無比的簡單。
還是看些使用程式碼比較簡單明瞭。
怎麼使用goconvey測試程式
第一步當然是安裝goconvey
go get github.com/smartystreets/goconvey看下被測試的程式碼
package main import "fmt" type Student struct { Num int Name string Chinaese int English int Math int } func NewStudent(num int, name string) (*Student,error) { if num < 1 || len(name) < 1 { return nil,fmt.Errorf("num name empty") } stu := new(Student) stu.Num = num stu.Name = name return stu,nil } func (this *Student) GetAve() (int,error) { score := this.Chinaese + this.English + this.Math if score == 0 { return 0,fmt.Errorf("score is 0") } return score/3,nil }
主要看下goconvey的測試程式碼
package main import ( "testing" . "github.com/smartystreets/goconvey/convey" ) func TestNew(t *testing.T) { Convey("start test new", t, func() { stu,err := NewStudent(0,"") Convey("have error", func() { So(err, ShouldBeError) }) Convey("stu is nil", func() { So(stu, ShouldBeNil) }) }) } func TestScore(t *testing.T) { stu,_ := NewStudent(1,"test") Convey("if error", t, func() { _,err := stu.GetAve() Convey("have error", func() { So(err, ShouldBeError) }) }) Convey("normal", t, func() { stu.Math = 60 stu.Chinaese = 70 stu.English = 80 score,err := stu.GetAve() Convey("have error", func() { So(err, ShouldBeError) }) Convey("score > 60", func() { So(score, ShouldBeGreaterThan, 60) }) }) }
進入到test程式碼目錄,執行 go test
=== RUN TestNew start test new have error ✔ stu is nil ✔ 2 total assertions --- PASS: TestNew (0.00s) === RUN TestScore if error have error ✔ 3 total assertions normal have error ✘ score > 60 ✔ Failures: * /data/www/go/src/test/student_test.go Line 35:
其實命令列顯示的是有顏色標識的。期望出現的結果都會打上對勾,如果期望出現而沒有出現的都會打上叉。
還有更好玩的WEB介面。進入的test程式碼的目錄,然後執行 goconvey 會開啟一個WEB介面,更加友好的標識出了測試的結果,測試了多少次,有幾個通過,幾個失敗,一目瞭然。
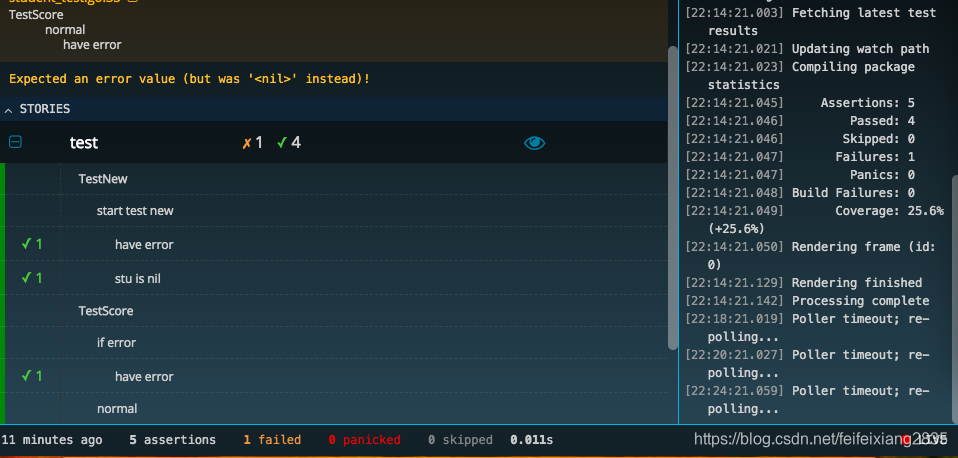
其實使用特別簡單
引入類庫,啟動Convey函式,剩下的就是呼叫So各種斷言各種比較
import (
"testing"
. "github.com/smartystreets/goconvey/convey"
)
Convey("desc", t, func() {
So(var, function)
})基本平常開發中的比較函式基本都有,看下比較的函式列表,看著貌似都涵蓋了。
Convey("Equality assertions should be accessible", t, func() {
thing1a := thing{a: "asdf"}
thing1b := thing{a: "asdf"}
thing2 := thing{a: "qwer"}
So(1, ShouldEqual, 1)
So(1, ShouldNotEqual, 2)
So(1, ShouldAlmostEqual, 1.000000000000001)
So(1, ShouldNotAlmostEqual, 2, 0.5)
So(thing1a, ShouldResemble, thing1b)
So(thing1a, ShouldNotResemble, thing2)
So(&thing1a, ShouldPointTo, &thing1a)
So(&thing1a, ShouldNotPointTo, &thing1b)
So(nil, ShouldBeNil)
So(1, ShouldNotBeNil)
So(true, ShouldBeTrue)
So(false, ShouldBeFalse)
So(0, ShouldBeZeroValue)
So(1, ShouldNotBeZeroValue)
})
Convey("Numeric comparison assertions should be accessible", t, func() {
So(1, ShouldBeGreaterThan, 0)
So(1, ShouldBeGreaterThanOrEqualTo, 1)
So(1, ShouldBeLessThan, 2)
So(1, ShouldBeLessThanOrEqualTo, 1)
So(1, ShouldBeBetween, 0, 2)
So(1, ShouldNotBeBetween, 2, 4)
So(1, ShouldBeBetweenOrEqual, 1, 2)
So(1, ShouldNotBeBetweenOrEqual, 2, 4)
})
Convey("Container assertions should be accessible", t, func() {
So([]int{1, 2, 3}, ShouldContain, 2)
So([]int{1, 2, 3}, ShouldNotContain, 4)
So(map[int]int{1: 1, 2: 2, 3: 3}, ShouldContainKey, 2)
So(map[int]int{1: 1, 2: 2, 3: 3}, ShouldNotContainKey, 4)
So(1, ShouldBeIn, []int{1, 2, 3})
So(4, ShouldNotBeIn, []int{1, 2, 3})
So([]int{}, ShouldBeEmpty)
So([]int{1}, ShouldNotBeEmpty)
So([]int{1, 2}, ShouldHaveLength, 2)
})
Convey("String assertions should be accessible", t, func() {
So("asdf", ShouldStartWith, "a")
So("asdf", ShouldNotStartWith, "z")
So("asdf", ShouldEndWith, "df")
So("asdf", ShouldNotEndWith, "as")
So("", ShouldBeBlank)
So("asdf", ShouldNotBeBlank)
So("asdf", ShouldContainSubstring, "sd")
So("asdf", ShouldNotContainSubstring, "af")
})
Convey("Panic recovery assertions should be accessible", t, func() {
So(panics, ShouldPanic)
So(func() {}, ShouldNotPanic)
So(panics, ShouldPanicWith, "Goofy Gophers!")
So(panics, ShouldNotPanicWith, "Guileless Gophers!")
})
Convey("Type-checking assertions should be accessible", t, func() {
// NOTE: Values or pointers may be checked. If a value is passed,
// it will be cast as a pointer to the value to avoid cases where
// the struct being tested takes pointer receivers. Go allows values
// or pointers to be passed as receivers on methods with a value
// receiver, but only pointers on methods with pointer receivers.
// See:
// http://golang.org/doc/effective_go.html#pointers_vs_values
// http://golang.org/doc/effective_go.html#blank_implements
// http://blog.golang.org/laws-of-reflection
So(1, ShouldHaveSameTypeAs, 0)
So(1, ShouldNotHaveSameTypeAs, "1")
So(bytes.NewBufferString(""), ShouldImplement, (*io.Reader)(nil))
So("string", ShouldNotImplement, (*io.Reader)(nil))
})
Convey("Time assertions should be accessible", t, func() {
january1, _ := time.Parse(timeLayout, "2013-01-01 00:00")
january2, _ := time.Parse(timeLayout, "2013-01-02 00:00")
january3, _ := time.Parse(timeLayout, "2013-01-03 00:00")
january4, _ := time.Parse(timeLayout, "2013-01-04 00:00")
january5, _ := time.Parse(timeLayout, "2013-01-05 00:00")
oneDay, _ := time.ParseDuration("24h0m0s")
So(january1, ShouldHappenBefore, january4)
So(january1, ShouldHappenOnOrBefore, january1)
So(january2, ShouldHappenAfter, january1)
So(january2, ShouldHappenOnOrAfter, january2)
So(january3, ShouldHappenBetween, january2, january5)
So(january3, ShouldHappenOnOrBetween, january3, january5)
So(january1, ShouldNotHappenOnOrBetween, january2, january5)
So(january2, ShouldHappenWithin, oneDay, january3)
So(january5, ShouldNotHappenWithin, oneDay, january1)
So([]time.Time{january1, january2}, ShouldBeChronological)
})特別實用的一個測試類庫,養成寫完程式碼使用goconvey做測試的好習慣,也順便覆蓋下使用方法和案例,定能讓開發事半功倍,減少Bug率
