直接緩衝區與非直接緩衝區
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-10-02
緩衝區存取資料的兩個方法
- put():存入資料到緩衝區中
- get(): 獲取緩衝區的資料
緩衝區的四個核心屬性
- capacity: 容量,表示緩衝區中最大儲存資料的容量,一旦宣告不能改變
- limit: 界限, 表示緩衝區中可以操作資料的大小(limit後的資料不能讀寫)
- position: 位置, 表示緩衝區中正在操作資料的位置
- mark: 標記, 表示記錄當前position的位置, 可以通過reset() 恢復到mark的位置
0 <= mark <= position <= limit <= capacity
非直接緩衝區
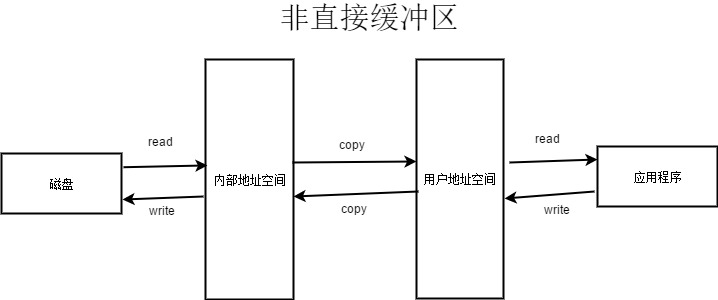
使用非直接緩衝區時, 資料要經由核心地址空間和使用者地址空間, 且兩者之間有複製的過程, 效能較低
通過allocate()方法分配緩衝區, 將緩衝區建立在JVM的記憶體中
程式碼示例
@Test public void test1(){ // 1.分配一個指定大小的緩衝區 final ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); System.out.println("----allocate----"); System.out.println(buf.position()); System.out.println(buf.limit()); System.out.println(buf.capacity()); // 2.利用get()存入緩衝區中 buf.put("2333".getBytes()); System.out.println("----put()----"); System.out.println(buf.position()); System.out.println(buf.limit()); System.out.println(buf.capacity()); // 3.切換成讀取資料模式 buf.flip(); System.out.println("----flip----"); System.out.println(buf.position()); System.out.println(buf.limit()); System.out.println(buf.capacity()); // 4.利用get() 讀取資料 byte[] dst = new byte[buf.limit()]; buf.get(dst); System.out.println(new String(dst, 0, dst.length)); System.out.println("----get----"); System.out.println(buf.position()); System.out.println(buf.limit()); System.out.println(buf.capacity()); // 5.rewind 可重複讀 buf.rewind(); System.out.println("----rewind----"); System.out.println(buf.position()); System.out.println(buf.limit()); System.out.println(buf.capacity()); // 6.clear 清空緩衝區, 但是資料還在 buf.clear(); System.out.println("----clear----"); System.out.println(buf.position()); System.out.println(buf.limit()); System.out.println(buf.capacity()); } @Test public void test2(){ String str = "2333"; final ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); buf.put(str.getBytes()); buf.flip(); byte[] dst = new byte[buf.limit()]; buf.get(dst, 0, 2); // System.out.println(new String(dst, 0, 2)); System.out.println(buf.position()); buf.mark(); buf.get(dst, 2, 2); // System.out.println(new String(dst, 2, 2)); System.out.println(buf.position()); // reset 恢復到mark的位置 buf.reset(); System.out.println(buf.position()); // buf.hasRemaining() }
直接緩衝區
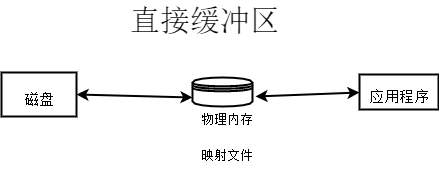
將快取資料直接放在記憶體中, 速到快,效能高
但是, 記憶體檔案由系統控制, 過程不可控、不安全,建議分配給易受基礎系統的本機IO操作影響的大型、持久的緩衝區。 通過allocateDirect()方法直接快取區, 將緩衝區建立在實體記憶體中 。
程式碼示例
@Test
public void test3(){
String str = "2333";
final ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(1024);
buf.put(str.getBytes());
buf.flip();
byte[] dst = new byte[buf.limit()];
buf.get(dst, 0, dst.length);
System.out.println(new String(dst));
