Unity - 存讀檔機制簡析
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-10-02
本文旨在於簡要分析Unity中的兩種存檔機制,即:PlayerPrefs資料持久化方法及Serialization資料序列化方法
較比與源專案,我另加了JSON方法、XML方法等及一些Unity設定,更便於讀者在使用中理解Unity的存檔機制。核心指令碼為Game.cs
- 源專案地址:How to Save and Load a Game in Unity - raywenderlich
- 個人專案地址:BattleSave - SouthBegonia
一、PlayerPrefs 資料持久化方法
- 儲存原理:採用鍵值對(key與value)的方法,將遊戲資料儲存到本地,是一種Unity自帶的儲存方法。
- 儲存型別:僅支援int、float、string三種
- 儲存地址:詳見官方文件 PlayerPrefs - Unity Documentation
- 讀寫示例:
//專案內未展示該用法,但以下程式碼即為常規用法 //新建存檔 PlayerPrefs.SetInt("Score", 20); PlayerPrefs.SetFloat("Health", 100.0F); PlayerPrefs.SetString("Name",m_PlayerName); //檢驗存檔資訊 if(!PlayerPrefs.HasKey("Name")) return; //讀取存檔 socre = PlayerPrefs.GetInt("Score"); health = PlayerPrefs.GetFloat("Health"); m_PlayerName = PlayerPrefs.GetString("Name"); //刪除存檔 PlayerPrefs.DeleteKey("Score");
- 優缺點:雖然以這種方式儲存遊戲資料方便快捷,但是當資料量龐大以後,鍵值對的大量建立使用,不僅指令碼控制繁瑣,也有可能造成資源的浪費。因此,只建議對一些基礎資料,例如影象設定、聲音設定等採用該方法儲存。
二、Serialization 序列化方法
- 儲存原理:將物件(Object)轉換為資料流(stream of bytes),再經過檔案流儲存到本地的方法。
- 物件(Object):可以是Unity中的任何檔案或是指令碼
- 資料流(stream of bytes):
- 序列化反序列化:
- Serialization:物件-->資料流
- Deserialization:資料流-->物件
- 序列化的方法:
- 二進位制方法
- JSON方法
- XML方法
1. 二進位制儲存(Binary Formatter):
//存檔資訊的類:
[System.Serializable]
public class Save
{
public int hits = 0;
public int shots = 0;
public List<int> livingTargetPositions = new List<int>();
public List<int> livingTargetsTypes = new List<int>();
}
//設定遊戲數值
public void SetGame(Save save)
{
hits = save.hits;
shots = save.shots;
for (int i = 0; i < save.livingTargetPositions.Count; i++)
{
int position = save.livingTargetPositions[i];
Target target = targets[position].GetComponent<Target>();
target.ActivateRobot((RobotTypes)save.livingTargetsTypes[i]);
target.GetComponent<Target>().ResetDeathTimer();
}
}
//存檔函式:
public void SaveGame()
{
//1. 序列化過程
//建立save物件儲存遊戲資訊
Save save = CreateSaveGameObject();
string filePath = Application.dataPath + "/gameSaveBySerialize.save";
//2. 建立二進位制格式化程式及檔案流
BinaryFormatter bf = new BinaryFormatter();
FileStream file = File.Create(filePath);
//3. 將save物件序列化到file流
bf.Serialize(file, save);
file.Close();
}
//讀檔函式:
public void LoadGame()
{
string filePath = Application.dataPath + "/gameSaveBySerialize.save";
//1. 檢驗目標位置是否有存檔
if (File.Exists(filePath))
{
//2. 建立二進位制格式化程式,開啟檔案流
BinaryFormatter bf = new BinaryFormatter();
FileStream file = File.Open(filePath, FileMode.Open);
//3. 將file流反序列化到save物件
Save save = (Save)bf.Deserialize(file);
file.Close();
//從save物件讀取資訊到本地
SetGame(save);
}
else
Debug.Log("No gamesaved!");
}2. JSON方法:
/*
* 注意:使用JSON存檔方法需要用到LitJson庫,LitJson.dll檔案可在專案Assets目錄下找到。
* 使用方法:將LitJson.dll拖拽到個人專案Assets目錄下即可
*/
//JSON存檔函式:
public void SaveAsJson()
{
//1. 建立save物件儲存遊戲資訊
Save save = CreateSaveGameobject();
string path = Application.dataPath + "/gameSaveByJson.json";
//2. 利用JsonMapper將save物件轉換為Json格式的字串
string saveJsonStr = JsonMapper.ToJson(save);
//3. 建立StreamWriter,將Json字串寫入檔案中
StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter(path);
sw.Write(saveJsonStr);
sw.Close();
}
//JSON讀檔函式:
public void LoadAsJson()
{
string path = Application.dataPath + "/gameSaveByJson.json";
//1. 檢驗目標位置是否有存檔
if(File.Exists(path))
{
//2. 建立一個StreamReader,用來讀取流
StreamReader sr = new StreamReader(path);
//3. 將讀取到的流賦值給jsonStr
string jsonStr = sr.ReadToEnd();
sr.Close();
//4. 將字串jsonStr轉換為Save物件
Save save = JsonMapper.ToObject<Save>(jsonStr);
//從save物件讀取資訊到本地
SetGame(save);
}
else
Debug.Log("No gamesaved!");
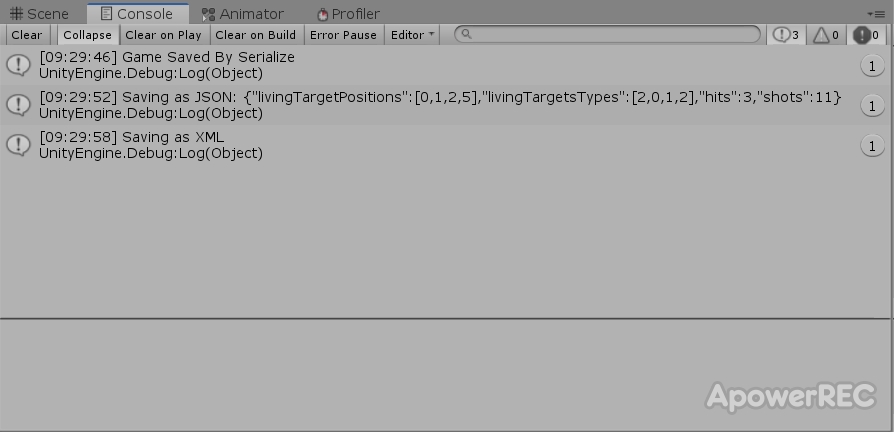
}JSON存檔格式:
{
"livingTargetPositions":[0,1,2,4],
"livingTargetsTypes":[2,2,2,1],
"hits":1,
"shots":8
}3. XML方法:
//XML儲存
public void SaveAsXml()
{
Save save = CreateSaveGameObject();
//建立XML檔案的儲存路徑
string filePath = Application.dataPath + "/gameSaveByXML.txt";
//建立XML文件
XmlDocument xmlDoc = new XmlDocument();
//建立根節點,即最上層節點
XmlElement root = xmlDoc.CreateElement("save");
//設定根節點中的值
root.SetAttribute("name", "saveFile1");
//建立XmlElement
XmlElement target;
XmlElement targetPosition;
XmlElement targetType;
//遍歷save中儲存的資料,將資料轉換成XML格式
for (int i = 0; i < save.livingTargetPositions.Count; i++)
{
target = xmlDoc.CreateElement("target");
targetPosition = xmlDoc.CreateElement("targetPosition");
//設定InnerText值
targetPosition.InnerText = save.livingTargetPositions[i].ToString();
targetType = xmlDoc.CreateElement("targetType");
targetType.InnerText = save.livingTargetsTypes[i].ToString();
//設定節點間的層級關係 root -- target -- (targetPosition, monsterType)
target.AppendChild(targetPosition);
target.AppendChild(targetType);
root.AppendChild(target);
}
//設定射擊數和分數節點並設定層級關係
XmlElement shots = xmlDoc.CreateElement("shoots");
shots.InnerText = save.shots.ToString();
root.AppendChild(shots);
XmlElement hits = xmlDoc.CreateElement("hits");
hits.InnerText = save.hits.ToString();
root.AppendChild(hits);
xmlDoc.AppendChild(root);
xmlDoc.Save(filePath);
if (File.Exists(Application.dataPath + "/gameSaveByXML.txt"))
{
Debug.Log("Saving as XML");
}
}
//XML讀取
public void LoadAsXml()
{
string filePath = Application.dataPath + "/gameSaveByXML.txt";
if (File.Exists(filePath))
{
Save save = new Save();
//載入XML文件
XmlDocument xmlDoc = new XmlDocument();
xmlDoc.Load(filePath);
//通過節點名稱來獲取元素,結果為XmlNodeList型別
XmlNodeList targets = xmlDoc.GetElementsByTagName("target");
//遍歷所有的target節點,並獲得子節點和子節點的InnerText
if (targets.Count != 0)
{
foreach (XmlNode target in targets)
{
//把得到的值儲存到save中
XmlNode targetPosition = target.ChildNodes[0];
int targetPositionIndex = int.Parse(targetPosition.InnerText);
save.livingTargetPositions.Add(targetPositionIndex);
XmlNode targetType = target.ChildNodes[1];
int targetTypeIndex = int.Parse(targetType.InnerText);
save.livingTargetsTypes.Add(targetTypeIndex);
}
}
//得到儲存的射擊數和分數
XmlNodeList shoots = xmlDoc.GetElementsByTagName("shoots");
int shootNumCount = int.Parse(shoots[0].InnerText);
save.shots = shootNumCount;
XmlNodeList hits = xmlDoc.GetElementsByTagName("hits");
int hitsCount = int.Parse(hits[0].InnerText);
save.hits = hitsCount;
SetGame(save);
}
else
{
Debug.Log("No game saved!");
}
}XML存檔格式:
<save name="saveFile1">
<target>
<targetPosition>0</targetPosition>
<targetType>2</targetType>
</target>
<target>
<targetPosition>1</targetPosition>
<targetType>2</targetType>
</target>
<target>
<targetPosition>2</targetPosition>
<targetType>2</targetType>
</target>
<target>
<targetPosition>3</targetPosition>
<targetType>2</targetType>
</target>
<shoots>13</shoots>
<hits>3</hits>
</save>三、總述
無論是資料持久化方法還是序列化方法都可以實現Unity的存檔機制。資料持久化方法操作方便,適用於數值較少的小專案。序列化方法的存檔格式較為規範,其中二進位制方法操作簡單,但可讀性差;JSON方法存檔格式規範易讀,具有一定的可讀性;XML方法操作繁瑣,但是存檔格式可讀性強,JSON和XML存檔都可以用文字讀取便於檢視。
綜上所述,Unity存檔機制眾多,但還應按照個人專案需求選擇合適的存檔方法。
四、參考
- PlayerPrefs - Unity Documentation
- How to Save and Load a Game in Unity - raywenderlich
- 對於PlayerPrefs學習以及儲存的研究 - 果vinegar
- Save&Load Unity存檔讀檔的學習總結 - JoharWong
- C#中File和FileStream的用法 - 憶汐辰
- Application.dataPath - Unity Documentation
